Mobile apps often run on risky networks and devices. They face threats like harmful code and data theft. Without the proper protection, apps can leak user data, break rules, and put companies at risk.
In fact, the global average cost of a data breach hit USD 4.88 million in 2024, the highest ever recorded. As threats grow more expensive and complex, strong mobile app security is no longer optional.
Mobile app security helps stop these problems. It keeps data safe, secures logins, protects the code, and watches for threats at every stage.
This guide shows how to protect your app from build to launch. It explains what to do, what rules to follow, and how to design your app for long-term safety.
Key Takeaways
- Mobile app security best practices help mitigate risks associated with common vulnerabilities, including insecure storage, weak authentication, and reverse engineering.
- Add security at every step, writing code, checking tools, storing data, and launching updates.
- Use strong tools like two-factor login, TLS 1.3, certificate pinning, and access control.
- Keep the app safe with auto-fixes, threat alerts, quick action plans, and by adhering to rules such as GDPR and HIPAA.
What Is Mobile App Security?
Mobile app security involves protecting apps from threats like data breaches, unauthorized access, and code tampering. It covers every layer of the app, including the user interface, backend systems, and the flow of data between them.
Apps often run in risky conditions. Devices may connect to public networks, store sensitive data, or run outdated software, which can compromise their security. These issues create more chances for attackers to break in if the proper protections are missing.
Strong security focuses on three key goals: maintaining data privacy, preventing tampering, and ensuring the app remains available. Teams utilize tools such as encryption, secure login flows, runtime protection, and regular audits to mitigate risk and safeguard users.
Why Mobile App Security Is Important?

Mobile app security protects user data, prevents unauthorized access, and reduces the risk of financial, legal, and operational damage. Without it, businesses expose themselves to avoidable threats that can derail product growth and break customer trust.
Here are the core reasons why it must be a priority:
- Financial Risk: Breaches can result in millions of dollars in losses, remediation costs, and penalties. Mobile-specific attacks often result in higher exposure due to the sensitive personal data they compromise.
- Compliance Violations: Applications that process health, financial, or personal data must comply with regulations such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. Missing the mark can result in fines or the loss of market access.
- Customer Churn: Users expect privacy. Security incidents can quickly damage a brand’s reputation, and many users may permanently stop using an app after a breach.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: Unprotected code can be reverse-engineered, exposing proprietary logic, algorithms, and trade secrets to competitors or attackers.
- Downtime and Disruption: Responding to a breach diverts teams from product work, delays updates, and consumes valuable resources.
- Missed Growth Opportunities: A poor security posture can block enterprise deals, slow global expansion, and disqualify vendors from government contracts.
Substantial mobile app security limits damage, supports long-term scale, and helps meet the expectations of modern users, regulators, and enterprise buyers.
Common Mobile App Security Risks
Mobile apps face repeatable, well-known threats. These issues frequently appear in production apps, particularly those developed without a security-first architecture.
Listed below are the most common risks teams encounter:
- Insecure Data Storage: Many apps store tokens, passwords, or PII in plain text on the device. Attackers can retrieve this data from lost or compromised phones, primarily if file encryption or secure storage APIs are not used.
- Weak Authentication and Authorization: Developers often skip multi-factor authentication or use predictable login flows, which can compromise security. Combined with poor session management, this allows attackers to hijack accounts or bypass access controls.
- Insecure Communication: Even today, apps are shipped without proper SSL enforcement or certificate pinning. Public Wi-Fi and proxy tools make it easy to intercept unprotected data.
- Code Tampering and Reverse Engineering: Mobile apps distributed without obfuscation or tamper checks are easy targets. Attackers modify business logic, extract sensitive information, or inject unauthorized features, particularly in gaming, fintech, and subscription-based applications.
- Insecure Third-Party Libraries: Many teams integrate SDKs without checking for known vulnerabilities. Outdated or poorly maintained libraries can silently introduce data leaks or security flaws.
- Improper Session Management: Common issues include session tokens that never expire, reused cookies, or the absence of logout logic. These mistakes make it easy for attackers to stay authenticated longer than they should.
- Client-Side Injection: Apps that fail to validate input on-device are vulnerable to SQL injection, XSS, or command execution, especially in chat, search, or dynamic form features.
- Lack of Binary Protection: On Android, in particular, attackers can decompile APKs and inspect or modify source code unless proper protections are applied. Many apps lack basic hardening.
Most security gaps can be avoided with exemplary architecture and processes. Development partners like DEVtrust help businesses build mobile applications with secure code, encrypted storage, and built-in compliance. Book a call if your app requires security upgrades or a comprehensive audit.
How to Implement Mobile App Security?
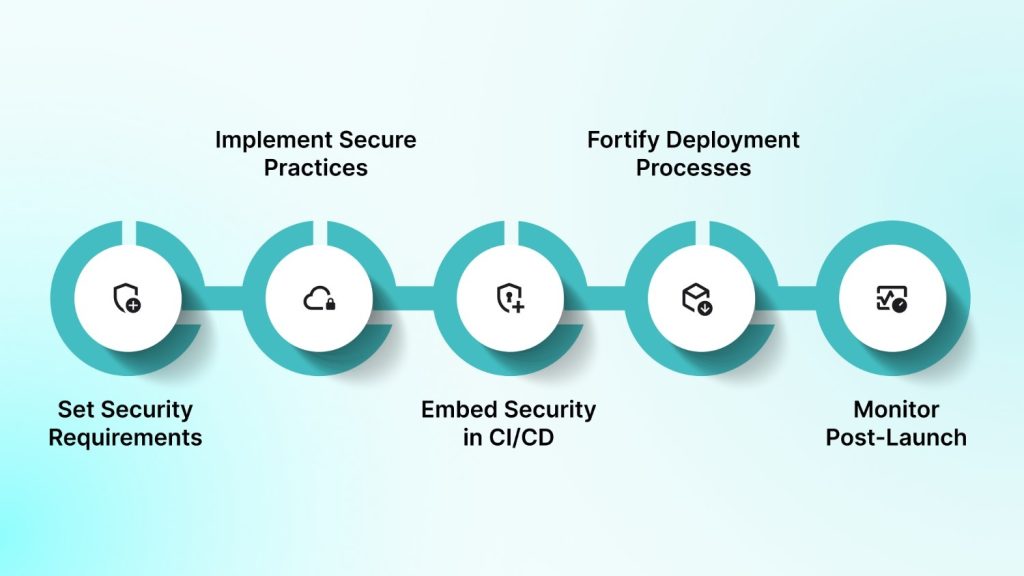
Security implementation works best when it is embedded into every stage of the mobile app lifecycle. Here is a step-by-step model teams can follow to build and maintain secure applications.
Step 1: Define Security Requirements Upfront
Start by identifying the data your app handles, the regulations that apply, and the attack vectors that must be accounted for. Set clear security goals, define risk tolerance, and document technical requirements for authentication, encryption, storage, and access control.
Step 2: Apply Secure Development Practices
During development, enforce code reviews, static analysis, and secure coding standards to ensure quality and security. Limit third-party libraries, isolate SDKs, and document security decisions. Use protected keys and secure APIs from the start to reduce rework later.
Step 3: Integrate Security into CI/CD
Automate security testing with tools that scan for known vulnerabilities (SAST, DAST, dependency checkers). Block builds that fail basic checks. Add manual penetration tests for major releases. All findings should be tracked and verified before deployment.
Step 4: Harden Deployment and Release Processes
Use signed builds, secure distribution channels, and version control to prevent tampering. Configure update mechanisms that verify integrity before installation. Avoid hardcoded secrets and minimize attack surfaces in production builds.
Step 5: Maintain and Monitor Post-Launch
Set up runtime monitoring, logging, and anomaly detection. Stay updated with threat intelligence feeds, apply patches promptly, and have a plan in place for rotating credentials as needed. Train your teams regularly and run periodic security audits.
Mobile App Security Best Practices
Security in mobile apps must be built in from the start. It affects how the app handles data, connects with external systems, and scales under real use. Each stage of development should reinforce protection without compromising performance or usability.
The best practices outlined below help teams reduce risk and deliver secure applications that are ready for production environments.
1. User Authentication and Authorization
Authentication and authorization determine who can access the app and what they can do. Strong controls prevent unauthorized access, reduce data exposure, and protect user sessions across devices.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all user accounts: Use TOTP apps, SMS codes, hardware security keys, or biometric options. Ensure the system supports MFA even during network interruptions without reducing verification strength.
- Use biometrics as a second factor: Integrate fingerprint, facial, or voice recognition through platform-secure elements that isolate biometric data and processing. Keep biometric data stored locally on secure hardware to prevent unauthorized access.
- Secure sessions with token-based authentication: Use JWT or OAuth 2.0 to manage sessions without constant server calls. Apply strict token expiration, refresh logic, and safe storage. Keep token payloads minimal and permissions tightly scoped.
- Enforce role-based access control (RBAC): Map users to roles with clearly defined access rights. Apply permission checks on both the client and server to prevent bypass attempts or elevation of privilege.
- Manage sessions with clear timeouts and complete logout logic: Automatically expire inactive sessions, restrict concurrent sessions if needed, and ensure logouts terminate all active tokens across devices.
2. Data Protection
Protecting user and application data requires securing it at rest, in transit, and during processing without degrading performance or reliability. These practices help teams implement security at the data layer.
- Use strong encryption standards: Protect stored data with AES-256 and secure transmissions with TLS 1.3. Never use custom encryption. Store and manage keys through HSMs or secure cloud services.
- Classify data by sensitivity: Label data as public, internal, confidential, or restricted. Implement stronger encryption and more stringent access controls for high-risk data. Use the separation of duties to limit internal access.
- Go beyond basic HTTPS: Add certificate pinning and verify server certificates to stop interception. Use secure retry settings and avoid fallbacks that weaken encryption during connection drops.
- Collect and retain only what is necessary: Limit data collection to what the app truly requires. Set retention rules, allow users to delete their data, and regularly review stored data to remove what is no longer needed.
- Treat backups like production: Encrypt all backup data and restrict access to it. Only allow trusted users to restore data. Test backup recovery under real-world conditions to ensure it works.
3. Mobile Network Security Measures
Protecting data in transit requires securing every layer of the communication process, especially in mobile environments where apps connect through untrusted networks.
- Use certificate pinning to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. Embed trusted certificates in the app and include backup pins to support certificate renewal. Handle failures securely without disabling checks.
- Log and monitor all network activity for anomalies. Capture request/response patterns, failed connections, and unexpected destinations. Use this data to detect unauthorized traffic or data exfiltration attempts.
- Apply a strict Content Security Policy (CSP), a security standard that specifies trusted sources for scripts and resources, to control what can load in the app; block inline scripts and limit third-party domains to prevent injection attacks and data leaks via unauthorized external calls.
- Segment network layers to isolate critical services. Use firewalls, private networks, and zero-trust access controls. Never assume internal traffic is safe; validate every connection explicitly.
4. Testing and Vulnerability Scanning
Security issues left undetected in staging often become production incidents. Teams must test early, simulate real-world attacks, and act on the results. These testing and scanning practices help prevent breaches before the code goes live.
- Run Static Application Security Testing (SAST) early and often: Add SAST tools to your CI/CD pipeline. These tools scan code during development to find unsafe functions, common flaws, and setup mistakes in frameworks.
- Use Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) for live testing: DAST checks how your app behaves while running. It simulates real attack methods, such as injection, broken logins, and weak sessions. Run tests in different environments to catch issues SAST may miss.
- Add Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST): IAST tools watch how the app behaves during functional testing. They identify hidden issues that only become apparent at runtime. IAST also provides clear reports to help teams resolve issues more quickly.
- Conduct regular manual penetration testing: Hire skilled security testers to identify complex issues that tools may miss. Include your APIs, network layers, and full user flows in the test.
- Create a solid vulnerability management process: Scan your app often. Keep a list of known issues and prioritize fixing them based on their risk level. Track each fix until it is complete.
5. Ongoing Security Maintenance and Updates
Securing a mobile app does not end at deployment. Teams must maintain visibility, act on threats, and keep the security posture current.
- Watch for threats at all times: Track user actions, network activity, and app performance in real-time. Set alerts to identify any unusual activity and take immediate action.
- Send security updates quickly: Utilize tools to expedite patch distribution. Test updates before release. Inform users and include version checks and rollback options to prevent bugs.
- Use real-time threat intelligence: Connect to threat data feeds and detection tools. Update your security rules based on new attack methods.
- Train your development team: Conduct regular sessions on secure coding, testing, and incident handling. Keep the training up to date with new threats and tools.
- Have a clear response plan: Write down what to do in the event of a security issue. Include steps to stop the attack, find the cause, and fix the damage. Also, plan how to communicate and review what happened afterward.
6. Compliance and Legal Considerations
Mobile apps must adhere to local and industry regulations regarding data, privacy, and security. These rules help teams stay legal without slowing down work.
For GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- Collect only the data you need (data minimization).
- Ask users clearly before collecting their data (explicit consent).
- Let users access, delete, or move their data.
- Keep records of data processing and explain your legal reason for collecting it.
For HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- Implement access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can view health data.
- Turn on audit logging to track who views the data.
- Encrypt protected health information (PHI) in transit and at rest.
- Sign Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with vendors who handle PHI.
- Conduct yearly risk assessments to identify areas for improvement.
For PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- Use tokenization to replace card numbers.
- Encrypt cardholder data during use and storage.
- Avoid storing sensitive payment data when possible.
- Run regular security scans and document all PCI controls.
For CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
- Let users opt out of having their data sold.
- Inform users about the data you collect and its purpose.
- Respond to deletion or access requests within the required timeline.
- Track and document how you share personal data.
For international data transfers
- Use Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) for cross-border transfers.
- Check for risks when sending data outside your region.
- Follow data residency laws where required.
- Keep all legal documents up to date as rules change.
7. Code Obfuscation and Reverse Engineering Prevention
Preventing reverse engineering helps protect proprietary logic, sensitive data, and app integrity. These best practices make it harder for attackers to inspect or modify mobile applications.
- Encrypt all sensitive strings and constants: Protect API keys, URLs, and configuration values from static analysis. Use runtime decryption and secure key derivation instead of hardcoding values.
- Implement layered anti-debugging measures: Detect debuggers with timing checks, environment validation, and system call monitoring. Combine multiple techniques to slow down analysis and force bypass attempts to fail.
- Use binary packing with integrity checks: Compress and encrypt your app binary to prevent disassembly. Add runtime unpacking and verify binary integrity to detect tampering or repackaging.
- Protect app resources from extraction and abuse: Encrypt images, config files, and embedded assets. Load them dynamically at runtime with access control checks and usage tracking to detect anomalies.
8. Root/Jailbreak Detection
Rooted or jailbroken devices expose mobile apps to elevated risks by bypassing system protections. These practices help detect compromised environments and respond without disrupting legitimate users.
- Validate device integrity both at launch and during runtime: Scan for altered system files to disable OS security features or jailbreak indicators.
- Analyze system behavior for tampering patterns: Monitor runtime activity, intercept system calls, and flag anomalies that suggest a compromised environment. Continuously refine detection logic based on new threat techniques.
- Use platform-specific hardware attestation: Integrate secure boot validation, trusted execution environments, and attestation APIs (e.g., SafetyNet on Android, DeviceCheck on iOS) to confirm device authenticity.
- Define adaptive response strategies for compromised devices: Restrict access to sensitive features, increase logging, or terminate the session based on severity.
- Reduce false positives through layered verification: Correlate multiple detection signals before acting. Allow verified exceptions, log every detection event, and support appeal flows where legitimate users are blocked.
9. Secure Third-Party Libraries and SDKs
Third-party components expand functionality but introduce external risk. Each library must meet your security, compliance, and reliability standards before being deployed in a production environment.
- Maintain a real-time inventory of all dependencies: Track component versions, licenses, and known CVEs. Automate scanning for vulnerabilities and enforce update policies across environments.
- Vet libraries before adoption: Review available source code, validate vendor security practices, and test in isolation. Confirm the SDK does not introduce unsafe permissions, telemetry, or hardcoded secrets.
- Isolate risky components at runtime: Restrict third-party access using sandboxing, scoped permissions, and runtime monitors. Block unnecessary file, network, or API access from external SDKs.
- Harden your software supply chain: Assess the integrity of vendor build pipelines, monitor for tampered updates, and require signed packages or SBOMs when possible.
- Prepare backup options for high-risk libraries: Keep replacement candidates evaluated and ready to deploy if a component becomes vulnerable, deprecated, or non-compliant.
How DEVtrust Builds Secure Mobile Applications?
DEVtrust builds mobile apps for industries where security cannot fail, such as finance, healthcare, and enterprise systems. Every app is built on a secure foundation, with verified code and tested infrastructure. These apps meet strict legal and operational requirements from day one.
In a recent project, DEVtrust developed a mobile leasing platform called Payvantage. The new onboarding flow reduced drop-offs and improved user completion rates, all while maintaining strong security controls.
- They added secure bank verification.
- They built a fraud-resistant payment system.
- They maintained a fast and smooth user experience.
DEVtrust manages security across the full development lifecycle. This includes:
- Threat modeling and secure API design.
- Encrypted data storage.
- Built-in compliance for HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI.
- Regular vulnerability scans and code reviews.
Security does not stop at launch. DEVtrust also provides:
- Patch cycles and updates.
- Threat monitoring.
- Audit-ready documentation to support compliance reviews.
This whole approach helps clients launch mobile apps that stay reliable under pressure and meet the security standards users, partners, and regulators expect.
Conclusion
Strong mobile app security reduces operational risk, prevents costly incidents, and ensures long-term product stability. The practices outlined above help close common security gaps across development, deployment, and ongoing operations.
Adequate security relies on expertise, transparent processes, and ongoing monitoring. Teams that treat security as a core requirement are better equipped to meet compliance standards and resist evolving threats.
DEVtrust builds on a secure architecture from day one. Book a call to create mobile applications that meet the highest security and compliance standards.
Mobile App Security Best Practices for Secure Development
Enhance mobile app security by addressing vulnerabilities, encrypting data, and ensuring compliance. Secure your app development now!
Contact Us