Healthcare didn’t go digital by choice. It was pushed there. After COVID, patients expect care to be as easy as booking a ride or ordering food. But many healthcare apps still feel slow, confusing, or risky to use. The real problem isn’t ideas or funding. It’s building apps that actually work in a highly regulated, high-stakes industry.
This matters now because most health systems know they’re behind. A McKinsey survey found that 75% of healthcare executives believe their digital and AI investments are not delivering real value. That gap is costing time, trust, and money, and poorly built apps only make it worse.
This guide is for healthcare founders, product managers, hospital IT teams, and decision-makers planning to build or improve a healthcare app. You’ll learn what types of healthcare apps work, which features matter at each stage, how the development process really works, and what challenges to plan for before you write a single line of code.
Key takeaways
- Healthcare apps are essential for improving patient care by offering features like telemedicine, appointment scheduling, and health tracking while providing doctors with simplified workflows and data-driven insights.
- Key features of healthcare apps include secure registration, EHR access, telehealth functionality, and medication reminders, all of which improve both patient engagement and care efficiency.
- The development process involves planning, design, coding, and regulatory compliance (such as HIPAA), with major challenges including data security, system integration, and user adoption.
- Emerging technologies like AI, wearables, and blockchain are shaping the future of healthcare apps, offering personalized care, enhanced security, and real-time monitoring.
- Post-launch considerations are important, including ongoing maintenance, user feedback, and adapting to new regulations and technologies to ensure long-term success and app relevance.
What is a Healthcare Mobile App?
A healthcare mobile app is a digital product that helps patients or care teams manage health-related tasks, including appointments, telehealth, access to records, medication routines, care coordination, and clinical workflows.
Depending on the use case, it may need to follow healthcare regulations, integrate with EHR systems, and meet strict security and privacy requirements.
Benefits and Importance of Healthcare Apps for Doctors and Patients
The impact of healthcare apps on both sides of the medical spectrum is profound. Let’s have a look at how these apps benefit patients and healthcare providers.
For Patients:
- Enhanced Accessibility: Patients gain easy access to their medical records, appointment booking, telehealth consultations, and health information from anywhere, at any time. The 2022 Medication Access Report revealed that 82% of patients experienced delays in accessing medications, with 10% of these delays caused by communication barriers, issues that can be resolved through mobile access to patient records, pharmacists, and healthcare providers.
- Improved Self-Management: Apps offer tools for tracking symptoms, setting medication reminders, managing chronic diseases, and achieving fitness goals, encouraging patients to participate in their own health.
- Convenience: The need for physical visits is reduced, waiting times are shorter, and communication with healthcare providers is simplified.
- Personalized Care: Apps can offer tailored advice and insights based on individual health data, connecting patients with specialists as needed.
- Reduced Treatment Costs: According to the 2022 Medication Access Report, 79% of patients encountered unexpectedly higher prescription prices. By enabling remote consultations, healthcare apps reduce the need for physical appointments and the expenses of travel and missed work. Additionally, medication non-adherence, which can cost between $5,271 and $52,341 per patient, can be mitigated through apps that promote adherence, further lowering treatment expenses.
For Doctors and Healthcare Providers:
- Simplified Workflows: Apps facilitate efficient patient management, access to electronic health records (EHRs), appointment scheduling, and communication with patients and colleagues.
- Improved Patient Engagement: This leads to better adherence to treatment plans, remote monitoring of patient conditions, and proactive care delivery.
- Data-Driven Insights: The collection and analysis of vast amounts of patient data inform treatment decisions, identify trends, and optimize care.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Automating routine tasks allows for more patient interaction and less professional burnout.
- Expanded Reach: Healthcare providers can offer virtual consultations, allowing them to serve patients in remote or underserved communities.
As these benefits become expected, not optional, healthcare apps must scale fast. Emerging technologies, shifting patient behavior, and stricter regulations are now redefining how modern healthcare apps are built.
Also Read: Guide to Healthcare Software Development in 2026 with Expert Insights
Current Trends in Healthcare App Development
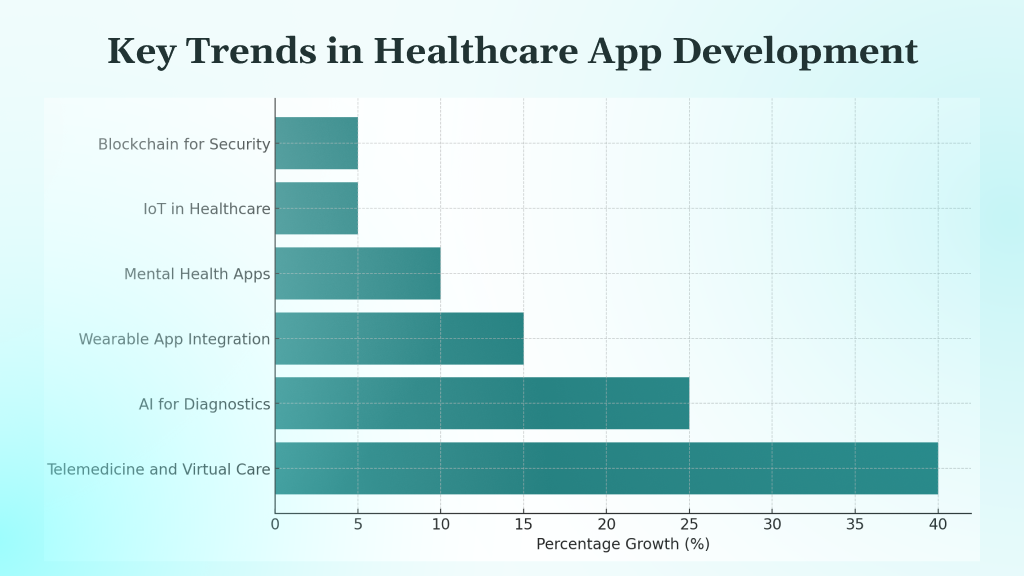
The healthcare app landscape is rapidly evolving due to technological advancements and changing patient demands. Current key trends include:
- Telemedicine and Virtual Care: Continued growth in remote consultations, diagnostics, and monitoring enhances healthcare accessibility.
- AI for Diagnostics and Personalized Insights: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) use algorithms to analyze medical data, enabling earlier disease detection, customized treatment plans, and forecasting of health outcomes.
- Wearable App Integration: Seamless connection with smartwatches and other wearable devices enables continuous health monitoring and data collection.
- Mental Health and Wellness Apps: A surge in demand for apps addressing mental well-being, stress management, and virtual therapy is underway.
- IoT in Healthcare: By integrating with medical devices, healthcare systems can achieve real-time data collection and remote patient monitoring.
- Blockchain for Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger system that enhances security and transparency in managing patient data and medical records by enabling immutable audit trails and controlled access.
- Data Intelligence and Analytics: Big data is key to unlocking actionable insights, leading to better patient care and more efficient operations.
As healthcare apps adopt these trends, success depends on execution. The next section breaks down the essential features required to support these trends safely and at scale.
Healthcare App Development: Must-Have Essential Features
Despite variations by app type, essential features of a robust healthcare app typically include:
- User Registration & Profile Management: Secure sign-up with identity verification and personalised profiles for patients, clinicians, and administrators.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granular access permissions based on clinical role (doctor, nurse, admin, pharmacist) to ensure users only see what they are authorised to access.
- Appointment Scheduling and Management: Online booking, rescheduling, cancellations, calendar sync, and automated reminders.
- Telehealth Functionality: Secure video and audio consultations, chat, and file sharing with low-latency and clinical-grade reliability.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Access: Secure, role-restricted access to patient medical history, diagnostics, prescriptions, and clinical notes.
- Emergency Access Rules (Break-Glass Access): Controlled emergency access to patient data with mandatory justification and automatic audit logging.
- Medication Reminders and Management: Dosage alerts, adherence tracking, refill reminders, and prescription history.
- Secure Messaging / Clinical Chat: End-to-end encrypted communication between patients and providers, with message retention controls.
- Consent Management: Explicit patient consent capture, updates, and revocation for data sharing, treatments, and third-party integrations.
- Audit Logs and Activity Tracking: Immutable logs for all data access, edits, exports, and system actions to support compliance and forensic audits.
- Payment Gateway Integration: Secure processing for consultations, diagnostics, subscriptions, and insurance-linked payments.
- Wearable Device Integration: Syncing data from fitness trackers and medical wearables for continuous monitoring.
- Push Notifications: Alerts for appointments, medication, lab results, care updates, and system notifications.
- Data Retention and Deletion Policies: Configurable retention rules aligned with healthcare regulations, including automated archival and secure deletion.
- Accessibility Compliance (WCAG): Support for screen readers, contrast controls, keyboard navigation, and inclusive UX for patients with disabilities.
- Downtime / Offline Mode for Clinics: Read-only or cached access to critical patient data during network or system outages to ensure care continuity.
- Data Security and Privacy Measures: Encryption at rest and in transit, strong authentication, session controls, and regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.).
- User Support and Feedback: In-app support, FAQs, ticketing, and feedback loops for continuous improvement.
Once these core features are defined, the next decision is application type. Different healthcare use cases demand different architectures, workflows, and compliance priorities, which directly shape how the product is built.
Healthcare Development: App Types
Healthcare apps serve different users and workflows. A clearer way to classify them is by workflow ownership: patient, provider, operations, and research.
Patient Apps
Apps where the primary user is the patient.
- Telehealth Apps: Virtual consultations, chat, prescriptions, follow-ups.
Examples: Teladoc, Amwell - Medication Management Apps: Reminders, dosage tracking, adherence logs, refill prompts.
Examples: Medisafe, MyTherapy - Wellness Apps: Fitness, sleep, meditation, habit tracking, stress management.
Examples: Fitbit, Headspace, Calm - Chronic Care Apps: Condition tracking, vitals logging, care plans, coaching, alerts.
Examples: mySugr - Mental Health Apps: Therapy support, CBT tools, mood tracking, guided programs.
Examples: Headspace, Calm - Women’s Health Apps: Cycle and symptom tracking, pregnancy tools, personalised insights.
Examples: Flo
Provider Apps
Apps where the primary user is a clinician or care team.
- Clinical Workflow Apps: Documentation, orders, care pathways, tasking, handoffs. (Often integrated with EHRs rather than replacing them.)
- Care Team Communication Apps: Secure messaging, role-based channels, escalation, on-call workflows.
Examples: Doximity (secure clinician communication/networking) - EHR Companion Tools: Mobile-first access to schedules, patient lists, notes, results, and in-basket workflows that extend an existing EHR.
Example: Epic (as an EHR ecosystem with companion apps)
Operations Apps
Apps owned by non-clinical teams who run the business of care delivery.
- Scheduling and Capacity Management: Centralised scheduling, resource allocation, queue management.
- Billing and Claims Support: Coding support, charge capture, claim status tracking, payment workflows.
- Inventory and Asset Management: Supplies, equipment tracking, procurement, usage reporting.
- Workforce and Shift Management: Rostering, time tracking, staffing demand planning.
Research And Trials Apps
Apps owned by research teams running studies and trials.
- E-Consent and Participant Onboarding: Digital consent flows, comprehension checks, versioning.
- Recruitment and Screening: Eligibility workflows, outreach, matching, intake.
- PRO Collection (Patient-Reported Outcomes): Surveys, diaries, symptom scoring, reminders, adherence monitoring.
After identifying the right app type, execution becomes the priority. Up next, we will outline a practical, step-by-step development process that turns healthcare requirements into a compliant, scalable product.
Also Read: Insurance Mobile App Development: A Comprehensive Guide
7-Step Guide to Healthcare Mobile App Development

Developing a successful healthcare app requires a structured approach. Below, we will learn seven steps to do so:
Note: HIPAA applies only in the US and depends on whether you are a covered entity/business associate
1. Defining the Purpose and Objectives
Before writing code, define the exact business and healthcare problem your app will solve. Be specific about the outcome, reducing appointment no-shows, improving medication adherence, or enabling remote care, so every feature, budget decision, and compliance effort stays focused.
2. Research and Analysis of the Target Audience
Healthcare apps fail when they assume users behave the same. Patients, doctors, and administrators have very different workflows and pain points. Use interviews, surveys, and real usage data to understand daily habits, frustrations, and expectations before finalizing requirements.
3. Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Your technology choices affect security, compliance, performance, and long-term scalability. Decide early between native or cross-platform development, select a secure backend, and ensure compatibility with healthcare standards like HL7 and FHIR to avoid costly rebuilds later.
4. Designing the User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI)
In healthcare, usability is not optional. Design for clarity, speed, and accessibility so users can complete tasks under stress. Simple navigation, readable interfaces, and accessibility support directly impact adoption, trust, and patient safety.
5. App Development Process
Development should balance speed with control. Build secure backend systems first, followed by stable front-end experiences. Integrate APIs for EHRs, payments, and telehealth carefully, while enforcing strict access controls and security measures from day one.
6. Testing for Functionality and Compliance
Testing goes beyond bugs. Healthcare apps must undergo security audits, performance testing, and regulatory validation. HIPAA compliance, data handling checks, and penetration testing are essential to prevent breaches, legal risks, and operational failures after launch.
7. Deployment and Launch Strategies
Launching a healthcare app requires more than store approval. Plan submissions carefully, prepare user onboarding, and consider phased rollouts. Early feedback helps reduce risk, improve usability, and stabilize the platform before scaling to a wider audience.
However, even with a structured development process, healthcare apps face unique obstacles. The next section breaks down the most common challenges teams face and how to plan for them.
Challenges in Healthcare App Development
Developing healthcare apps comes with unique, high-stakes hurdles:
- Ensuring Compliance with Regulations: Navigating complex and evolving regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and country-specific healthcare laws is non-negotiable. Non-compliance can lead to legal exposure, fines, and loss of market access.
- Data Security and User Privacy Concerns: Healthcare apps handle highly sensitive data. Preventing breaches and unauthorised access requires encryption at rest and in transit, strong authentication, audit logging, and continuous security monitoring.
- Interoperability and System Integration Complexity:
While standards like FHIR exist, real-world interoperability remains fragmented. FHIR adoption varies widely by vendor and even by version within the same system. Many EHRs impose vendor-specific constraints, partial implementations, or gated APIs. Data mapping between inconsistent schemas, terminologies, and workflows often becomes a significant engineering and maintenance burden rather than a one-time integration effort. - Legacy Infrastructure Constraints: Many healthcare organisations still rely on outdated or heavily customised systems that were not designed for modern APIs, cloud architectures, or real-time data exchange.
- Managing Approval and Certification Processes: Apps involved in diagnosis, treatment, or clinical decision support may require regulatory clearance (e.g., FDA, MDR), introducing long timelines, documentation overhead, and design constraints.
- User Adoption and Workflow Fit: Healthcare users operate under time pressure. Poor UX, extra clicks, or workflow misalignment can cause resistance from clinicians and low engagement from patients, even if the app is technically sound.
While addressing these challenges is critical to success, the work doesn’t stop at launch. Post-launch monitoring, compliance upkeep, and system evolution are essential to ensure long-term adoption and scalability.
Post-Launch Considerations
The journey does not end at launch; ongoing efforts are essential for long-term success. Key post-launch considerations include:
- Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: Regularly fix bugs, optimise performance, update dependencies, and release enhancements to keep the app stable and secure.
- Security Maintenance and Readiness: Maintain a defined patch cadence for infrastructure and third-party libraries, run scheduled penetration tests (and re-tests after major changes), and keep documented incident response playbooks covering detection, containment, notification, and recovery.
- User Feedback and Iterative Improvements: Actively collect and analyse feedback from patients, clinicians, and operations teams to guide prioritised improvements.
- Measuring App Performance and Effectiveness: Track metrics such as user engagement, retention, workflow completion, crash rates, and clinical or operational outcomes where applicable.
- Adapting to Changing Technologies and Regulations: Monitor regulatory updates, evolving security expectations, and platform changes to ensure continued compliance and competitiveness.
Post-launch performance shows what works today, but healthcare apps cannot stand still. Continuous improvement, security discipline, and regulatory vigilance are required to remain viable as the ecosystem evolves.
Future Directions in Healthcare App Development

Healthcare innovation is accelerating, but turning emerging technologies into production-ready healthcare apps comes with real-world constraints.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: Models can support earlier and more accurate detection, but training data quality, bias, explainability, and regulatory liability remain major barriers to clinical deployment.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting health risks and outcomes is powerful, yet models often struggle with incomplete data, shifting populations, and ongoing validation requirements.
- Personalised Treatment Plans: Tailoring interventions using genetic, lifestyle, and clinical data requires complex data integration, consent management, and careful clinical oversight.
- Healthcare Chatbots: AI-driven chat and triage tools improve access, but maintaining accuracy, managing edge cases, and preventing unsafe advice at scale is difficult in practice.
Advancements in Remote Patient Monitoring
- Wearable and IoT Integration: Continuous data from devices enables proactive care, but signal noise, device variability, patient adherence, and data reconciliation limit reliability.
- Proactive Alerts and Interventions: Triggering timely interventions sounds straightforward, yet defining clinically meaningful thresholds without overwhelming clinicians remains a persistent challenge.
Personalised Medicine and Precision Care Apps
- Genomics and Biomarker-Based Care: Precision care apps promise better outcomes, but genomic data interpretation, regulatory approvals, and limited clinical standardisation slow adoption.
- Guided Personalised Regimens: Apps can support complex care plans, but long-term patient adherence and measurable clinical impact are hard to sustain outside controlled environments.
Potential of Augmented and Virtual Reality in Healthcare Apps
- Medical Training and Education: Immersive simulations improve learning, yet content validation, cost, and integration into formal medical curricula limit widespread use.
- Therapeutic Applications: VR-based therapies show promise, but clinical evidence, reimbursement pathways, and consistent patient response remain unresolved.
- Remote Assistance and AR in Surgery: AR overlays and remote guidance can enhance procedures, but latency, hardware constraints, and medicolegal responsibility create high adoption barriers.
As AI, wearables, AR/VR, and precision medicine shape the next generation of healthcare apps, success depends less on adopting new technology and more on managing data quality, regulatory approval, model drift, and clinical risk. Choosing the right development partner becomes critical to turning innovation into safe, compliant, real-world healthcare solutions.
How to Choose The Right Healthcare Mobile App Development Partner
Finding the right development partner is important to turning your healthcare app vision into a secure, compliant, and high-impact solution. Here’s how to do it:
- Possesses Deep Industry Expertise: They should have a proven track record in healthcare app development and a strong understanding of medical workflows, terminology, and specific challenges.
- Prioritizes Regulatory Compliance: They must have in-depth knowledge of HIPAA and other relevant healthcare regulations, demonstrating a “privacy by design” approach.
- Demonstrates Strong Technical Proficiency: Evaluates their experience with diverse technologies, security protocols, and integration capabilities (EHR, APIs).
- Emphasizes Robust Security Measures: Inquire about their data encryption, access control, and vulnerability mitigation strategies.
- Offers Comprehensive Support and Maintenance: Ensure they provide post-launch support, regular updates, and a long-term partnership vision.
- Has a Transparent Development Process: Look for clear communication, agile methodologies, and defined project milestones.
- Provides a Strong Portfolio and Client Testimonials: Review their past work and seek references to gauge client satisfaction and project success.
- Understands User Experience (UX) in Healthcare: They should prioritize intuitive design and accessibility for diverse user groups.
Also Read: Ultimate Guide to EdTech App Development in 2025
Develop Your Healthcare Mobile App with DEVtrust
At DEVtrust, we focus on building healthcare applications that are secure, compliant, and operationally reliable in real-world clinical environments. Our approach prioritises regulatory alignment, workflow fit, and long-term maintainability over surface-level features.
We offer:
- Healthcare Domain Experience: We understand clinical workflows, patient journeys, and operational constraints, enabling us to design apps that fit within existing care delivery models rather than disrupt them unnecessarily.
- Compliance-Driven Development: Our delivery processes are aligned with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR, with compliance considerations embedded into architecture, data handling, and access controls from the start.
- Security-First Architecture: Multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, encryption, and audit logs protect sensitive health data. OTP can be used as one authentication factor, but it operates within a broader, layered security model rather than serving as a standalone safeguard.
- Scalable and Maintainable Technology Stack: We select proven frameworks and architectures that support performance, interoperability, and long-term system evolution.
- User-Centred, Workflow-Aware Design: Interfaces are designed to reduce cognitive load for clinicians and friction for patients, supporting adoption in time-constrained healthcare settings.
- End-to-End Delivery and Ongoing Support: From discovery and development to post-launch maintenance, security updates, and compliance upkeep, we support the full lifecycle of your healthcare product.
Case Study: Precina – Revolutionizing Healthcare
Precina, with DEVtrust, transformed healthcare by digitizing medication management and patient monitoring. It offers doctors real-time patient data and sends automated reminders for missed dosages, enhancing coordination and patient self-awareness. OTP authentication ensures robust data security for all health information. This platform ultimately boosts patient satisfaction and improves health outcomes.
Conclusion
Healthcare apps are revolutionizing patient care with features like telemedicine, appointment scheduling, and health tracking. With advancements in AI, wearable tech, and secure data handling, these apps are improving accessibility and outcomes. The right app can enhance both patient and provider experiences.
DEVtrust specializes in creating secure, compliant, and user-friendly healthcare apps. Our expertise ensures your app delivers on all essential features, from robust security to seamless user experiences, providing long-term value and efficient healthcare solutions.
Ready to turn healthcare with your app idea? Contact DEVtrust today for a consultation, and let us build the future of digital health together.