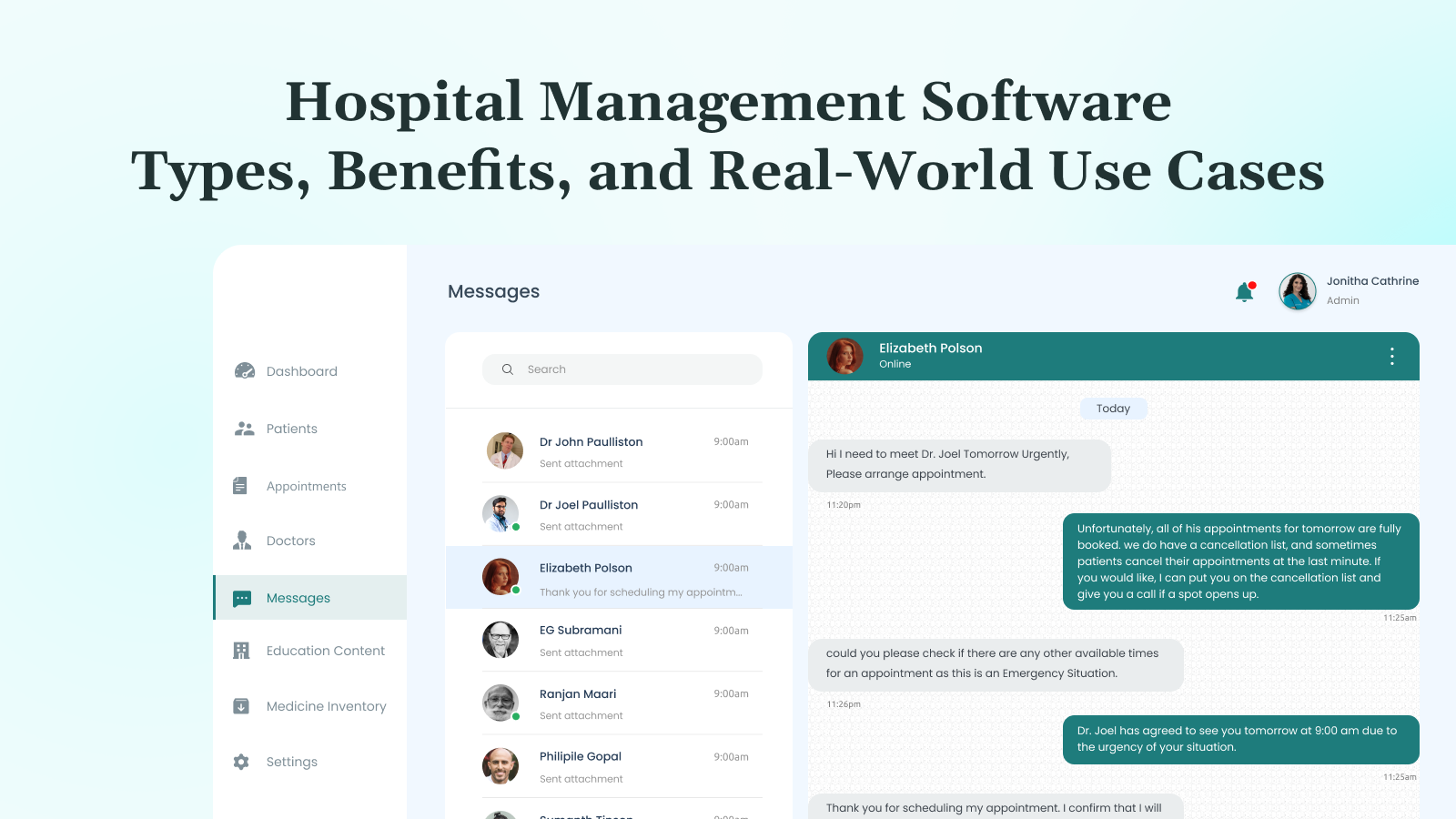
Hospitals manage a wide range of clinical and administrative tasks daily, which become increasingly complex with rising patient loads, workflows, and compliance requirements.
Every admission triggers dozens of actions across departments, making it harder to deliver care without delays or errors. Medical mistakes now cost the US healthcare system over $20 billion each year. Many of these issues stem from the use of separate, unconnected software systems and manual paperwork processes that hinder team productivity.
Hospital management software helps solve this. It replaces outdated tools with connected digital systems that coordinate everything from scheduling and billing to diagnostics and compliance.
This guide provides an overview of how these systems work, the types of software hospitals utilize, and the steps for implementing them to enhance care and streamline operations.
Key Takeaways
- Hospital management software integrates clinical, administrative, and financial operations through a single, unified platform.
- Hospitals rely on 16 essential software types, including EHRs, billing systems, inventory tools, and patient engagement apps.
- AI, analytics, and cloud technology enhance decision-making, increase efficiency, and facilitate regulatory compliance.
- A successful rollout depends on clear goals, strong vendor selection, data readiness, team training, and ongoing refinement.
What Is a Hospital Management Software System?
A hospital management software system helps hospitals run their daily tasks through one connected platform. It replaces paper files and scattered tools with digital systems that work together.
The software manages patient check-ins, doctor appointments, billing, reports, and other tasks. All parts of the system share data in real time. This removes delays and avoids errors caused by disconnected tools.
Hospitals use it to manage both medical and non-medical work. That includes surgery planning, bed assignments, pharmacy stock, and lab test results. It also protects patient data using strong security rules.
There are three main areas the system supports:
- Clinical work includes patient records, test results, and prescriptions.
- Admin tasks like staff shifts and room use.
- Money matters like billing, insurance, and payments.
The goal is simple: better care, fewer mistakes, and faster hospital operations.
Types of Hospital Management Software Systems
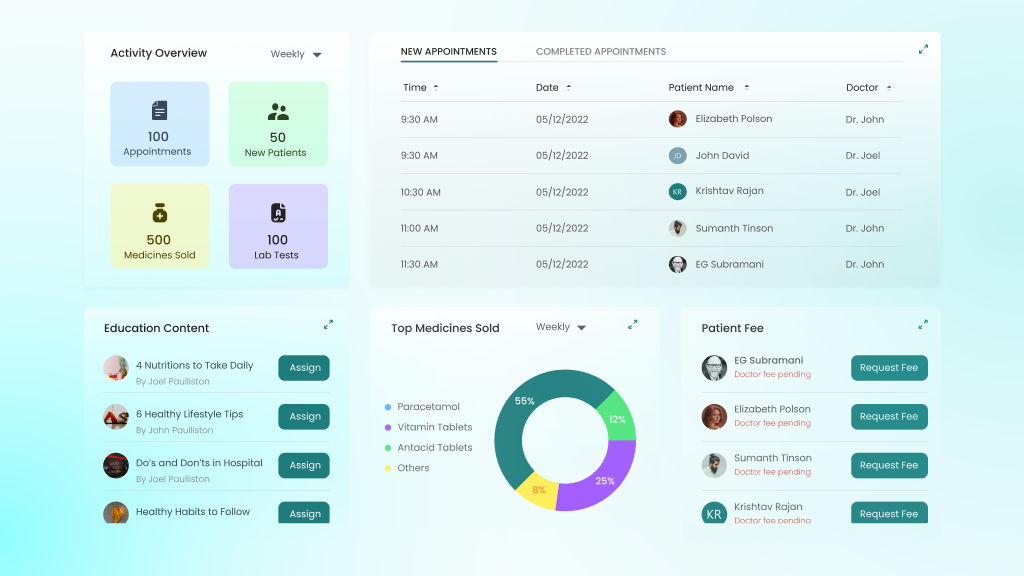
Hospitals do not rely on a single software to run everything. Instead, they utilize a combination of digital tools that each handle specific tasks, including billing, scheduling, inventory, compliance, and more. These systems form a connected environment where patient care, admin work, and data management happen without delays or errors.
Here is a breakdown of 16 widely used hospital software types and their support for real-world operations.
1. Practice Management Software
Practice management software is designed to streamline the daily operations of outpatient clinics and specialty departments. It centralizes administrative tasks, allowing your front-desk and billing staff to manage patient flow efficiently.
Key Features
- Manages patient registration and appointment scheduling.
- Verifies insurance and manages pre-authorizations.
- Handles billing workflows and co-payment collection.
- Generates financial reports and performance summaries.
Examples: DrChrono and Practice Fusion
2. Electronic Health Records (EHR) and EMR Systems
EHR and EMR systems manage digital patient medical records. While EMRs are used within a single department, EHRs enable hospitals to share data across multiple facilities and care teams.
Key Features
- Stores patient history, allergies, medications, and lab results.
- Supports clinical note-taking and charting.
- Includes alerts for drug interactions and allergies.
- Allows secure information sharing between care providers.
3. Telemedicine Software
Telemedicine software enables hospitals to deliver remote care. It allows clinicians to consult, diagnose, and treat patients using secure digital platforms, expanding access to care.
Key Features
- Enables video and audio consultations.
- Offers secure patient messaging and chat.
- Supports e-prescriptions and digital documentation.
- Integrates with EHR systems for continuity of care.
Examples: Zoom for Healthcare, doxy.me, Amwell
4. Medical Billing Software
Medical billing software automates the complex tasks involved in healthcare billing. It ensures accurate coding, faster payments, and improved cash flow.
Key Features
- Automates claims generation and submission.
- Assists with ICD/CPT coding accuracy.
- Tracks denials and payment status.
- Offers dashboards for billing analytics.
Examples: AthenaCollector, AdvancedMD, NextGen
5. Patient Engagement Software
Patient engagement software enables patients to interact with hospitals through secure portals or mobile applications, allowing them to access information and services conveniently. It enhances communication, reduces no-shows, and encourages better health outcomes.
Key Features
- Allows self-scheduling and appointment reminders.
- Offers secure access to medical records.
- Supports prescription refill requests and messaging.
- Provides health education content.
Examples: MyChart, Luma Health
6. Healthcare Analytics Software
Healthcare analytics software helps hospitals make data-driven decisions. It aggregates and analyzes clinical and operational data to improve care delivery and reduce costs.
Key Features
- Tracks operational and patient outcome metrics.
- Supports risk stratification and cohort analysis.
- Generates custom dashboards and reports.
- Uses predictive modeling to forecast trends.
Examples: IBM Watson Health, Arcadia
7. Medical Inventory Management Software
This software gives hospitals real-time visibility into their supplies. It reduces waste and prevents stockouts by automating inventory tracking and restocking.
Key Features
- Tracks stock levels and reordering thresholds.
- Manages supplier information and POs.
- Uses barcode/RFID tracking.
- Integrates with pharmacy and EHR systems.
Examples: Cardinal Health Inventory Manager, Oracle NetSuite
8. Clinical Trial Management Software
Clinical trial management software is built for hospitals that conduct research studies. It ensures trials stay compliant, organized, and on schedule.
Key Features
- Manages study protocols and site documentation.
- Tracks patient recruitment and consent.
- Supports data collection and monitoring.
- Generates reports for audits and submissions.
Examples: Medidata, Veeva, OpenClinica
9. Healthcare CRM Software
Healthcare CRM software supports patient relationship management. It helps hospitals improve engagement and referral coordination through targeted communication.
Key Features
- Tracks patient interactions and preferences.
- Manages referral networks and campaigns.
- Automates follow-ups and reminders.
- Analyzes marketing and retention performance.
Example: HC1
10. Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
HIS software provides hospitals with a centralized system that connects all departments. It manages clinical, administrative, and financial operations under one platform.
Key Features
- Connects clinical, administrative, and financial workflows.
- Provides real-time visibility into hospital operations.
- Supports bed management, pharmacy, and lab workflows.
- Offers centralized data access across departments.
Examples: MEDITECH, InterSystems TrakCare
11. Medical Imaging Software
Medical imaging software enables radiologists to store, access, and interpret diagnostic images effectively. It ensures fast and accurate image analysis and collaboration.
Key Features
- Stores and retrieves X-rays, CTs, MRIs, and ultrasounds.
- Supports image annotation and report generation.
- Integrates with PACS and EHR systems.
- Enables AI-assisted diagnostics.
Examples: Philips IntelliSpace, Merge PACS
12. Appointment Scheduling Software
This software enables hospitals to manage patient bookings, staff calendars, and resource allocation effectively. It improves scheduling accuracy and reduces appointment gaps.
Key Features
- Supports online booking and automated reminders.
- Manages waitlists and no-show prevention.
- Coordinate room and equipment availability.
- Integrates with EHR and billing systems.
Examples: Zocdoc, SimplyBook.me, athenaScheduling
13. Population Health Management Software
Population health software enables hospitals to monitor health trends across various groups. It identifies care gaps and helps teams improve community health outcomes.
Key Features
- Aggregates patient data from multiple sources.
- Identifies gaps in care and high-risk groups.
- Supports quality measure tracking and reporting.
- Helps coordinate care teams across providers.
Examples: Arcadia, Health Catalyst, Innovaccer
14. Behavioral Health Software
Behavioral health software supports the care of patients with mental health and substance use conditions. It is designed to meet specialized documentation and treatment needs.
Key Features
- Tracks therapy sessions, assessments, and treatment plans.
- Manages secure documentation and compliance.
- Supports e-prescriptions and care coordination.
- Offers tools tailored to behavioral workflows.
Examples: Oracle Behavioral Health, Valant, TherapyNotes
15. Compliance Management Software
Compliance management software enables hospitals to meet their legal and regulatory obligations. It reduces compliance risk through automation and monitoring.
Key Features
- Tracks audits, policy changes, and incidents.
- Supports mandatory report generation.
- Flag noncompliance issues in real time.
- Provides role-based access and action tracking.
Example: MetricStream
16. Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Software
RCM software automates billing from check-in to final payment. It improves claim accuracy, speeds up collections, and strengthens hospital revenue.
Key Features
- Verifies insurance eligibility and co-pays.
- Automates claims processing and denial tracking.
- Offers dashboards for revenue analytics.
- Integrates with billing and patient access systems.
Example: Change Healthcare
Key Technologies Powering Smarter, Safer Hospital Software
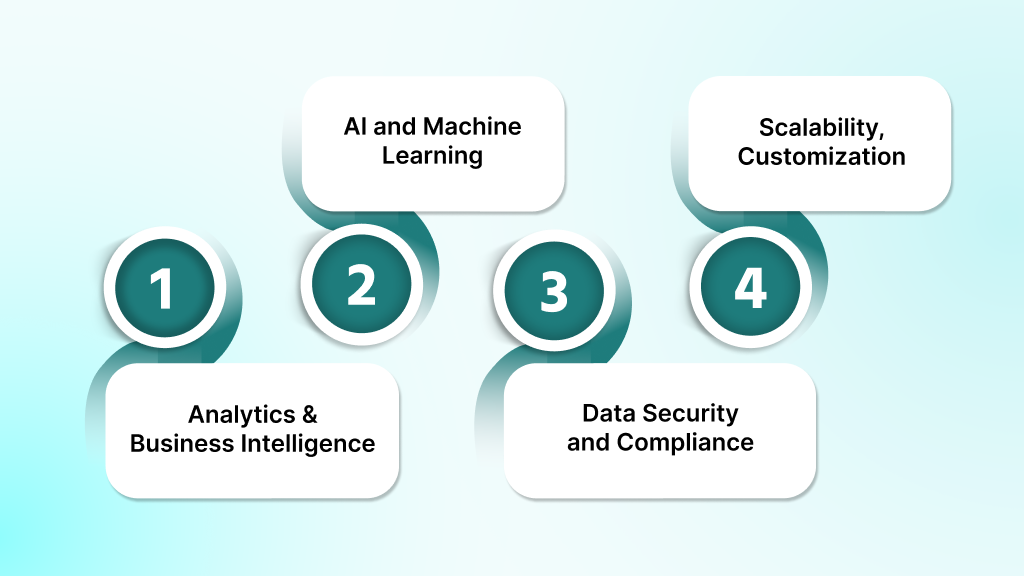
Modern hospital systems rely on advanced technologies to manage growing workloads, secure sensitive data, and improve care delivery. These tools transform traditional hospital operations into faster, more intelligent, and more efficient systems, allowing your team to focus more on patient care.
Let us break down the key technologies behind today’s best-performing hospital software.
1. Analytics, Reporting, and Business Intelligence
Hospital data is often extensive and spread across various systems. Analytics platforms consolidate this data to support quicker and more informed decision-making.
These tools help you:
- Monitor patient flow, wait times, and readmission rates to ensure optimal patient care.
- Spot underused resources or bottlenecks.
- Forecast patient volumes and staff needs.
Most hospitals now use real-time dashboards to track KPIs across departments. These dashboards surface what is working and what needs fixing, without requiring you to dig through spreadsheets.
2. AI and Machine Learning
AI is more than hype. Hospitals utilize it daily to automate tasks, reduce delays, and make informed decisions.
Key uses include:
- Auto-scheduling appointments based on past trends.
- Flagging billing errors before claim submission.
- Predicting which patients are likely to develop complications.
- Recommending personalized treatment options.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) extracts insights from messy notes and voice dictations. That means doctors spend less time typing and more time treating.
- AI in healthcare is expected to reach $187 billion by 2030, indicating the rapid adoption of AI by hospitals.
3. Data Security and Compliance
Hospitals manage thousands of records every day. Every one of them must be secure.
Modern systems use:
- End-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest.
- Multi-factor authentication for system access.
- Role-based access to prevent unauthorized data views.
- Real-time monitoring to flag abnormal system behavior.
Audit trails keep a record of who did what and when. This helps during internal reviews and external audits. Plus, built-in compliance tools ensure you are aligned with HIPAA, NABH, and other frameworks.
- Example: Behavioral analytics can flag suspicious login attempts, helping to prevent data breaches before they occur.
4. Scalability, Customization, and Integration
Hospitals are dynamic. Your software should be too.
Smart platforms offer:
- Cloud infrastructure that scales with patient volume.
- Custom modules and forms built for your departments.
- API-ready design to connect with labs, pharmacies, or national health records.
You can start with core modules and expand as your hospital grows, without having to redo your entire system.
Many organizations utilize a microservices architecture, which enables updates or feature rollouts to occur without system downtime. You upgrade what you need, when you need it.
- Why it matters: A scalable platform keeps your hospital future-ready while minimizing tech disruptions.
How to Implement a Hospital Management System Successfully?
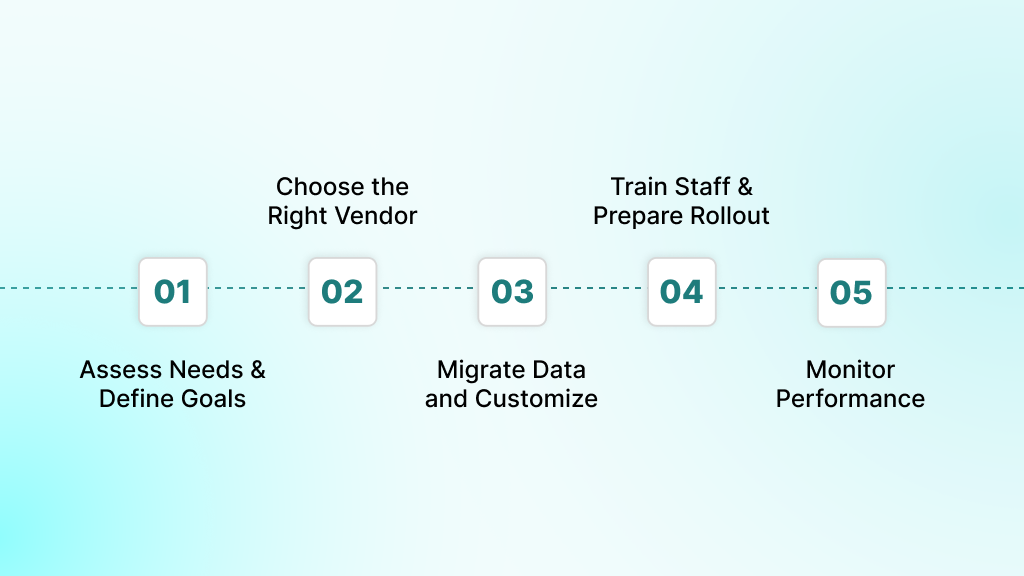
Rolling out a hospital management system requires a focus on organizational change and user adoption, rather than just technology deployment. A full implementation can take 12-18 months and needs strong planning, committed leadership, and regular follow-through.
Hospitals that succeed treat this as a phased transformation. Below are the five steps that help ensure adoption and long-term value.
Step 1: Assess Needs and Define Goals
Begin by understanding how your hospital operates today and identifying areas where it falls short.
- Map your existing workflows.
- Identify bottlenecks in care, billing, or communication.
- Engage staff across departments to gather input.
From there, define what you want the new system to solve. Set measurable goals, such as reducing patient wait times, increasing claim approval rates, or improving care coordination.
Tip: Build a realistic project timeline that covers planning, testing, training, and go-live. Add buffer time for delays.
Step 2: Choose the Right Vendor
Look beyond software features. Choose a vendor that understands hospital operations and has real implementation experience.
- Request demos tailored to your workflows.
- Talk to 2-3 client references in similar hospital settings.
- Review the financial health of the vendor and support model.
Do not skip the contract details. Clarify system ownership, data access, customization rights, and upgrade costs. Lock in post-launch support levels in writing to ensure continuity and stability. If you are looking for a starting point, consider a partner like DEVtrust. Their project record shows how the right team can simplify complex implementations while keeping long-term needs in focus.
Step 3: Migrate Data and Customize Modules
Clean your data before you move it. Insufficient data can cause system errors and slow down your staff.
- Remove duplicates, fix outdated records, and standardize formats.
- Define clear data mapping rules.
- Validate all migrated data before go-live.
Next, configure the software to match how your teams work. Customize only what is necessary; over-customization can lead to long-term maintenance problems.
Establish backup and recovery procedures before launch. Test them with real scenarios to reduce risk.
Step 4: Train Staff and Prepare Rollout
People make or break your rollout. Training must be hands-on, role-specific, and repeatable.
- Build custom training paths for doctors, nurses, admin, and billing staff.
- Use a mix of live sessions, videos, and practice environments.
- Appoint “super users” in each department for peer support.
Test the system with real workflows. Fix usability issues before the full rollout. Rolling out in phases, if needed, starting with non-critical departments first, can lower pressure.
Step 5: Monitor Performance and Refine System
Once live, your work continues. Track what is working and where users struggle.
- Use dashboards to monitor adoption, downtime, and usage.
- Gather weekly feedback from each department.
- Set up a dedicated help desk for the first 3 to 6 months.
Conduct monthly system reviews to refine workflows and incorporate any necessary features that may be missing. Budget for updates, support, and future upgrades. A strong post-launch plan ensures that your system continues to improve over time.
How Hospitals Turn Implementation Plans Into Real Results?
A hospital software rollout only works if the system fits real clinical and operational needs. Many fail because off-the-shelf tools cannot handle the complexity of day-to-day hospital workflows. That is why the right development partner matters as much as the software itself.
Hospitals that succeed choose partners who understand healthcare from the inside, how departments operate, where risks occur, and how systems need to adapt over time.
What to Look for in a Development Partner
- Healthcare domain knowledge: A team that understands clinical workflows, compliance needs, and patient safety.
- Custom fit: Systems built around how your hospital works, not rigid templates that force teams to adjust.
- End-to-end support: From data migration to post-launch tuning, the partner stays involved beyond go-live.
- Proven healthcare results: Look for experience delivering systems used in real hospital environments.
What DEVtrust Brings?
DEVtrust has delivered healthcare platforms designed to improve care quality, streamline operations, and meet strict compliance standards.
- Precina: A web and mobile platform that improves how wellness and clinical services are delivered, helping hospitals boost patient satisfaction and outcomes.
- Spero Institute: A secure tool for tracking clinical progress, managing documents, scheduling, and supporting clinician and patient communication.
- Must Motivate: A mental health platform focused on motivation, community support, and long-term well-being, built with privacy and engagement in mind.
Each solution was tailored to the organization’s needs, with DEVtrust working closely with leadership and clinical teams to ensure the software delivered real-world results.
But don’t just take our words for it, here’s what our clients say-
“DEVtrust’s Ezeryeshiva app has transformed our appointment management process. The tailored user roles and efficient scheduling system have significantly reduced our workload and improved our service efficiency.”
Mordy Stern, Project Lead – Ezeryeshiva.
Future Trends in Hospital Management Software
Hospital software continues to evolve. New capabilities now focus on automation, personalization, and continuous care beyond the hospital.
These trends enable healthcare organizations to enhance decision-making, minimize delays, and maintain greater control over clinical and operational outcomes.
1. Generative AI for Documentation
Hospitals are adopting generative tools to simplify clinical documentation.
- These tools create SOAP notes, discharge summaries, and care plans from provider, patient conversations.
- They reduce manual entry while improving note accuracy and consistency.
- Some systems populate fields in the EHR and suggest ICD or CPT codes.
Real-time documentation is also becoming available, along with auto-suggestions aligned with care guidelines. This helps reduce documentation time while maintaining high compliance and billing accuracy.
2. Voice-First EHR and Ambient Clinical Tools
Voice-enabled platforms now allow providers to interact with systems using natural speech.
- Clinicians can update records, pull lab results, or check medication orders without manual input.
- Ambient tools record key information during patient visits and convert it into structured data.
- These systems integrate directly with hospital workflows, supporting hands-free operation.
Future advancements will include multilingual interfaces and predictive prompts based on patient history and conversation context.
3. Wearable Integration and Remote Monitoring
Hospitals are extending care with connected health devices.
- Devices like smartwatches, blood pressure monitors, and glucose sensors feed real-time data into hospital systems.
- This enables early detection of complications and more informed care planning.
- Data is automatically integrated into the patient’s medical record.
Upcoming features will support inputs from smart home systems and environmental sensors, providing care teams with a more comprehensive view of patient health conditions.
4. Predictive Analytics for Patient Volumes
Forecasting patient volume helps hospitals prepare more effectively.
- Platforms analyze past admissions, seasonal trends, and external events to predict resource demand.
- Hospitals use this data to adjust staffing levels, manage patient beds, and plan for potential surges.
- Alerts notify teams when volume exceeds planned capacity.
Advanced tools will include real-time recalibration, integration with supply chain platforms, and automated recommendations for scheduling and logistics.
Conclusion
Hospital management software has become essential to running efficient, compliant, and patient-focused healthcare operations. With the right systems and strategic implementation, hospitals can reduce errors, streamline workflows, and improve outcomes at every level.
DEVtrust helps healthcare organizations build and deploy custom software tailored to real-world clinical and operational needs.
Contact DEVtrust to discuss your goals and develop a customized solution tailored to your hospital’s needs.
Hospital Management Software: Types, Benefits, and Real-World Use Cases
Explore hospital management software in 2025 with AI integration, EHR systems, telehealth, and smart scheduling. Stay ahead of future trends! Learn more.
Contact Us