Over a billion websites exist today, but only around 200 million are operating actively. That highlights both the challenge of standing out and the potential of building something valuable online.
If you’d like to learn how to develop a web application from scratch, this guide will walk you through the process from setup to launch using clear, beginner-friendly steps.
You’ll learn what web applications are, how they differ from traditional websites, and why they matter in business. We’ll cover the development process, key technologies, and common challenges so you have a solid foundation to start building your own web apps.
Key Takeaways
- Front-End & Back-End Integration: Web application development combines front-end (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and back-end (Node.js, Python) technologies to create dynamic, interactive apps accessed via browsers.
- Popular Web Apps: Popular apps like Facebook, Google Docs, and WhatsApp showcase the versatility and impact of web apps across industries.
- Development Process: A transparent development process, including planning, design, coding, testing, and deployment, ensures functional, secure, and user-friendly web apps.
- Importance of Testing: Testing (unit, integration, and end-to-end) is crucial for ensuring your app is reliable and works seamlessly across devices and browsers.
- Learning Resources: Learning resources like Codecademy, freeCodeCamp, and GitHub are essential for ongoing growth in the fast-paced field of web development.
What is a Web Application?
A web application is an interactive program that runs in a web browser, rather than being installed on a device.
They typically consist of two main parts:
- Client-side (front-end): Where users interact and provide data.
- Server-side (back-end): Where the data is processed, stored, and managed.
Unlike traditional desktop apps, web apps are hosted on external servers and accessed via any internet-connected device with a web browser.
5 Examples of Web Applications
To stay ahead in the current digital market, almost every business needs a reliable web app. Web apps have set new expectations for design, usability, security, and reliability. Here are five solid examples that have shaped the digital environment:
| App | Description |
| A social networking platform offering live chat, video streaming, photo sharing, and content linking. It integrates with other services, providing a seamless experience. | |
| Google Docs | A web-based tool for creating and editing documents. It enables cloud storage and collaboration, accessible from any device with internet access. |
| A messaging app that supports video calls, texting, and payments, all across platforms, with just an internet connection. | |
| Mailchimp | A marketing automation tool focused on email marketing, offering an intuitive interface for creating and managing campaigns. |
| Airtable | A database solution with an Excel-like interface, enabling organizations to manage projects, workflows, and records in a simple but powerful web app. |
Each of these applications shows the versatility of web apps in addressing diverse user needs, from communication to project management.
What Is Web Application Development?
Web application development is the process of building software that runs on web browsers, delivering interactive and dynamic experiences to users. Unlike static websites that display fixed content, web applications allow you to perform tasks like sending emails, managing projects, or streaming videos.
They combine front-end interfaces, back-end logic, and databases to create functional tools accessible over the internet. Popular web apps, such as Gmail (for email), Trello (for task management), and Netflix (for streaming), demonstrate the power of this approach.
Also Read: Website Development Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Now that you understand the basics of web apps, let’s break down the roles of front-end and back-end development.
Front-End vs Back-End: Understanding the Basics
Creating a web application involves two main areas: front-end and back-end development. The front-end is what users see and interact with, while the back-end handles the logic and data behind the scenes. Grasping the differences between these areas is crucial for building a cohesive application.
Front-End Development
The front-end is the visual and interactive part of your web app, including buttons, forms, and layouts. You use technologies like HTML (for structure), CSS (for styling), and JavaScript (for interactivity) to create user-friendly interfaces.
Frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular simplify building complex, dynamic front-ends by providing reusable components and efficient state management.
Responsive design is also key, ensuring your app looks great and functions well on devices like phones, tablets, and desktops, using techniques like media queries or frameworks like Bootstrap.
- Role: Builds the user interface and handles client-side interactions.
- Key Technologies: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Vue.
- Why It Matters: A well-designed front-end enhances user experience and accessibility.
Back-End Development
The back-end powers the functionality of your app, managing business logic, database interactions, and server communication. You use languages like Python, Node.js, PHP, Ruby, or Java to process data and handle requests.
Frameworks like Express.js (Node.js), Django (Python), or Laravel (PHP) provide server setup and routing. APIs, especially RESTful ones, allow your front-end to communicate with the back-end, fetching or updating data securely.
- Role: Manages server-side logic, data processing, and API connectivity.
- Key Technologies: Python, Node.js, Django, Laravel, and REST APIs.
- Why It Matters: A robust back-end ensures reliable functionality and data management.
Now that you’ve got a handle on how front-end and back-end work, let’s explore why developing web applications is so important in the first place.
Benefits of Web Application Development
When deciding whether to develop a web application, it’s essential to weigh it against other alternatives, such as websites, native applications, or local software packages. Here are some key benefits of opting for a custom web application over these alternatives
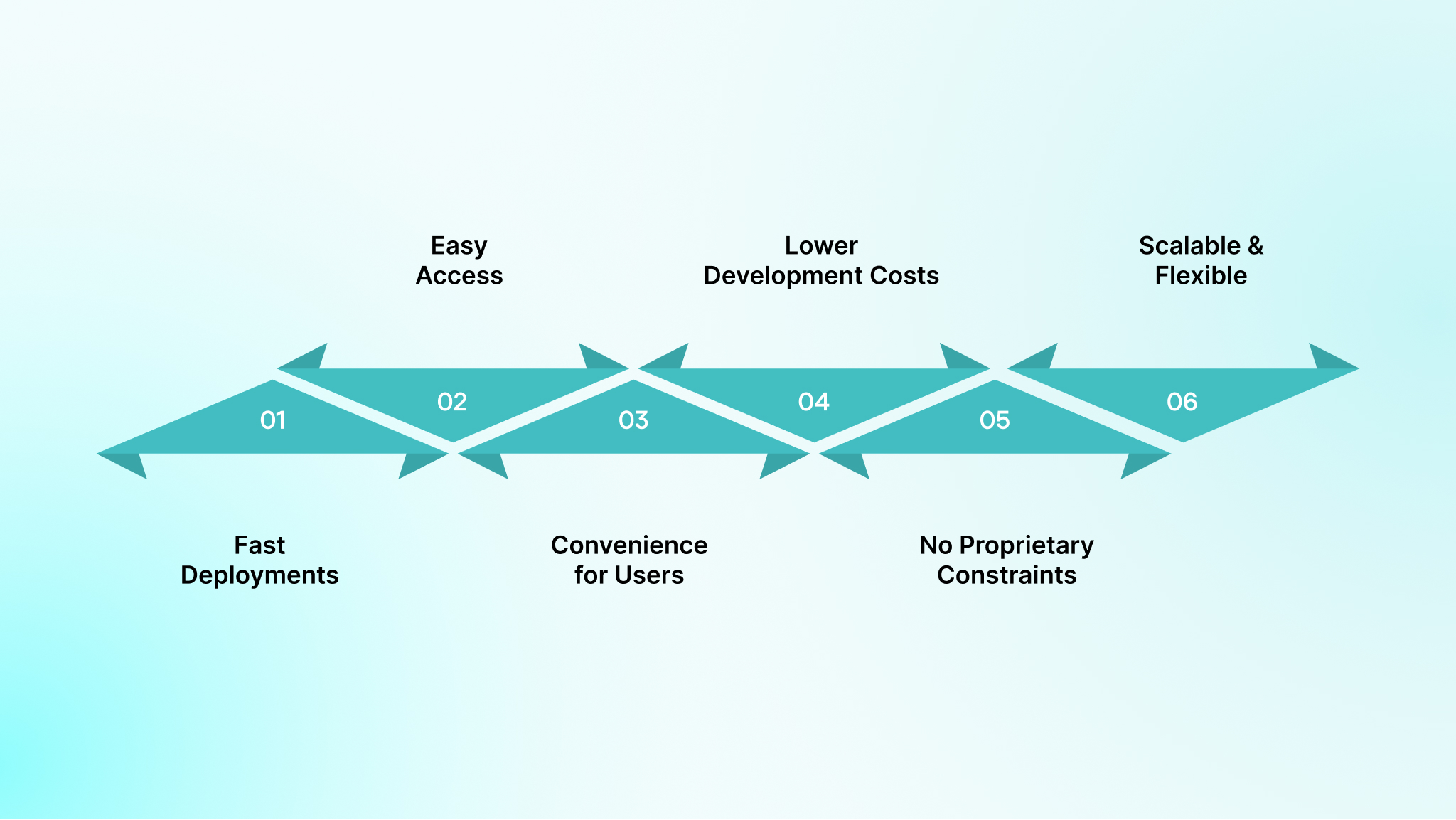
- Fast Deployments: Web applications offer quick deployment. Once your app is ready, you only need to share the URL. This is much faster than distributing native apps or installing desktop software, which can take days or even weeks.
- Easy Access: Web apps are accessible from any device with a web browser. Users can access the same tools on phones, desktops, or tablets, making it easier for employees to work across devices and customers to engage seamlessly.
- Convenience for Users: People prefer web apps because they’re easy to access without the hassle of app store downloads, reducing battery drain and storage issues.
- Lower Development Costs: Web apps utilize common frameworks and libraries, reducing custom work and eliminating the need for proprietary tools and lengthy approval processes, such as those required for app stores.
- No Proprietary Constraints: Unlike native mobile apps, which depend on platform-specific languages and app stores, web apps run in any modern browser. You can choose the best-fit tools and frameworks without being locked into a single ecosystem.
- Scalable and Flexible: Web apps are built to scale efficiently and are easier to maintain, as updates are deployed to a central server, allowing all users to benefit from the latest version without manual installations.
Web application development offers fast deployment, making it a convenient solution for businesses aiming to reach a broad audience without the complexities of traditional software.
Tired of the long, complicated process of app store approvals or limited functionality with desktop software?
At DEVtrust, we remove those roadblocks by developing custom web applications that are quick to deploy, scalable, and accessible from any device. With our expertise, you get faster access to your tools and the flexibility to scale without the headaches of proprietary constraints.
Contact DEVtrust today to build a web app that helps your business move faster and more efficiently.
Also Read: Custom Web Application Development Guide and Benefits
Now that we’ve seen the advantages of web apps, let’s see how thoughtful design patterns and application architecture help turn those benefits into effective, practical products.
Web App Design Patterns and Architecture
Understanding the basic components of a web application is crucial for selecting the right design and architecture. Here are three common web app architecture patterns:
1. Model View Controller (MVC)
The MVC architecture divides a web application into three distinct components:
- Model: Represents the app’s data and business logic.
- View: Displays the app’s UI to the user.
- Controller: Handles user inputs, updates the View and Model accordingly.
A modular approach allows developers to work on different components independently, making it easier to test, maintain, and reuse.
2. Single Page Application (SPA)
SPA is a web app built on a single HTML page that dynamically updates as users interact with it, without the need for page reloads.
- Client-Side Logic: Most of the app’s logic and rendering is handled on the front-end.
SPA reduces server load, improving performance on repeat visits or long sessions.
3. Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture divides a web app into small, independent services that communicate through HTTP or message queues. Each service handles a specific function and can be scaled, modified, or maintained separately, offering agility and flexibility.
Understanding each architectural pattern can help you make an informed decision for your development process.
Once you’ve got a grasp on the different architectures, it’s time to get into the nitty-gritty steps of building your web application.
Steps in Web Application Development
Building a web application follows a structured process, from planning to deployment. Each step ensures your app is user-focused, functional, and ready for production. Below, we outline the key stages to guide you through creating your first web app.
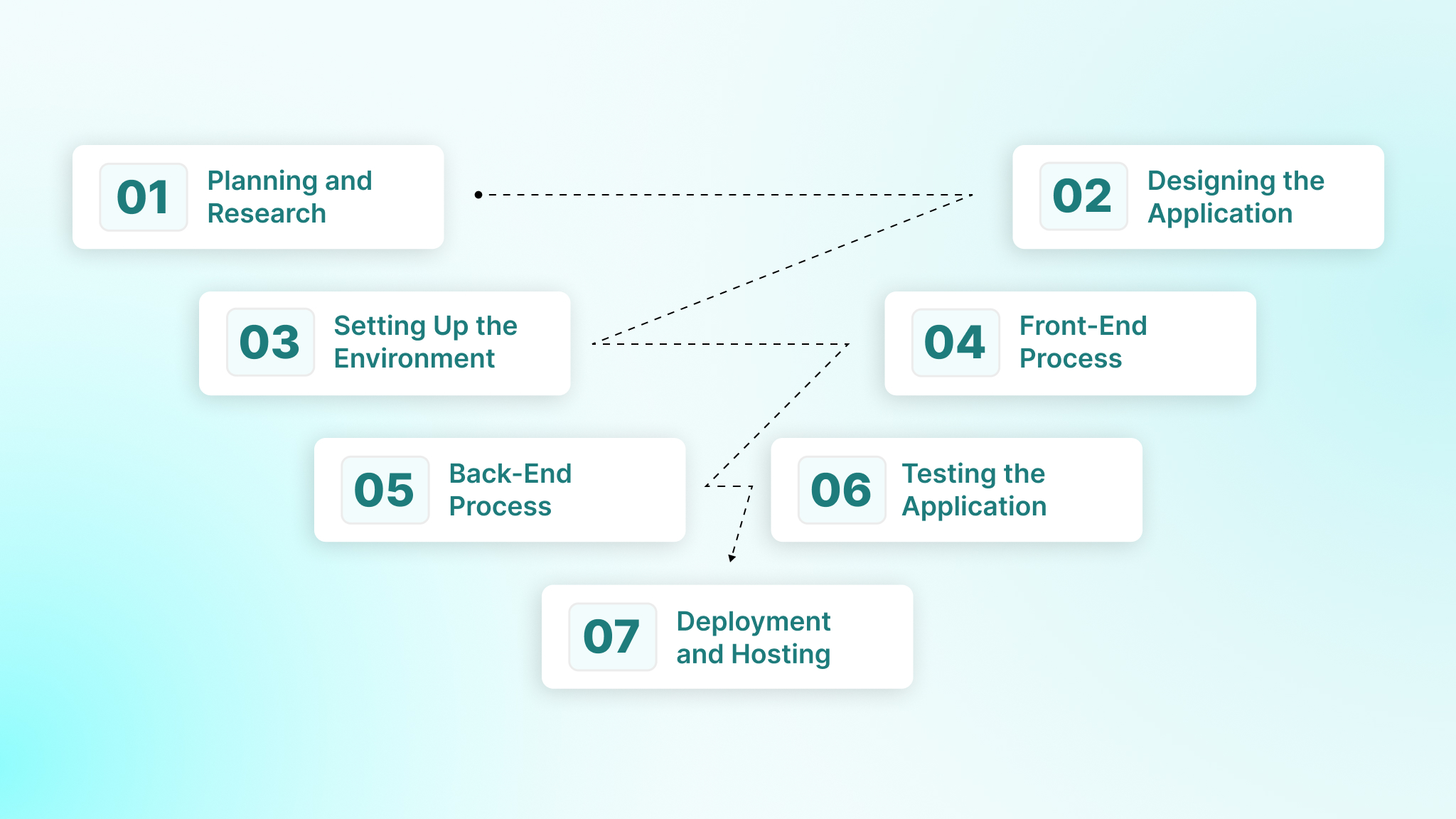
Step 1: Planning and Research
The foundation of any successful web app is clear planning and research. Follow these steps:
- Define the purpose: What problem does the app solve? For example, project management or online purchases.
- Understand your target audience: Conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather insights on their needs and preferences.
- Analyze competitors: Identify gaps or opportunities that distinguish your app from others.
- Set measurable goals: Aim for tangible targets, such as 500 daily users or processing 100 transactions per hour.
- Create a project scope document: Outline features, timelines, and resources to ensure alignment within the team.
Step 2: Designing the Application
Effective design is crucial for functionality and user experience. Focus on these key areas:
- Wireframes: Sketch the app layout using tools like Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD to map out essential pages (home, login, dashboard).
- Interactive prototypes: Simulate user interactions, such as clicking buttons or filling out forms, to test usability.
- User flows: Ensure tasks like sign-up or search are intuitive.
- Accessibility: Prioritize inclusive design features, such as high-contrast colors and keyboard navigation, to reach a broader audience.
Step 3: Setting Up the Development Environment
A well-configured development environment is essential for smooth coding and collaboration:
- Choose a code editor: Use Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text for syntax highlighting and web development extensions.
- Install necessary tools: For JavaScript-based projects, use Node.js; for Python apps, use Django.
- Version control: Set up Git for managing code changes and collaborating via GitHub.
- Package managers: Install npm or Yarn to manage dependencies and libraries.
- Local server: Set up a local development server to test your app as you build it.
Step 4: Front-End Development Process
The front-end brings your app’s design to life, focusing on user interaction and experience:
- HTML Structure: Build the layout using HTML, defining key elements such as headers, forms, and buttons.
- CSS Styling: Utilize CSS for visual design, including the application of colors, fonts, and layouts. Use Flexbox or CSS Grid for responsive design.
- Interactivity with JavaScript: Add dynamic elements, such as form validation or real-time content updates.
- Frameworks: Consider using React or Vue.js for reusable components to improve efficiency and maintainability.
- Regular testing: Test across devices to ensure a smooth, responsive user experience.
Step 5: Back-End Development Process
The back-end powers your app’s core logic, data handling, and server operations:
- Set up a server: Utilize frameworks such as Express.js (Node.js) or Django (Python) to handle client requests.
- Choose a database: Use MongoDB (NoSQL) or PostgreSQL (relational) based on your data structure needs.
- Create APIs: Build RESTful APIs to enable communication between the front-end and back-end, such as fetching user profiles or submitting form data.
- User authentication: Implement secure authentication methods using tools like JSON Web Tokens (JWT) or OAuth.
Step 6: Testing the Application
Testing is critical to ensure your app functions as expected across all environments:
- Unit tests: Verify individual components, such as a login function.
- Integration tests: Ensure all components work together seamlessly.
- End-to-end tests: Simulate user actions, such as completing a purchase or submitting a form.
- Cross-browser compatibility: Test the app across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
- Performance testing: Evaluate app performance under real-world conditions, such as high traffic.
Case study – healthcare credentialing platform
In one healthcare project, DEVtrust built a custom credential management platform for over 1,000 doctors using Laravel and MySQL.
Key Results:
- Reduced manual workload by 45%.
- Automated form filling, saving 3–5 hours per week.
- Increased user satisfaction by 30%.
- Cut operational costs by 25% through targeted third-party integrations.
Step 7: Deployment and Hosting
Once your web app is ready, it’s time to deploy it:
- Code optimization: Minify CSS, JavaScript, and compress images to reduce load times.
- Security: Implement input validation and HTTPS encryption to protect user data.
- Choose a hosting platform: Options include Netlify for static sites, Heroku for PaaS, or AWS for scalable infrastructure.
- Domain and SSL: Configure your domain and SSL certificate to ensure secure connections.
- Staging environment: Deploy to a staging environment first, thoroughly test it, and then push the changes to production.
This structured process ensures your web application is built efficiently and performs well.
Ready to create a web app that works for you? At DEVtrust, we specialize in turning your ideas into smooth, high-performance web applications specific to your needs. Let’s build your future together.
Also Read: How to Develop AI Software: A Complete Guide
With the development process outlined, let’s cover the tools that make it easier.
Essential Tools for Web App Development
The right tools expedite your development workflow, helping you code, test, and manage your project efficiently. Here’s a rundown of essential tools for beginners:
- Code Editors and web-based application development software: Tools like Visual Studio Code (VS Code) are widely used, featuring extensions such as Prettier for code formatting and Live Server for real-time previews. WebStorm offers advanced debugging capabilities, but it is paid
- Browser DevTools: Chrome and Firefox DevTools allow you to inspect HTML, debug JavaScript, and analyze performance. Use them to tweak CSS, check network requests, and ensure cross-browser compatibility.
- Package Managers: npm or Yarn manage dependencies like React or Axios, simplifying installation and updates. They also handle scripts for tasks like testing or building your app.
- API Testing Tools: Postman and Insomnia help you test APIs, debug errors, and ensure your back-end communicates properly with the front-end.
- Project Management Tools: Trello organizes tasks using boards and cards, while Notion combines notes, databases, and task tracking for team collaboration and project alignment.
- Version Control Platforms: GitHub is essential for hosting code, collaborating, and tracking changes. It helps with branch management, pull requests, and maintaining a reliable project history.These tools form the backbone of your development process, making it easier to build and maintain your app.
Now, let’s discuss best practices to guide your work as a beginner.
Best Practices for Beginners
Following best practices ensures your code is clean, secure, and maintainable. As a beginner, focusing on these principles sets you up for long-term success and makes your projects more manageable. Here are some best practices you should follow:
- Write Clean, Readable Code: Use clear variable names (e.g., userName instead of x) and consistent formatting. Tools like ESLint can enforce coding standards, making your code easier for you and others to understand and maintain over time.
- Commit Frequently with Version Control: Use Git to commit changes regularly with descriptive messages, like “Added user login form.” This creates a clear project history, allows you to revert mistakes, and supports team collaboration through platforms like GitHub.
- Break Features into Small Tasks: Divide your app into manageable pieces, such as “build login page” or “set up database connection.” This keeps you focused, reduces overwhelm, and makes it easier to track progress and debug issues.
- Prioritize Security from the Start: Validate all user inputs to prevent injection attacks, use HTTPS for secure communication, and implement strong authentication (e.g., bcrypt for passwords). Regularly update dependencies to patch vulnerabilities and protect user data.
- Document Your Code Thoroughly: Add comments to explain complex logic, like why you chose a specific algorithm. Maintain a README file with setup instructions and project details to help new developers or future you understand the codebase.
- Test Early and Often: Incorporate testing into your workflow from the start, using tools like Jest or Cypress. Write tests for critical features, like user authentication, to catch bugs early and ensure your app remains reliable as it grows.
These habits help you build professional, reliable applications from the start.
With best practices in mind, let’s address common challenges you might face.
Common Challenges for Beginners
Starting web development can be tough, but knowing common hurdles helps you prepare. As a beginner, you’ll likely face hurdles that test your patience and skills. Understanding these challenges and how to tackle them helps you stay motivated and progress steadily toward building your web application. Watch out for these pitfalls:
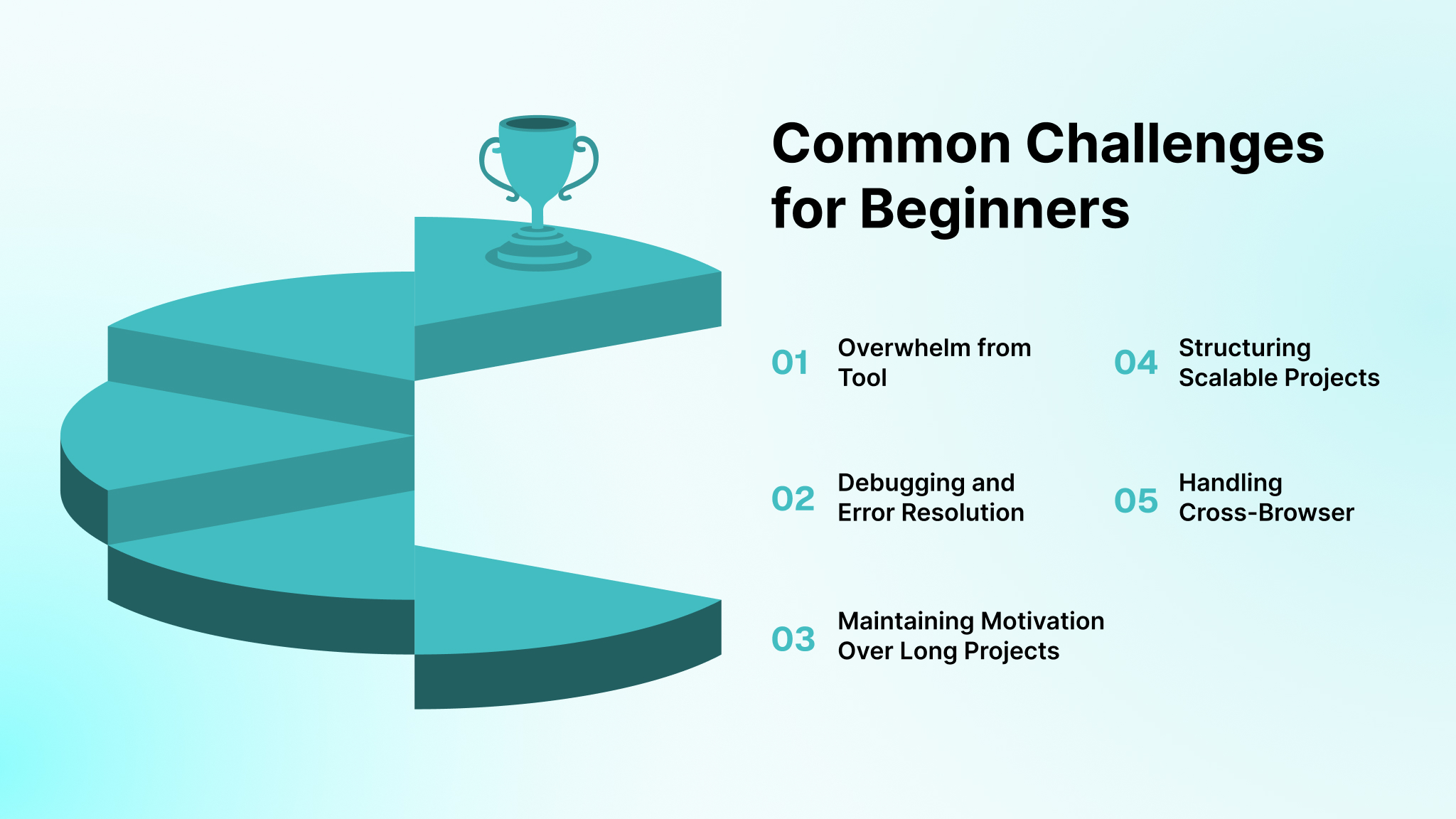
- Overwhelm from Tool and Language Choices: The vast array of tools, frameworks, and languages (e.g., React vs. Vue, Node.js vs. Python) can confuse you. Start with one stack, like MERN, and use beginner-friendly tutorials to focus your learning and build confidence.
- Debugging and Error Resolution: Errors like “undefined is not a function” can be frustrating. Use browser DevTools to inspect elements, log variables with console.log, and search error messages on Stack Overflow to systematically identify and fix issues.
- Maintaining Motivation Over Long Projects: Complex projects can feel endless, especially with slow progress. Set small, achievable milestones, like completing a single page, and reward yourself for hitting them to stay engaged and avoid burnout.
- Structuring Scalable Projects: Designing an app that grows without breaking is tough. Follow modular design principles, like separating concerns (e.g., keeping UI and logic apart), and use frameworks to enforce structure, making scaling easier as your app expands.
- Handling Cross-Browser Compatibility: Your app may look great in Chrome, but fail in Safari. Test across browsers early using tools like BrowserStack, and apply CSS prefixes or polyfills to ensure consistent performance and appearance for all users.
By anticipating these challenges, you can stay focused and keep learning.
Finally, let’s explore resources to support your ongoing learning.
Resources to Keep Learning
Web development is a field that advances quickly, and continuous learning is essential to stay current and improve your skills. Below, we highlight a range of platforms, communities, and opportunities to keep you learning and growing.
- Online Learning Platforms: freeCodeCamp offers free, hands-on tutorials for HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and more, with projects to build your portfolio. Codecademy provides interactive courses on frameworks like React, while MDN Web Docs offers detailed, beginner-friendly documentation on web standards and APIs.
- YouTube Channels and Podcasts: Channels like The Net Ninja provide step-by-step tutorials on modern stacks, while podcasts like CodeNewbie offer insights from developers at all levels. These resources break down complex topics into digestible lessons, perfect for visual or auditory learners.
- Developer Communities: Stack Overflow is a go-to for asking technical questions and finding solutions. Reddit’s r/webdev and Discord communities, like The Odin Project, connect you with peers for advice, code reviews, and networking, fostering a sense of collaboration.
- Open-Source Contribution: Contributing to open-source projects on GitHub lets you work on real-world code, learn from experienced developers, and build your portfolio. Start with “good first issue” tags on projects like freeCodeCamp or smaller libraries to gain practical experience.
- Online Courses and Certifications: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer structured courses in web development, often accompanied by certifications. For example, Coursera’s Meta Front-End Developer Certificate covers React and UI design, giving you credentials to showcase your skills.
These resources keep you informed and connected as you build your skills.
Why Partner With DEVtrust for Web Application Development?
Building a web app is not just about writing code. It’s about shipping a product that’s fast, secure, and easy to evolve as your business grows. That’s where DEVtrust comes in.
At DEVtrust, we work as an extension of your product and engineering team, helping you move from idea to live, reliable web application without the usual trial-and-error.
- End-to-end ownership: From UX and system design to front-end, back-end, and DevOps, we handle the full web application lifecycle so you don’t juggle multiple vendors.
- Scalable, secure architecture: We design web apps to handle growth from day one, with clean APIs, robust security, and cloud-native infrastructure that won’t need a rewrite in a year.
- Performance and usability first: Every build focuses on fast load times, intuitive flows, and real-world usage, not just “it works on localhost.”
- Outcome-focused delivery: We tie features to business goals—conversion, automation, or internal efficiency—so your web app delivers measurable impact, not just a checklist of screens.
If you need a web application that’s built to last, not just to launch, DEVtrust can help you get there with clarity, speed, and confidence.
Conclusion
Now that you understand the process of developing a web application, from planning and design to coding and deployment, it’s time to take action. Start sketching out your idea, choose a simple stack, and build something functional. As you grow your skills, explore more complex features and tools.
At DEVtrust, we specialize in bringing your ideas to life with custom web applications tailored to your unique needs. Our experienced developers use advanced technologies and proven methodologies to deliver scalable, secure, and user-focused solutions that drive business success.
Whether you’re starting a new project or enhancing an existing one, we’re here to help. Contact DEVtrust todayto discuss your vision and start building a web application that stands out.