Building software is expensive, and guessing costs wrong can sink projects before they even start. Many teams struggle with surprises in budgets, timelines, or resources, making it hard to deliver on time or scale effectively.
Spending on hardware, software, and IT services is growing faster than it has since 1996. That means getting your software budget right is urgent. Overpaying wastes money, and underestimating costs can stall growth or leave you behind competitors.
This guide is for anyone planning, building, or managing software. You’ll learn what drives costs, how to estimate budgets realistically, control spending, and make smarter decisions for long-term value.
Key Takeaways
- Software development costs vary based on complexity, team size, and project type, ranging from $10,000 for simple apps to $250,000+ for enterprise-level systems.
- Estimating costs requires accounting for both direct (developer salaries, software licenses) and indirect (project management, technical debt) expenses.
- Choosing the right cost model (fixed, hourly, or dedicated team) and development partner can significantly impact overall spend.
- Focusing on core features and using agile methods helps reduce initial development costs without compromising quality.
- Ongoing costs such as maintenance, scaling, and compliance should be included in the overall budget for long-term sustainability.
What Is Software Development Cost?
Software development cost refers to every expense involved in building, launching, and maintaining a software product. It spans the entire lifecycle, from early planning to long-term support and upgrades.
In practical terms, software development costs in 2026 typically range from $10,000-$60,000 for simple MVPs, $30,000-$100,000 for mid-range custom software, and $80,000-$250,000+ for enterprise-grade systems. The final figure depends on factors such as scope, technical complexity, delivery model, and ongoing operational requirements.
It covers:
1. The Development Lifecycle
o Conceptualization and planning
o Design and user experience
o Engineering and quality assurance
o Deployment and ongoing updates
2. Direct and Indirect Costs
o Direct: Developer salaries, contractor rates, software licenses, hosting, and third-party integrations
o Indirect: Project management, team communication, scope changes, and technical debt
3. Long-Term Considerations
o Maintenance and feature enhancements
o Infrastructure scaling
o Regulatory compliance and security updates
o Accounting treatment, like cost capitalization and amortization
By viewing development costs as an end-to-end investment, from initial concept to long-term sustainability, you can budget more accurately and align project decisions with your broader business objectives.
How to Estimate Software Development Cost for Your Project?
Estimating software development cost becomes far easier when you focus on project-specific decisions instead of relying on general benchmarks.
- Define your business outcome clearly: Decide whether the software is intended to test a concept, simplify internal processes, or support enterprise growth. This clarity guides what features are essential, which stakeholders to involve, and how much initial investment is sensible.
- Prioritize must-have functionality: Identify the features critical for the first release and separate optional enhancements for later phases. Including future additions in the initial estimate is a common reason projects go over budget.
- Evaluate technical requirements in detail: List all necessary workflows, integrations, and security or compliance needs upfront. Understanding these requirements early helps produce realistic estimates and reduces the risk of scope surprises.
- Select the right engagement strategy: Choose between fixed-scope, iterative, or hybrid models based on how defined your requirements are. Clear agreements on milestones and deliverables help manage expectations and keep the project financially predictable.
- Include ongoing costs from the start: Consider recurring expenses such as updates, server costs, performance optimization, and support. Accounting for these in your estimate prevents budget shortfalls post-launch.
With this foundation in place, let’s now look at average software development costs and how they differ by project type and scale.
Average Software Development Cost Ranges By Project Type & Size
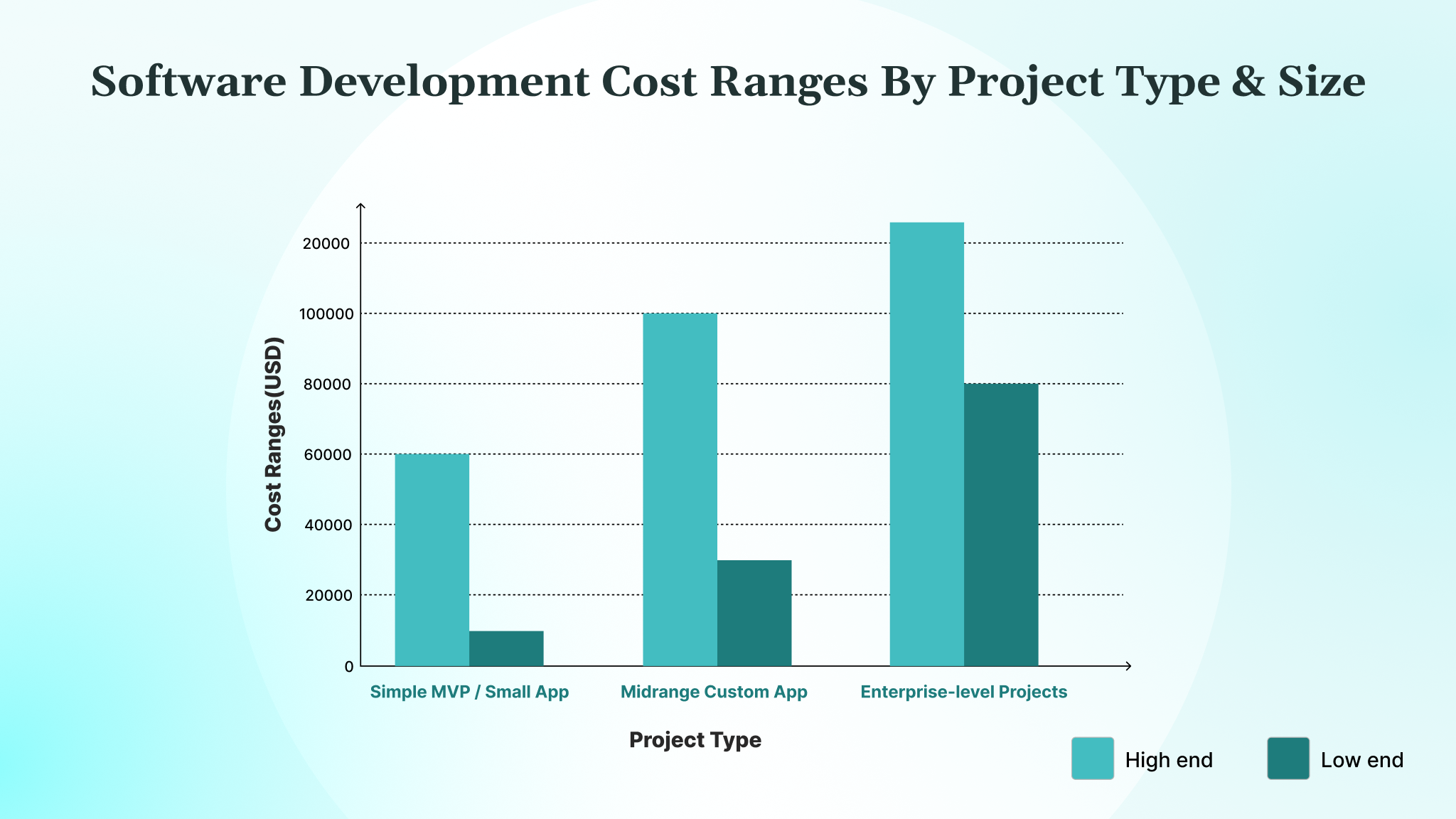
The average software development process costs between $50,000-$250,000. When it comes to custom software development, the prices can vary. Let’s begin by understanding how costs change dramatically based on project scope, complexity, and intended users.
Some apps serve niche audiences; others power entire enterprises. As a result, budgets scale accordingly, with each tier bringing its own requirements and considerations.
Simple MVP / Small App
A simple app or MVP (minimum viable product) focuses on the core idea. It typically includes basic features like login, simple workflows, and minimal integrations. The average development cost in this area ranges from $10,000 to $60,000.
Ideal for startups testing a concept, this type of project is efficient and quick. Developers can validate assumptions and get market feedback without getting bogged down in complexity.
Midrange Custom App
Stepping up in complexity, a mid-range app adds richer features, such as dashboards, custom databases, user permissions, or third-party integrations, like payment gateways. These projects require more architectural planning and design effort, costing between $30,000 and $100,000.
The development team also grows to include UX/UI designers, backend specialists, and QA resources. Midrange apps are strong business tools, often adopted by growing startups and small businesses.
Enterprise-level Projects
Enterprise software is designed for large organizations or those with complex workflows. These systems handle multiple user types, complex data flows, compliance requirements, and integrations with legacy or third-party systems. Software development costs for these fall between $80,000 and $125,000.
Architecting such platforms demands senior developers, system architects, business analysts, and dedicated QA teams. It often follows formal project methods, like formal requirement analysis and multi-stage testing.
Each tier signals different expectations, risks, and resource demands. Understanding where your project fits helps you plan effectively and choose the right development partner.
Cost by Business Stage
Software development priorities and costs vary significantly depending on your business stage. Understanding these differences helps allocate your budget efficiently and align spending with strategic goals.
Startups
Focus on speed and validating the core idea. Costs are driven by building an MVP with essential features, rapid prototyping, and minimal integrations. Typical software development budgets range from $10,000–$60,000. Prioritize launch-critical functionality over advanced architecture to keep budgets lean.
SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises)
Scalability and system integrations take center stage. Costs rise due to custom workflows, multi-platform support, and integration with existing business tools like CRMs, ERPs, or payment systems. Typical budgets fall between $30,000–$100,000. A balanced approach between speed and maintainability is key.
Enterprises
Enterprise projects demand robust architecture, strict compliance, and advanced security. Costs are higher due to multiple user roles, complex data flows, legacy system integrations, and regulatory audits. Budget ranges typically start from $80,000 and can exceed $250,000, depending on scope. Long-term maintainability and future-proofing the system are critical investment factors.
By mapping your development needs to your business stage, you can estimate costs more accurately and plan for both immediate and long-term requirements.
Hourly Rate Benchmarks For Software Development
Understanding the range of hourly rates is crucial for accurate budgeting and financial planning. These rates vary widely by region, agency type, and developer background. Here is a deeper look based on recent research and reports.
Regional Variation
Hourly developer rates vary notably across the globe. Most development providers charge between $20–$99/hour, with $20–$29/hour being the most common bracket.
Regions such as Eastern Europe and Latin America typically fall within the $30–$60/hour range for senior engineers, while Africa often offers rates from $20–$45/hour, depending on experience.
A recent global outsourcing report indicates a downward trend. For example, rates in Eastern Europe have declined by about 9%, while those in South and Southeast Asia have dropped nearly 16%.
Latin America, however, remained stable, bolstered by its proximity and cultural affinity with US clients.
These regional differences matter not just for cost, but also for ease of collaboration, time zone alignment, and regulatory compliance.
Agency And Tiered Rates
Agencies often segment their rates based on size and client type. Large consultancies, especially those operating in North America, commonly charge $200–$300/hour, with premium enterprise-level firms reaching up to $850/hour.
Mid-sized agencies typically charge between $125 and $200 per hour, while smaller firms and startups may cost between $75 and $125/hour, offering substantial value for targeted projects.
This tiered structure reflects differences in staff expertise, process maturity, and target project scale. Larger firms may offer comprehensive services, such as architecture planning and governance, whereas smaller ones tend to be more agile and cost-effective.
Freelancer And Full Stack Devs
Freelance and full-stack developers offer a broad spectrum of prices, depending on their skill set and location. Global platforms report average freelance rates from $70 to $150+/hour, driven by experience level and specialization.
In markets like the US and UK, experienced full-stack professionals often command $100–$150/hr, while counterparts in developing regions may charge $20–$60/hr.
Freelancers can offer flexibility and fast engagement. But with lower oversight, they may require more direction and management.
Full-stack devs bring multi-disciplinary skills, which suit mid-sized projects, but again, rate differences reflect both depth and regional cost standards.
By understanding regional trends, agency tiers, and freelancer dynamics, you can align your hiring strategy with both your budget and project needs.
Moving on, we will explore the building blocks behind these rates so you can get the full picture and make informed decisions.
Software Development Cost Components Breakdown
To accurately determine the actual cost of a software project, it is essential to consider not only visible expenses but also those that are less apparent.
This section walks you through the layers of cost, including direct investments, operational overhead, and accounting rules, so you can budget more accurately and make informed strategic decisions.
Direct Costs
Direct costs are the expenses that are visible in project budgets. These include salaries for developers, designers, and testers. They also cover software licenses, cloud hosting, API subscriptions, and third-party integrations.
Building a software system depends heavily on the “effective size” of code, development environment, and system complexity, each of which directly drives labor and infrastructure expenses. Precise direct cost estimates stem from careful measurement of these factors. Without understanding them, estimates can misfire.
For example, here are some estimated direct costs related to integrations you may encounter in your software development:
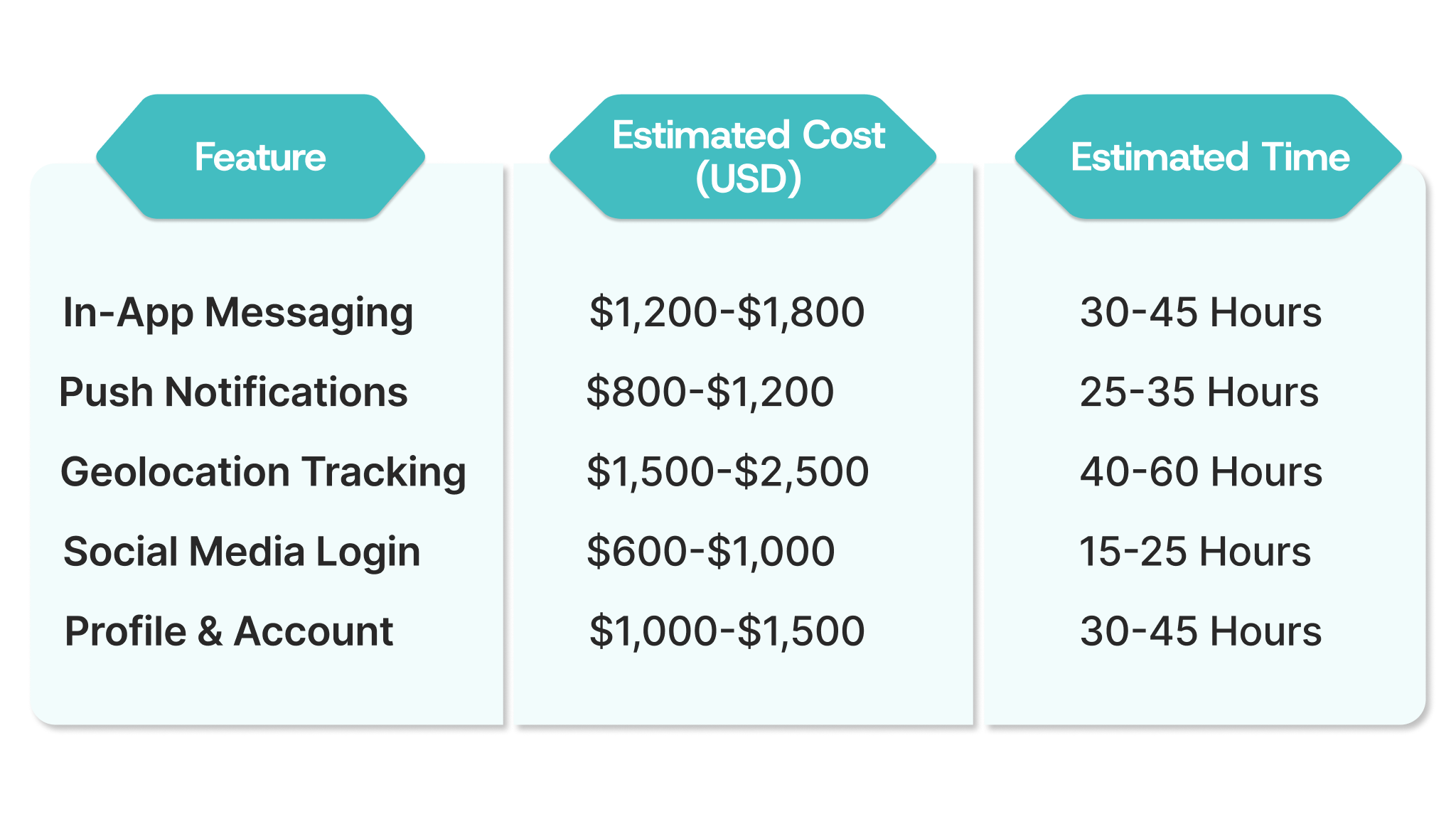
These estimates highlight the resources required to develop these features, both in terms of time and cost.
Indirect & Hidden Costs
Beyond salaries and tools, every project incurs indirect and hidden costs. These include project management effort, communication overhead, office space, onboarding, and technical debt. Academic studies highlight that actual fully burdened labor costs are often 2–3 times the developer’s base salary due to these hidden components.
For example, shortcuts in design or rushed deployments can create technical debt. That, in turn, increases future expenses in bug fixes and maintenance. Overlooking these subtleties leads to under-budgeted projects that overrun both schedule and cost.
Tax & Accounting Considerations
Finally, accounting standards and tax rules influence how costs are recorded and when cash flow is impacted. Under U.S. IRC Section 174, software development costs, as a subset of R&D expenditures, must now be capitalized and amortized over five years for domestic projects and fifteen years for foreign projects.
This shift has a significant impact on post-launch financial statements and tax deductions. Organizations must log individual labor, materials, and overhead expenses linked to SRE (specified research or experimental) activities as assets and amortize them systematically.
Accounting guides, such as the IRS’s Notice 2023‑63, clarify that labor for developers (including salaries, benefits, and contractor costs), plus associated overheads like rent and supplies for R&D staff, are included in the capitalization requirement.
Firms must now monitor non-billable time, categorize expenses by project, and adjust ledger systems to align with these rules. For startups and scaleups, this shift complicates cash-flow planning and budgeting, turning a simple cost into a multi-year financial commitment.
Cost Components Breakdown Scenario
Let us behold an e-commerce portal meant for the mid-market. Their average budget is approximately $250,000, covering the costs of the various processes involved in software development. Here is how the cost breaks down across different steps:
| Stage | What It Comprises | % of Total Cost | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Planning & Requirements | Includes stakeholder interviews, requirement documentation, roadmap creation, and risk assessment. | 5 – 10 % | $12,500 – $25,000 |
| UI/UX & Architecture Design | Covers wireframes, prototypes, UI design, and high-level system architecture specifications. | 10 – 20 % | $25,000 – $50,000 |
| Core Development (Coding) | Encompasses front‑end and back‑end implementation, database setup, and business logic. | 40 – 60 % | $100,000 – $150,000 |
| Testing & QA | Encompasses manual and automated testing, functional, integration, and regression testing. | 10 – 20 % | $25,000 – $50,000 |
| Deployment & Launch | Includes CI/CD setup, production environment configuration, and release processes. | 5 – 10 % | $12,500 – $25,000 |
| Maintenance & Support | Covers bug fixes, performance tuning, updates, and support after go-live. | 10 – 15 % | $25,000 – $37,500 |
| Indirect / Hidden Overhead | Includes project management, technical debt, team coordination, rent, training, and shared services. | Approximately equals direct labor cost | ~$125,000 (supporting all stages) |
By unpacking direct costs, hidden overhead, and strict accounting rules, you can map a realistic budget. If you are working with an experienced partner like DEVtrust, you will gain clarity on each cost layer, helping to avoid surprises that can derail delivery or inflate the total investment. So, which factors drive cost variation in the first place?
Factors Driving Cost Variation
Every software project is unique. Costs vary based on several factors, including the nature of the app and the way your team works. Understanding these elements helps you plan a realistic budget and select the most effective development strategy.
1. App/Software Type & Complexity
The type of software and its complexity significantly drive costs. Academic research using bank datasets shows that complexity is one of the strongest cost influencers.
Greater complexity consistently leads to higher estimated development effort. When your project integrates advanced workflows, AI, or real-time data, expect costs to rise accordingly.
For example, a healthcare company typically requires specialized software development focused on patient medication reminders and enhanced security. Discover how DEVtrust strategically assisted Precina with innovative solutions, including real-time data syncing and health alerts.
2. Platform Count
Delivering an app on web, iOS, and Android requires more work and more money. Research into bank software projects revealed that the primary platform choice has a significant impact on overall costs.
Each platform adds separate development, testing, and release cycles. Balancing cost and reach means choosing wisely or investing in cross-platform frameworks.
3. UI/UX & Integrations
Building sophisticated interfaces and connecting with third-party systems costs time and effort. Although harder to quantify, academic models consider integration complexity and user interface requirements as notable cost drivers.
Extensive integrations require custom APIs and robust testing, factors that multiply development time and introduce hidden costs.
4. Team Size
The makeup of your development team directly impacts costs. Both team size and member experience affect productivity and the effort required.
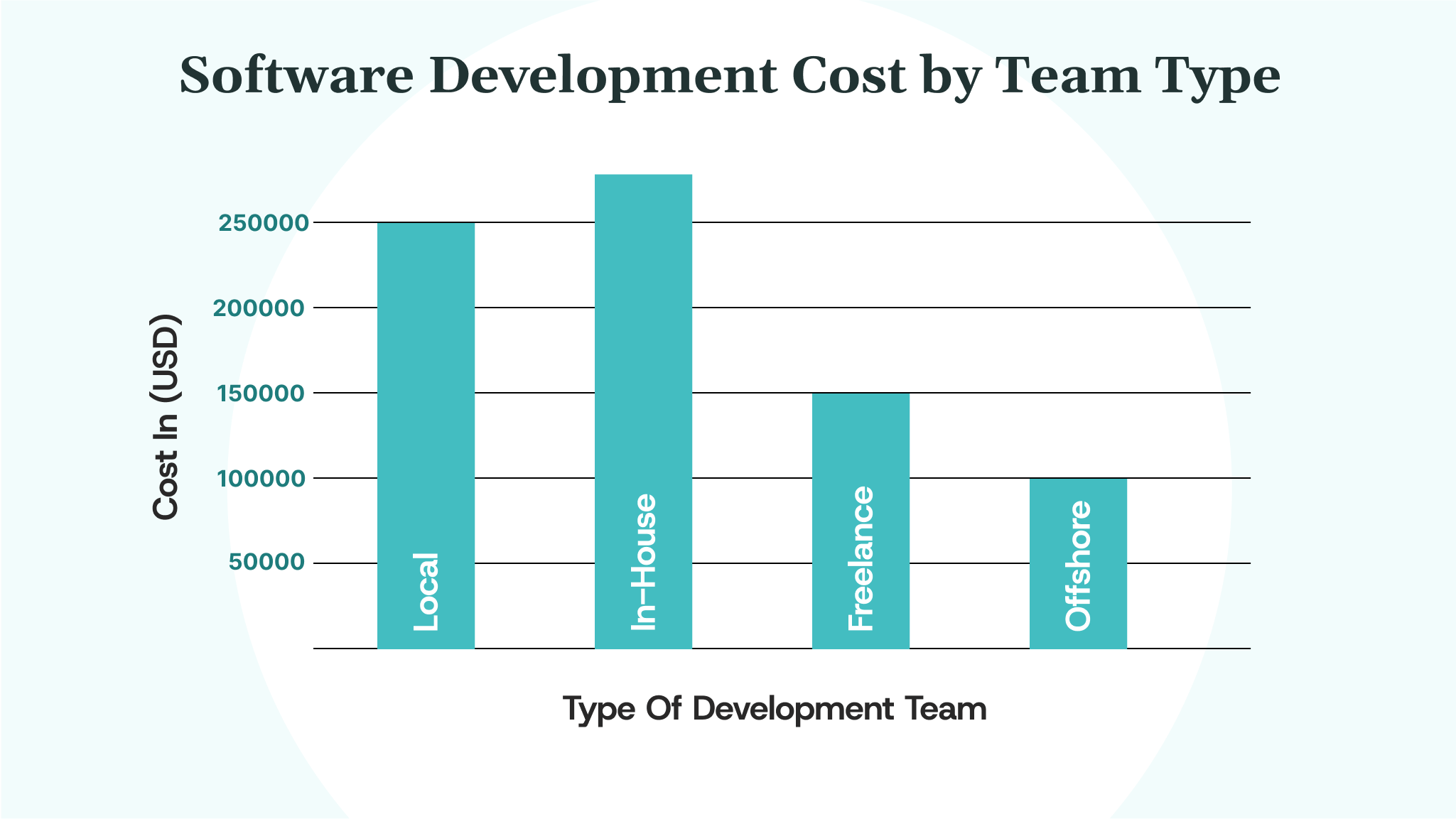
Larger teams may tackle more work, but this also leads to communication issues and slower decision-making. Senior developers cost more but can build faster. Your choice of region adds another layer to these variations. Here is a tabular representation of how costs vary across development team sizes:
5. Delivery Model
How you engage the team, through fixed-price, hourly, or dedicated crew, also drives cost variation. While not always quantified in academic cost models, delivery models shape risk, oversight, and flexibility.
Project context factors, such as procurement style and requirement count, have a profound impact on cost outcomes. A rigid model may limit adaptability, while a flexible model may slow progress if not closely managed.
6. Emerging Trends
New practices, such as agile, DevOps, and low-code, change cost structures. Systematic reviews show that time pressure, often a result of aggressive schedules, can boost effort and raise cost.
Adopting modern methodologies might increase upfront investment, but they reduce hidden effort later through better planning and fewer defects.
These six dimensions combine uniquely in every project. At DEVtrust, we carefully assess each factor. We build cost models tailored to your goals and context. That ensures transparency and helps safeguard your project budget.
AI & Modern Development Trends That Impact Cost
Artificial intelligence is increasingly reshaping software development budgets. Understanding how AI affects cost is essential for planning your project realistically. Here’s what you must know:
1. AI-enabled software vs. traditional software
Applications using AI, such as predictive analytics, recommendation engines, or natural language processing, require additional development effort, specialized talent, and data pipelines. This can raise upfront costs compared to conventional software, but it often delivers higher long-term business value.
2. AI infrastructure & ongoing costs
AI solutions demand robust infrastructure: cloud GPUs, scalable storage, and continuous model training. These recurring expenses must be factored into your total cost of ownership, including compute hours, data management, and monitoring systems.
3. AI-assisted development (cost reduction)
Using AI-assisted coding, automated testing, or low-code platforms can reduce manual effort and shorten timelines. While there is an initial investment in tools and setup, AI can help lower labor costs, boost delivery, and reduce error-related overhead.
Integrating AI thoughtfully allows businesses to balance higher upfront investment with long-term efficiency and innovation.
Deciding Between Low-Code/No-Code and Custom Development
Choosing the right development approach directly impacts both cost and delivery speed. Low-code/no-code platforms often reduce upfront development time and expense by providing pre-built components, visual workflows, and automated testing. This makes them ideal for:
- Internal tools or process automation
- MVPs and pilot projects
- Applications with predictable workflows and limited custom logic
However, costs can rise if your project requires extensive custom integrations, advanced AI features, or highly specialized workflows. In such cases, the platform may hit limitations, forcing workarounds or a full custom rebuild.
Custom development, though costlier initially, offers:
- Complete flexibility for complex or scalable products
- Tailored integrations with existing systems
- Greater long-term maintainability and adaptability
By evaluating your project’s complexity, integration needs, and scalability goals, you can choose the approach that balances speed, cost, and long-term value.
Software Development Cost Control Strategies
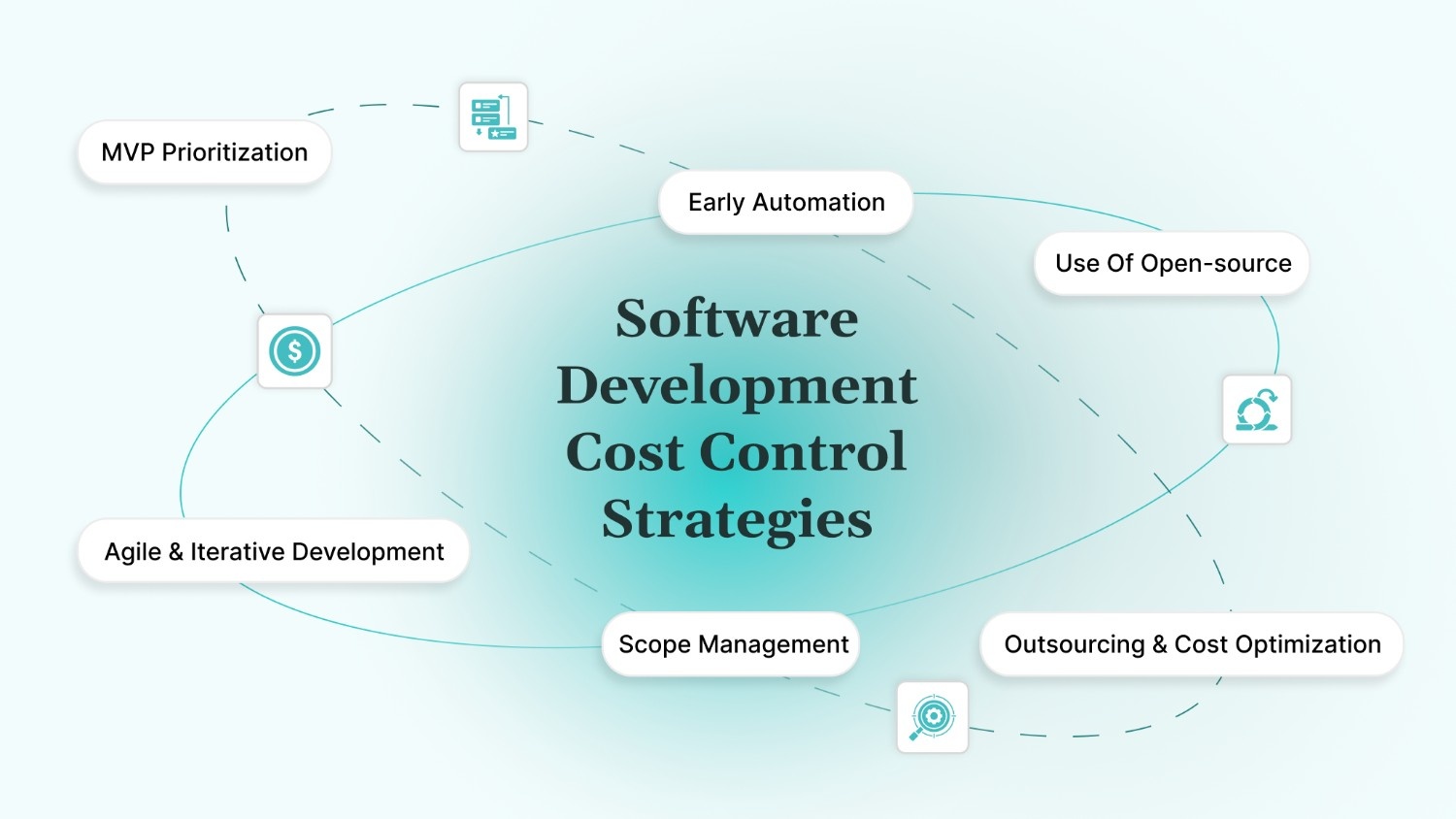
Effective cost control begins with more than just cutting budgets; it requires strategic decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
By focusing on prioritized development, using modern methodologies, and choosing the right tools and partners, you can optimize your spend without sacrificing quality. DEVtrust specializes in applying these strategies to support efficient, high-value delivery.
Feature Prioritization & MVP Focus
Focusing on core features first helps teams validate ideas and reduce unnecessary work. Academic research shows MVPs serve as both learning tools and communication aids, helping teams discover and refine what truly matters early in development.
By building only what is needed, you avoid over-engineering. As a result, your initial investment is lower, and you gain faster feedback for better-informed next steps.
Agile And Iterative Development
Agile practices like Scrum and XP have been shown to manage cost and scope in software projects effectively. Breaking work into short cycles makes it easier to adapt to changes and catch issues early.
This reduces surprises and keeps the project aligned with business goals. Teams become more efficient, and project managers retain tighter control over timelines and costs.
Use Of Open-source / Low-code Platforms
Low-code platforms have been proven to boost productivity and reduce development time, enabling faster market entry and cost savings. These tools allow both developers and non-technical team members to contribute, thereby reducing the need for custom development.
Careful governance ensures consistency and security. This approach offers speed and affordability, particularly for internal or process-based applications.
Outsourcing & Location-based Cost Optimization
Innovative outsourcing helps you align talent and expense efficiently. By combining in-house senior staff with offshore execution, you balance skill levels and cost.
This model limits overhead while ensuring strong technical oversight. DEVtrust often employs this hybrid approach to offer quality, performance, and financial control.
Early Automation
Introducing automation early, such as CI/CD and test automation, reduces manual effort and technical debt. Survey findings indicate that agile practices facilitate the systematic management of technical debt. Early automation keeps code clean and deployable.
This protects quality and speeds up development cycles over time, minimizing both time and cost overruns.
Clear Project Communication & Scope Management
Clear, ongoing communication is crucial for maintaining scope and preventing rework. Agile methodologies already incorporate regular check-ins and demos, but successful projects take it a step further.
They define roles, responsibilities, and approval workflows upfront. This emphasis on clarity reduces misunderstandings and ensures the team stays focused on shared objectives.
By combining these six strategies, you build a resilient, lean development process. DEVtrust applies this approach across projects to help clients deliver faster, smarter, and more cost-effectively. Companies need to ensure they take into account ongoing software development costs after launch.
Ongoing Software Development Costs After Launch
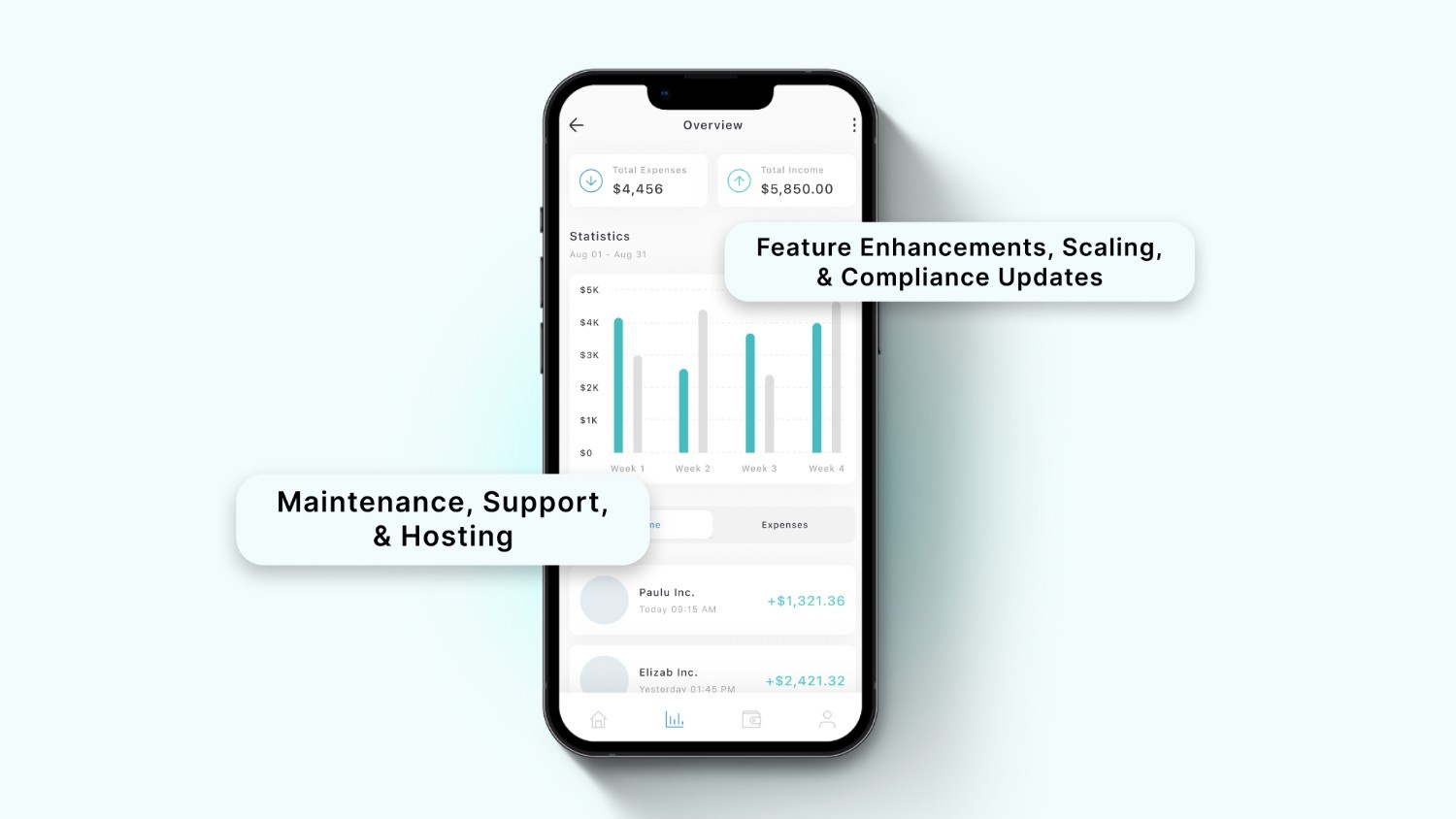
Once your software is live, the journey begins. The expenses do not end with deployment. Instead, maintenance, support, and continued updates become crucial. Failing to plan for these can lead to degraded performance, security risks, and user dissatisfaction.
Maintenance, Support, & Hosting
After launch, most of your software’s costs shift to maintenance and support. Academic studies indicate that over 70–80% of total lifecycle costs are allocated to this phase, primarily due to bug fixing, code updates, and adapting to new environments.
This cost includes technical debt cleanup, infrastructure hosting, monitoring systems, and user assistance. Since most live software requires constant upkeep, you need a partner who plans for this phase, like DEVtrust, to keep your system reliable without breaking the bank.
This is especially important if you are in an industry like real estate, where you require software that stays current with the latest market trends. Read more about how DEVtrust helped MySpace achieve integration with advanced APIs and automate its administrative tasks with ongoing support.
Feature Enhancements, Scaling, & Compliance Updates
As your user base grows and business needs evolve, your software must too. Research shows that a significant share of maintenance budgets is spent on enhancements rather than just fixing issues.
This includes adding new features, optimizing performance, and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. Adaptive and perfective maintenance, the activities that improve and evolve functionality, often represent a large portion of ongoing spend.
It is crucial to anticipate these needs and allocate a portion of your budget accordingly. DEVtrust emphasizes proactive scaling and compliance planning. This ensures that your software not only continues to work but also remains competitive and legally sound as it grows. In the long run, businesses should make ROI and business value considerations.
ROI And Business Value Considerations
Unlocking real business value from software goes beyond budgeting. It requires seeing your project as an investment, not an expense. Understanding return on investment (ROI) and strategic alignment helps guide smart development decisions and future-proof your choices.
Budget Vs. Strategic Investment In Digital Transformation
Even the most straightforward projects carry financial implications. But the real payoff comes from strategic investment. Custom software should be treated not as a cost but as a capital investment that can deliver measurable business returns over time.
That means considering both direct revenue gains, such as higher sales or reduced headcount, and indirect benefits, including a stronger brand reputation or improved employee morale.
When executives analyze software investments, they should apply both hard and soft ROI measures. Hard ROI tracks real financial impact. Soft ROI reflects intangible improvements, like team efficiency, customer satisfaction, or reduced risk.
Together, they provide a comprehensive view. This mindset helps companies justify costs and plan for long-term value. It is also worth noting that the ROI of software development varies significantly across companies.
For example, a logistics company may focus its budget more on efficient databases and carrier integrations to remain strategic in software development. Read more about how DEVtrust helped Moveit4U with comprehensive warehouse and driver management features.
Comparison: Low-cost Vs. Long-term Value Trade-Off
Opting for the lowest development cost can seem wise at first. But quality and flexibility often suffer. A cost-benefit framework called “total benefits of ownership” (TBO) shows that low upfront costs may miss long-term gains.
Sustainable value often comes from investments in maintainable code, strong architecture, and adaptable systems. These factors reduce technical debt, which, as multiple studies have linked, is associated with increased defects and slower development when neglected.
Pricing methodologies, such as the Incremental Funding Methodology (IFM), promote delivering value in small, revenue-generating increments.
Each increment is assessed for net present value (NPV) and ROI before being funded. This approach balances investment exposure with a rapid return on business.
At DEVtrust, we combine enterprise-grade engineering with ROI-focused delivery. That means pairing best-in-class code quality, staged delivery, and strategic oversight. The result is software that pays back, not just financially, but with real business impact and resilience.
Simplify Software Development Costs with DEVtrust
Software development costs often spiral out of control, from unforeseen expenses in platform selection to hidden charges like maintenance and compliance. The complexity of building secure, scalable systems can lead to budget overruns if not properly managed.
DEVtrust offers a proven solution to manage these challenges, providing cost-effective strategies for software development without compromising quality. Our approach ensures that projects are completed on time and within budget.
- AI-driven development for faster delivery
- Cloud-based solutions for scalable, cost-efficient apps
- Robust security features, including PCI-DSS and SOC 2 compliance
- Comprehensive quality assurance (QA) to minimize errors
- Expertise in mobile, FinTech, and enterprise software
With DEVtrust, you can control your software development costs while ensuring long-term success.
Conclusion
Understanding software development costs means looking beyond the price tag. It requires evaluating every stage, from ideation and hourly rates to hidden expenses, cost drivers, and long-term investments.
When these pieces come together, you gain clarity on how budgets align with quality, speed, and strategic outcomes.
A partner like DEVtrust can guide you through this complexity. We prioritize transparency in cost breakdowns, align budgets with business objectives, and help you invest in software that scales with your needs.
Talk with DEVtrust to start your journey toward cost-efficient, high-impact software delivery that truly matches your business’s needs.