Every patient’s fundamental need in a hospital is to experience a smooth treatment process, receive proper attention from doctors, and have a hassle-free payment experience. To achieve this, hospitals require robust management systems, advanced technologies like AI, and meticulous documentation. A primary agenda for any hospital is to implement all necessary software and systems. If you’re reading this, it likely means you’re in the process of deciding which essential software solutions to adopt for your hospital. In the following section, we will discuss the most important software systems for hospitals.
Key Takeaways
- Medical software digitizes healthcare, improving efficiency, safety, and patient care.
- EHR (Electronic Health Records) centralize patient data for better coordination and reduced errors.
- Practice Management and Medical Billing/RCM software streamline administrative and financial operations.
- Telemedicine and Patient Portals enhance patient access and engagement through virtual connections and self-service
- Advanced solutions like Medical Imaging, E-prescribing, CDSS, LMS, and Population Health Management boost diagnostics, safety, training, and preventative care.
What is Medical Software?
At its core, medical software refers to specialized computer programs and applications crafted to optimize and modernize healthcare operations.
These digital tools serve as the technological backbone for clinics, hospitals, and various medical facilities, automating complex tasks, ensuring accurate data management, and fostering seamless communication.
From the intricate systems that manage patient health records to innovative platforms enabling remote consultations and advanced diagnostics, medical software is integral to enhancing safety, efficiency, and the overall quality of patient care.
The Essential Pillars of Modern Healthcare Software
Let’s dive into the core software systems that are transforming healthcare delivery:
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Software
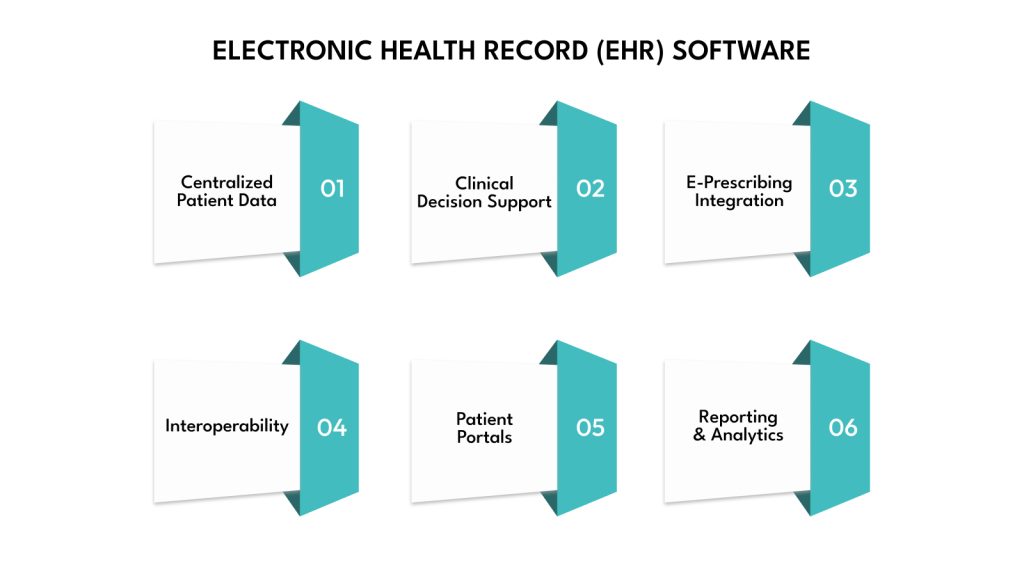
Electronic Health Record (EHR) software is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart. It includes a comprehensive overview of a patient’s medical diagnoses,history, medications, treatment plans, immunization dates, allergies, radiology images, and lab results. Key features often include:
- Centralized Patient Data: Consolidating all patient information in one accessible location.
- Clinical Decision Support (CDS): Providing alerts for drug interactions, allergies, and preventive care reminders.
- E-prescribing Integration: Allowing electronic submission of prescriptions to pharmacies.
- Interoperability: Facilitating the secure exchange of patient data among different healthcare providers and systems.
- Patient Portals: Enabling patients to view their health information, schedule appointments, and communicate with providers.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generating insights into patient outcomes, clinical performance, and trends.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
EHRs have dramatically improved care coordination and patient safety by reducing errors related to illegible handwriting and incomplete records. They enable faster access to critical patient information, leading to more informed and timely decision-making. The automation of administrative tasks streamlines workflows, allowing healthcare professionals to dedicate more time to patient care. Notably, 94% of providers report immediate access to records through their EHR.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Patient Safety: Reduced medication errors and improved accuracy in diagnoses.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined workflows, reduced paperwork, and faster access to information.
- Better Care Coordination: Seamless data exchange among providers for comprehensive care.
- Cost Savings: Reduced redundant testing and administrative overhead.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to standards like HIPAA for data security and privacy.
Examples: eClinicalWorks
Practice Management Software

Practice Management (PM) software is designed to streamline the administrative and financial operations of a medical practice. Its functionalities include:
- Appointment Scheduling: Managing patient appointments, reducing no-shows with automated reminders.
- Patient Registration and Check-in: Digital intake forms and efficient patient onboarding.
- Billing and Claims Processing: Automating billing tasks, verifying insurance eligibility, and submitting claims electronically.
- Reporting and Analytics: Tracking financial performance, claim statuses, and operational efficiency.
- Patient Communication: Sending personalized reminders, follow-up messages, and educational materials.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
PM software significantly reduces the administrative burden, allowing healthcare staff to focus more on patient care. By automating routine tasks and improving billing accuracy, it optimizes the revenue cycle, ensuring timely and accurate payments for the practice. It also enhances patient experience through efficient scheduling and communication.
Key Benefits:
- Streamlined Workflows: Optimized scheduling, patient intake, and billing processes.
- Improved Revenue Cycle Management (RCM): Faster reimbursements, reduced claim denials, and better financial health.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: Reduced wait times, convenient scheduling, and personalized communication.
- Increased Staff Efficiency: Automation of repetitive tasks, allowing staff to handle higher-value activities.
- Better Organization: Simplify the centralized management of patient records, billing, and scheduling with a solution tailored to your needs—partner with DEVtrust to develop custom healthcare software that streamlines your operations and enhances patient care.
Example: SimplePractice
Telemedicine Platforms
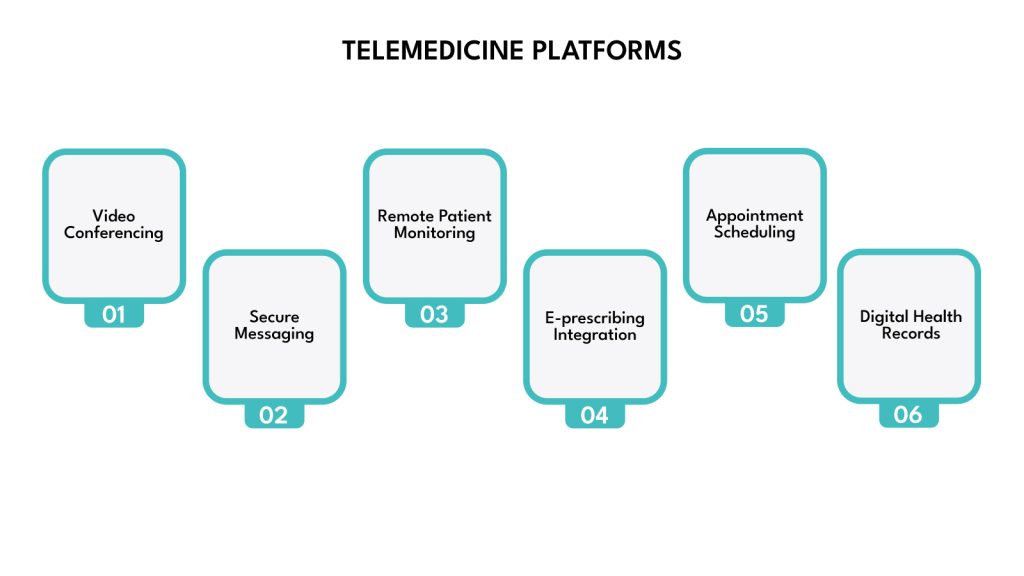
Telemedicine platforms facilitate remote healthcare services, allowing patients and providers to connect virtually. Key features typically include:
- Secure Video Conferencing: High-quality, HIPAA-compliant video calls for virtual consultations.
- Secure Messaging: Text-based communication between patients and providers.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Integration with wearable devices and home monitoring tools to collect vital signs and health data.
- E-prescribing Integration: Direct electronic submission of prescriptions.
- Appointment Scheduling: Easy booking and management of virtual appointments.
- Digital Health Records Access: Secure access to patient medical history during virtual visits.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
Telemedicine has revolutionized access to care, especially for patients in remote areas, those with mobility issues, or during public health crises. It reduces the need for in-person visits, minimizes travel time and costs, and allows for timely medical attention. It also facilitates specialist consultations and continuous monitoring of chronic conditions—ninety-four percent of patients who used telehealth services report being satisfied with their experience. Many reported shorter wait times and quicker follow-up.
Key Benefits:
- Increased Accessibility: Healthcare services become available to a broader population, regardless of location.
- Convenience and Time Savings: Patients can consult with providers from the comfort of their own homes, reducing travel and wait times.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower operational costs for providers and reduced travel expenses for patients.
- Continuity of Care: Enables ongoing management of chronic conditions and follow-up care.
- Reduced Infection Risk: Minimizes exposure to contagious diseases by reducing the number of clinic visits.
Examples: Amwell
Medical Imaging and Visualization Software
Medical Imaging and Visualization Software processes, analyzes, and displays medical images from various sources, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, which are different imaging techniques used to view internal body structures. Key functionalities include:
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): Storing, retrieving, managing, and displaying medical images.
- Radiology Information Systems (RIS): Managing radiology department workflows.
- Image Processing Tools: Enhancing image clarity, contrast, and details for better anomaly detection.
- 3D Visualization and Reconstruction: Creating three-dimensional models from scans for precise anatomical analysis and surgical planning.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Automates pattern recognition in medical images, improving speed and accuracy of diagnoses such as tumor detection and anomaly identification.
- Remote Imaging Access: Secure sharing of images among medical teams and specialists for teleradiology and remote consultations.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
This software significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy and speed, resulting in earlier and more effective treatments. It improves collaboration among specialists, allowing for comprehensive review and analysis of complex cases. AI integration further boosts efficiency and can predict disease progression, enabling proactive care.
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Early and precise detection of abnormalities.
- Improved Efficiency and Speed: Faster image analysis is crucial in emergency situations.
- Better Treatment Planning: Detailed 3D models facilitate precise planning for surgical and radiation therapy.
- Facilitated Collaboration: Secure sharing of images for remote consultations and second opinions.
- Predictive Analysis: AI-powered insights for risk assessment and preventative healthcare.
Examples: DICOM viewers
E-prescribing Systems
E-prescribing systems enable healthcare providers to generate and transmit prescriptions electronically to pharmacies. Core features include:
- Electronic Prescription Generation: Creating new prescriptions, managing renewals, and cancelations digitally.
- Drug Interaction Alerts: Automated checks for potential drug-drug, drug-allergy, and drug-disease interactions.
- Medication History Access: Comprehensive view of a patient’s current and past medications.
- Formulary and Eligibility Checks: Verifying insurance coverage and preferred drug lists.
- Pharmacy Directory Integration: Easy selection of the patient’s preferred pharmacy.
- Prescription Tracking: Monitoring the status of prescriptions and patient adherence.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
E-prescribing dramatically enhances patient safety by reducing medication errors caused by illegible handwriting, transcription mistakes, and missed drug interactions. It streamlines the prescribing workflow, saving time for both providers and pharmacists, and improves communication within the care team.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced Medication Errors: Enhanced legibility and automated interaction checks.
- Improved Patient Safety: Fewer adverse drug events and better adherence to clinical guidelines.
- Streamlined Workflows: Faster prescription processes and reduced administrative burden.
- Enhanced Communication: Seamless exchange of information between providers and pharmacies.
- Cost Savings: Minimized errors leading to fewer claim denials and callbacks.
Example: MEdiTab
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) provide clinicians with evidence-based information and recommendations at the point of care. Key functionalities include:
- Alerts and Reminders: Notifying providers about potential issues like drug interactions, overdue screenings, or abnormal lab results.
- Evidence-Based Guidelines: Offering recommendations based on the latest medical research and best practices.
- Patient-Specific Assessments: Analyzing individual patient data against a knowledge base to provide tailored suggestions.
- Order Sets and Protocols: Guiding clinicians through standardized care pathways.
- Diagnostic Assistance: Suggesting potential diagnoses based on patient symptoms and data.
- Integration with EHRs: Seamlessly leveraging patient data within the EHR system.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
CDSS significantly improves the quality and consistency of care by ensuring clinicians have access to critical information and adhere to best practices. It helps reduce diagnostic and medication errors, supports adherence to preventative care measures, and ultimately leads to better patient outcomes.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Quality of Care: Enhanced accuracy in diagnosis and treatment.
- Reduced Errors: Minimized medication errors and missed opportunities for preventive care.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined decision-making processes and automated tasks.
- Enhanced Adherence to Guidelines: Promotes consistent, evidence-based care.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Proactive Identification of Potential Issues.
Example: Oracle health, Clinicalkey
Patient Portal Software
Patient portal software provides a secure online platform for patients to access their health information and directly communicate with their healthcare providers. Common features include:
- Access to Medical Records: Viewing lab results, visit summaries, immunization records, and personal health information (PHI).
- Appointment Management: Scheduling, rescheduling, and canceling appointments online.
- Secure Messaging: Communicating directly with their care team.
- Prescription Refill Requests: Requesting Medication Refills Electronically
- Online Bill Pay: Managing and paying medical bills.
- Educational Resources: Access to personalized health information and educational content.
- Self-check-in: Streamlining the arrival process at clinics.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
Patient portals empower individuals to actively manage their health, fostering greater engagement and adherence to treatment plans. They reduce the administrative burden on front-desk staff by automating everyday tasks and improving communication channels between patients and providers.
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Greater involvement in their healthcare journey.
- Improved Communication: Direct and secure messaging with healthcare teams.
- Increased Convenience: 24/7 access to information and services.
- Reduced Administrative Workload: Fewer phone calls and manual tasks for staff.
- Better Health Outcomes: Patients are more informed and are more likely to follow their care plans.
Example: athenahealth
Healthcare Learning Management Systems (LMS)
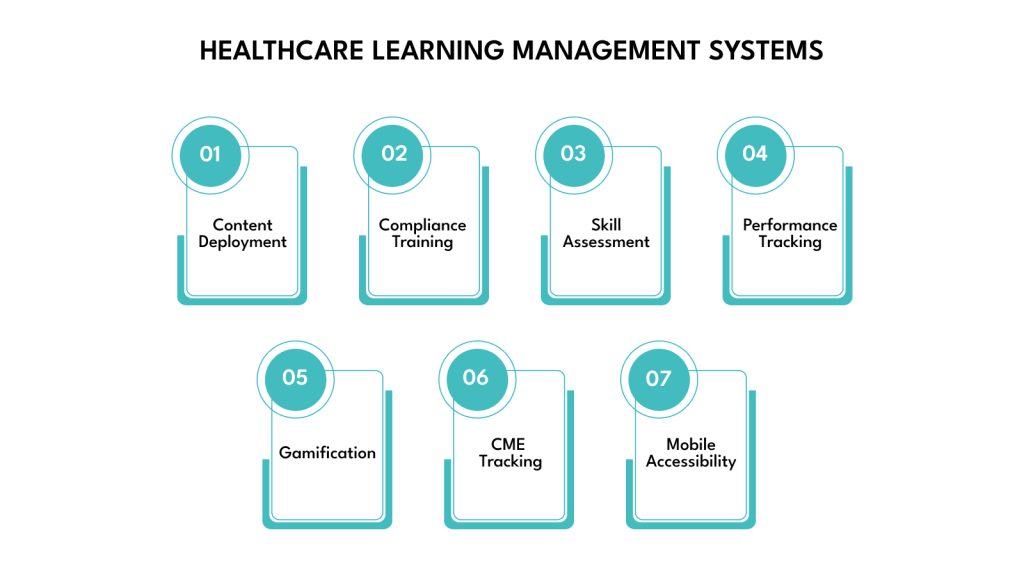
Healthcare Learning Management Systems (LMS) are platforms designed for training and education within the healthcare sector, catering to medical professionals, staff, and even patients. Key functionalities include:
- Course Creation and Delivery: Developing and distributing online courses, modules, and training materials.
- Compliance Training: Delivering mandatory training on regulations (e.g., HIPAA, OSHA) and certifications.
- Skill Assessment: Tools for evaluating clinical skills and knowledge gaps.
- Performance Tracking: Monitoring learner progress, completion rates, and assessment results.
- Gamification: Incorporating elements like points, badges, and leaderboards to boost engagement.
- Continuing Medical Education (CME) Tracking: Managing and crediting ongoing professional development.
- Mobile Accessibility: Allowing learners to access content anytime, anywhere.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
LMS platforms ensure that healthcare professionals are continuously updated on the latest medical practices, technologies, and compliance requirements. This leads to a more skilled workforce, improved patient safety through standardized procedures, and better overall quality of care. They also facilitate the efficient onboarding of new staff and can be used for patient education.
Key Benefits:
- Continuous Professional Development: Keeping healthcare staff updated with evolving medical knowledge.
- Enhanced Compliance: Ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and reducing risks.
- Improved Patient Safety: Through standardized training and skill enhancement.
- Cost-Effective Training: Delivering training to a large audience simultaneously and remotely.
- Efficient Onboarding: Faster integration of new employees into healthcare practices.
Example: TalentLMS
Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management Software
Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) software automates and optimizes the entire financial process of a healthcare organization, from patient registration to payment collection and reconciliation. Key features include:
- Patient Pre-registration and Insurance Verification: Capturing patient details and verifying eligibility before the visit.
- Automated Coding: Suggesting appropriate medical codes (CPT, ICD-10) for diagnoses and procedures.
- Claims Management: Electronic submission of claims, tracking their status, and managing denials.
- Payment Posting: Automatically records patient payments and insurance reimbursements.
- Accounts Receivable (AR) Management: Following up on unpaid claims and patient balances.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights into financial performance, denial rates, and cash flow.
- Compliance Checks: Ensuring adherence to billing regulations and payer-specific rules.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
RCM software is crucial for the financial health of medical practices. It significantly improves cash flow, reduces administrative overhead, and minimizes claim rejections, allowing practices to focus more on patient care rather than financial reconciliation. Its automation capabilities free up staff for more critical tasks. Optimize your billing with the help ofDEVtrust.
Key Benefits:
- Optimized Cash Flow: Faster reimbursements and reduced payment delays.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Automation of billing, coding, and claims processing.
- Lower Claim Denials: Improved accuracy in coding and compliance checks.
- Enhanced Financial Transparency: Detailed reports and analytics for better financial control.
- Improved Compliance: Adherence to billing regulations and reduced audit risks.
Example: Oracle
Population Health Management Platforms
Population Health Management (PHM) platforms utilize data analytics, care coordination, and patient engagement strategies to enhance health outcomes for targeted patient populations. Key features include:
- Data Aggregation and Integration: Consolidating data from EHRs, claims, pharmacies, and other sources.
- Risk Stratification: Identifying high-risk patients who need targeted interventions.
- Predictive Modeling: Using data trends to anticipate future health challenges and disease progression.
- Care Coordination Tools: Facilitating seamless collaboration among different providers and care settings.
- Patient Engagement Tools: Personalized communication, reminders, and educational resources to encourage active participation in care.
- Outcome Measurement and Reporting: Monitoring the impact of interventions on population health metrics.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery:
PHM shifts the focus from individual patient treatment to proactive prevention and management for entire communities. It enables healthcare systems to identify individuals at risk, implement targeted interventions, and reduce the burden of chronic diseases. This approach leads to better overall public health, reduced healthcare costs, and a more value-based care model.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Population Health Outcomes: Proactive prevention and early intervention for at-risk groups.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Lower emergency room visits and hospitalizations through preventive care.
- Enhanced Care Coordination: Seamless transitions and communication across the care continuum.
- Boosted Patient Engagement: Empowering individuals to manage their health effectively.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Insights for refining strategies and improving public health initiatives.
Examples: athenahealth
DEVtrust: Custom Healthcare Software Development and Integration Services
At DEVtrust, we understand the unique needs of the healthcare industry, and we create custom software solutions to address them. One of our core focuses is engineering healthcare software systems that comply with medical technology and data security requirements, healthcare workflows, patient-centric design, and specific regulations such as HIPAA. Our tailored technologies focus on integration and collaboration, improving real-time situational decision-making.
Custom Healthcare Software Development:
- Custom EMR System and EHR Development Service: DEVtrust designs customized EHR solutions that track patient visits, automate prescription processes, and manage laboratory billing, enhancing operational productivity.
- Healthcare Software Testing Services: DEVtrust employs integration and regression testing methodologies to provide comprehensive verification services, ensuring the proper functioning of healthcare software.
To illustrate the tangible impact of our work, let’s explore how DEVtrust’s expertise has driven success for our partners:
Case Studies: Driving Innovation with DEVtrust
Precina – Revolutionizing Chronic Disease Management
- Functionality and Features: DEVtrust developed custom EHR enhancements and AI-powered data integration for Precina, a leader in chronic disease management, and enabled personalized, scalable daily care for thousands of patients.
- Impact on Healthcare Delivery: Precina achieved a 98% patient success rate, accompanied by significant reductions in HbA1c levels. Our solutions fostered remarkable clinical outcomes, scalability, and substantial cost reductions.
Spero institute – Accelerating Drug Development with Data
- Functionality and Features: DEVtrust provided expertise in clinical trial data management and advanced analytics for Spero Therapeutics. This supported their pivotal Phase 3 trials, ensuring data integrity and rapid analysis.
- Impact on Healthcare Delivery: Our solutions enabled Spero Therapeutics to achieve early efficacy in their Phase 3 trial, thereby accelerating drug development. This enables the delivery of life-saving treatments to patients more quickly, addressing critical unmet needs.
The Fusion of Technology and Healthcare
The evolution of medical software is making healthcare more efficient, patient-centered, and accessible. From foundational EHR systems digitizing patient information to advanced AI-powered imaging and population health platforms, these technologies empower providers, engage patients, and optimize administrative processes.
It’s about delivering superior care in an increasingly complex and data-driven world, for businesses looking to navigate this dynamic landscape and develop solutions, partnering with experts is crucial.
Seize tomorrow’s technology today. Unleash the full potential of your organization with powerful medical software. Explore how DEVtrust can help you innovate and achieve your digital transformation goals.
Top Medical Software Types Transforming Healthcare
Explore top medical software revolutionizing healthcare! Discover EHR, Telemedicine, and E-prescribing systems' benefits. Click to learn more now!
Contact Us