Healthcare software product development is driving a shift toward more secure, efficient, and patient-focused medical solutions. By creating customized digital tools, healthcare providers can enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and improve patient outcomes.
The rapid expansion of the digital health market, from USD 362.36 billion in 2024 to an anticipated USD 1,019.89 billion by 2034, reflects the growing reliance on innovative software solutions across the industry. This growth highlights the pressing need for customized, compliant healthcare software solutions.
This guide offers an in-depth examination of healthcare software product development, providing actionable strategies and insights. It is designed to help organizations navigate key challenges, leverage emerging technologies, and achieve lasting success in delivering high-impact healthcare solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare software product development is essential for secure, efficient, and patient-focused medical solutions.
- Custom software ensures regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR) and meets unique healthcare operational needs.
- Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and telemedicine enhance care accessibility, diagnostics, and data security.
- Key challenges include UX/UI design, interoperability, cost management, and maintaining data privacy.
- Partnering with expert developers like DEVtrust supports scalable, compliant, and future-proof healthcare software solutions.
What Is Healthcare Software Product Development?
Healthcare software product development involves creating specialized software applications designed specifically for the healthcare industry. These solutions help healthcare providers, patients, and administrators by streamlining workflows, securely managing patient data, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
The process involves understanding user needs, designing secure and user-friendly systems integrated with healthcare technologies, thoroughly testing them, and maintaining updates post-deployment.
Custom healthcare software is vital because it meets unique operational challenges and strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. This tailored approach ensures efficient healthcare delivery and better patient outcomes.
Importance of Healthcare Software Product Development
Healthcare software product development involves building tailored applications, databases, web platforms, and mobile tools. These solutions support nearly every area of modern healthcare with accuracy and control.
- Efficient Data Management:
Custom-built systems eliminate manual errors and simplify complex workflows for faster, more reliable results. - Enhanced Diagnostics:
Automated tools help providers make informed decisions using real-time, structured clinical data. - Patient Engagement:
Digital portals and apps improve communication and access to care services at every touchpoint. - Regulatory Compliance:
Built-in privacy and access controls help organizations meet HIPAA and GDPR standards with confidence. - Scalability and Precision:
Solutions from expert teams like DEVtrust enable long-term growth with scalable architecture and performance-first design.
End-to-end product development ensures healthcare providers can meet growing demands while safeguarding outcomes and operations.
Adopting healthcare software developed with DEVtrust means embracing accuracy, security, and patient-centered care.
Benefits of Healthcare Software Development
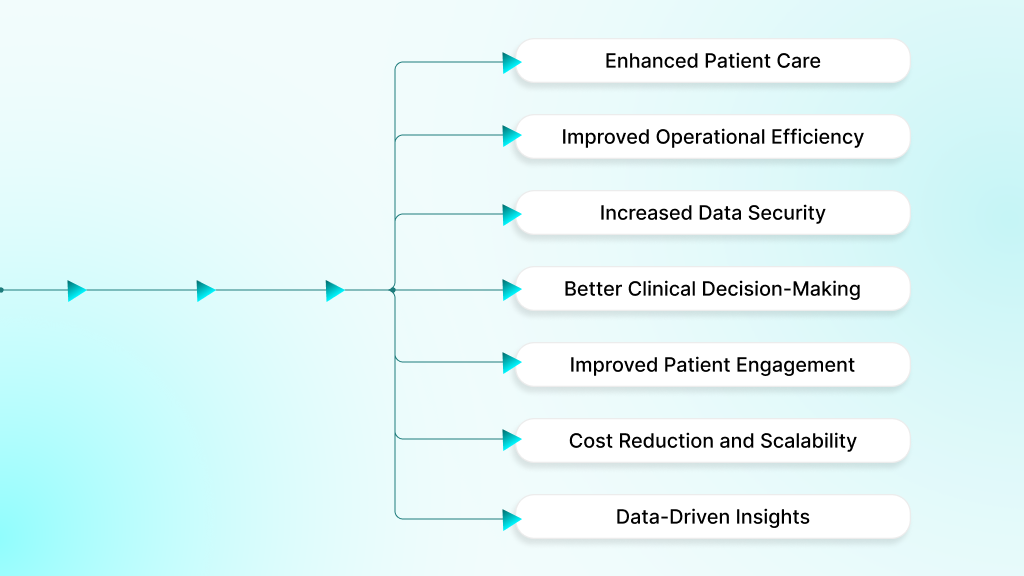
Healthcare software development delivers value across clinical, administrative, and patient-facing areas. Digital solutions streamline workflows, improve care quality, and increase organizational performance.
1. Enhanced Patient Care
- Accurate, complete medical records reduce errors.
- Personalized treatments leverage consolidated health data.
- Telemedicine and mobile apps improve care accessibility.
2. Improved Operational Efficiency
- Automation saves staff time by handling scheduling, billing, and prescriptions.
- Real-time tracking optimizes resource management.
- Faster billing reduces payment delays and errors.
3. Increased Data Security and Compliance
- Secure storage and transmission meet HIPAA, GDPR, and other standards.
- Advanced authentication protects sensitive data.
- Audit trails help monitor and prevent breaches.
4. Better Clinical Decision-Making
- Decision support tools alert clinicians to best practices.
- Data analytics guide resource allocation and predict health trends.
- Integration with labs and EHRs ensures timely information flow.
5. Improved Patient Engagement
- Patient portals allow easy access to results and scheduling.
- Automated reminders boost adherence.
- Digital education supports informed patient decisions.
6. Cost Reduction and Scalability
- Less paperwork and fewer mistakes reduce costs.
- Cloud-based platforms enable quick scaling and rapid feature deployment.
- Supports remote care and chronic disease management.
7. Data-Driven Insights
- Population health management identifies at-risk groups.
- Dashboards track performance metrics and regulatory compliance.
Learn more about Healthcare Application Development.
Current Trends in Healthcare IT
The digital health sector is rapidly evolving as providers, payers, and patients increasingly adopt healthcare software and digital solutions. This transformation is driven by advances in technology that improve health management, accessibility, and patient outcomes worldwide.
1. Digital Health Expansion
Telemedicine platforms are now a key part of healthcare, letting patients talk to doctors from home. Remote monitoring helps patients get care without having to travel, making it safer and easier to stay healthy.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Automation
Machine learning helps doctors by analyzing medical images and predicting health risks more accurately. It also makes healthcare easier by automating tasks like scheduling, billing, and entering data, which reduces the work for staff.
3. Data Privacy and Security
There is a stronger focus than ever on following HIPAA rules and protecting data with encryption. More healthcare organizations are also using zero-trust security models to reduce the risk of breaches and keep information safe.
4. Integration and Interoperability
Healthcare systems need to work well with electronic health records, hospital software, and other databases. Standards like HL7 and FHIR help make sure data can move easily and accurately between these systems.
These trends illustrate the dynamic nature of healthcare technology.
The Role of Software in Modern Healthcare
Healthcare software product development is reshaping how care is delivered, making it smarter, safer, and more connected. With rapid digital growth, it’s vital to improve outcomes and meet the evolving needs of the industry.
1. Operational Improvements
Scheduling tools and automated reminders help reduce missed appointments. At the same time, inventory and supply systems make sure hospitals always have the supplies they need.
2. Enhanced Patient Safety
Clinical decision support systems guide doctors to use the best treatments, while medication management platforms help prevent errors with prescriptions, keeping patients safer.
3. Increased Access to Care
Virtual care technologies connect healthcare providers with patients in rural and underserved areas, making it easier for them to get the care they need. Mobile health apps also give patients simple tools to manage their health right from their phones.
Software has become the foundation of forward-thinking healthcare organizations.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Regulatory compliance is vital in healthcare software to protect patient data and maintain trust. Following laws like HIPAA and GDPR, as well as standards like HL7 and DICOM, helps ensure the development of secure and reliable software.
| Standard | Purpose | Impact |
| HIPAA | US data privacy and security | Patient trust, legal exposure |
| GDPR | Data protection (EU and global clients) | Patient consent, data rights |
| HL7/FHIR | Enables interoperability | Data exchange, system linking |
| DICOM | Medical imaging data format | Seamless imaging workflows |
Missing compliance can result in severe penalties and system failures.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Protecting sensitive health data is both a legal requirement and an ethical imperative.
- Apply end-to-end data encryption.
- Use robust authentication protocols.
- Monitor access with detailed audit logs and real-time alerts.
Continuous security assessments are needed to keep up with threats.
Interoperability and Integration with Existing Systems
Healthcare platforms must fit into broad, multi-vendor environments.
- Built using flexible APIs and standard formats.
- Map data fields carefully to ensure accuracy.
- Conduct integration testing with existing EHRs and medical devices.
System compatibility and seamless communication are non-negotiable.
Types of Healthcare Software Solutions
Healthcare organizations now use a broad array of digital platforms to serve diverse objectives and user groups. Here are the key categories and their functions:
| Software Type | Key Purpose | Common Backend Technologies | Common Frontend/Mobile Technologies | Key Integration/Cloud/AI |
| Electronic Health Records (EHR) | Centralized patient medical records for holistic care. | Java (Spring Boot), Python (Django), C# (.NET Core) | React, Angular, Vue.js | HL7, FHIR, PostgreSQL/MS SQL Server, AWS/Azure/GCP |
| Telemedicine Platforms | Virtual consultations via video, audio, or chat. | Node.js (Express), Python, Go | React, Angular, Vue.js, React Native, Flutter | WebRTC, Twilio Video, AWS Chime SDK, Azure Comm Services |
| Healthcare Information Systems (HIS) / Hospital Management Systems (HMS) | Manages all hospital operations: admin, clinical, and financial. | Java (Spring), C# (.NET), Python (Django) | Angular, React | Oracle/MS SQL Server, RESTful APIs, Apache Kafka |
| Practice Management Software | Automates clinic scheduling, billing, and claims. | PHP (Laravel), Ruby on Rails, Node.js | React, Vue.js | Stripe, Authorize.Net, Zapier, EDI |
| Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Software | Continuous monitoring of patient health data from devices. | Node.js, Python (Flask/Django) | React Native, Flutter, Swift/Kotlin | AWS IoT Core, Azure IoT Hub, Bluetooth LE, Kafka |
| Medical Imaging & Diagnostic Software | Manages acquisition, visualization, and analysis of medical images. | C++, Python, Java | OHIF Viewer (Web), Dedicated Viewers | DICOM, ITK, VTK, OpenCV, TensorFlow, PyTorch |
| AI Diagnostic Tools / Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) | AI-driven assistance for diagnosis and treatment suggestions. | Python | Web UI (React/Angular) | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, NLP, Cloud AI Services |
| Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) & Medical Billing | Manages financial processes: coding, claims, and payments. | Java (Spring), C# (.NET), Python | Web UI | EDI (X12), Payment Gateways (Stripe), EHR APIs |
| Patient Portals & Engagement Platforms | Secure patient access to records, scheduling, and communication. | Node.js, Python, PHP | React, Angular, Vue.js, React Native, Flutter | FHIR APIs, OAuth 2.0, Firebase, Twilio SMS/SendGrid |
| Mobile Health Apps (mHealth) | Wellness, medication reminders, symptom tracking. | Firebase, AWS Amplify | React Native, Flutter, Swift/Kotlin | Apple HealthKit, Google Fit, Wearable APIs |
| Medication Management Apps | Tracks prescriptions, dosages, refills; alerts interactions. | Node.js, Python | React Native, Flutter, Swift/Kotlin | Drug Databases (RxNorm), e-Prescribing APIs |
| Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) | Manages lab workflow, specimen handling, and results reporting. | Java, C# (.NET) | Desktop/Web UI | HL7, Barcode/RFID |
| Pharmacy Management Software | Oversees inventory, prescription processing, and POS. | Java, C# (.NET) | Desktop/Web UI | e-Prescribing APIs, Insurance APIs |
| Medical Research & Education Software | Supports clinical studies, training simulations, and data sharing. | Python, Java, C++ | Web/Desktop UI, VR/AR Platforms | Pandas, NumPy, Unity/Unreal Engine, Cloud Compute |
UX/UI Challenges and Solutions in Healthcare Software Product Development
Designing intuitive and safe interfaces is critical in healthcare software product development. Each design decision impacts clinical efficiency, data accuracy, and patient safety. Addressing key challenges early ensures the software is usable, accessible, and practical across healthcare environments.
| UX/UI Challenge | Impact on Software Development | Effective Design Solutions |
| Cognitive Load & Information Overload | Leads to complex interfaces, increased errors, and low user adoption. | Use progressive disclosure, role-based dashboards, and focused layouts. |
| Inefficient Workflows | Slows down routine tasks, increases user frustration. | Implement task-based navigation, smart defaults, and contextual actions. |
| Error Prevention | Results in critical mistakes during data entry or treatment decisions. | Add confirmation prompts, validation feedback, and real-time warnings. |
| Alert Fatigue | Excessive alerts lead to ignored or missed critical notifications. | Use prioritized, actionable, and smartly grouped alerts. |
| Legibility & Data Clarity | Poor readability leads to data misinterpretation. | Apply visual hierarchy, consistent color coding, and responsive charts. |
| Diverse Operating Environments | Software fails in mobile or emergency settings. | Ensure responsive design, high contrast UI, and voice-input capabilities. |
| Accessibility & Inclusivity | Excludes users with disabilities or language barriers. | Support screen readers, adaptive fonts, localization, and inclusive testing. |
Steps in Healthcare Software Product Development
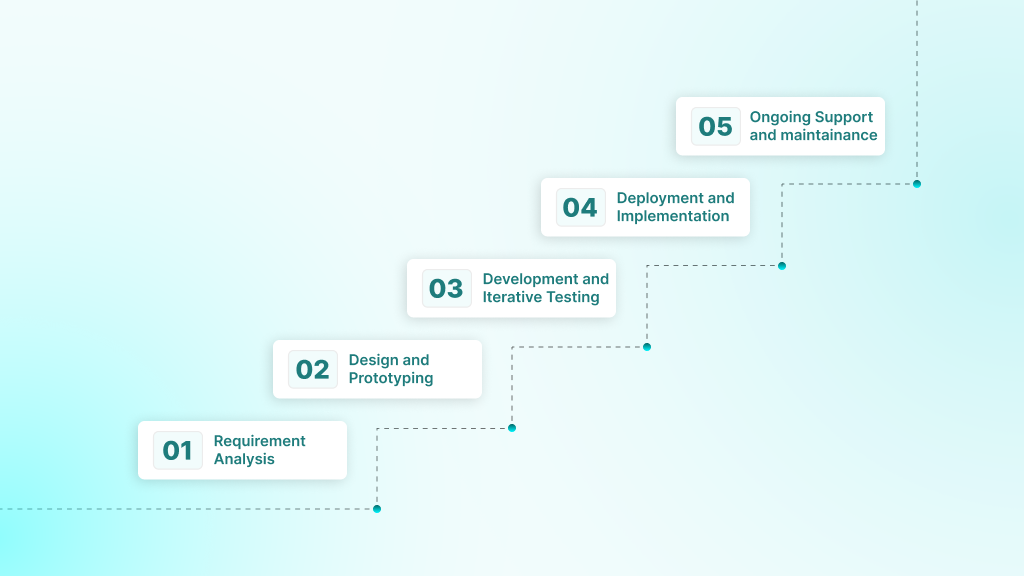
Healthcare software development demands a careful, flexible approach to meet provider and patient needs while ensuring compliance and seamless EHR integration. Here is the step-by-step process for building effective and secure healthcare software.
1. Requirement Analysis and Initial Research
The first step is to meet with stakeholders, including administrators, providers, and patients, to gather their input. It is important to benchmark the project against regulatory standards and competitor products. This helps identify the essential features and set clear project goals.
2. Design and Prototyping
Design begins with creating storyboards, wireframes, and prototypes. Accessibility standards ensure the software works for everyone. Early user feedback helps improve the design before development.
3. Development and Iterative Testing
Development begins by building core modules and necessary integrations. Multiple testing phases ensure the software is functional, usable, and secure. After each iteration, feedback from stakeholders is quickly used to improve the product.
4. Deployment and Implementation
The software is first launched in a test environment, then moved to live systems. Staff and administrators receive detailed training to use it effectively. Incident response plans are prepared before the final rollout.
5. Ongoing Support
Regular updates and patches are scheduled to keep the software secure and up to date. System performance and user satisfaction are continuously monitored. A 24/7 help desk is provided to ensure smooth and uninterrupted operations.
Cost of Software Product Development in the Healthcare Industry
Healthcare software development costs vary widely based on project scope and complexity. In 2025, prices typically range from $30,000 for simple apps to over $500,000 for full-featured platforms. Enterprise-level systems with advanced features can cost $1 million or more.
Typical Costs by Software Type
| Software Type | Cost Range | Timeframe |
| Basic Healthcare App | $30,000 to $80,000 | 3 to6 months |
| Telemedicine Platform | $100,000 to $300,000 | 8 to 15 months |
| EHR System | $75,000 to $250,000 | 6 to 12 months |
| Hospital Management | $200,000 to $500,000+ | 12 to 24 months |
Key Factors Affecting Cost
Understanding the key factors affecting the cost of healthcare software product development is crucial for effective budgeting and project planning. These factors influence how much time, resources, and expertise are required to deliver a compliant, functional, and scalable solution.
- Project Complexity and Required Features:
Project scope and complexity affect costs; simple features need less time, while advanced functions require more resources and expertise. - Security and Regulatory Compliance (HIPAA, GDPR):
Healthcare software must follow strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to protect patient data. Meeting these standards adds cost due to extra security, audits, and validation. - Integration with Existing Systems and Devices:
Integrating new software with legacy systems or devices requires custom work. This adds development time and increases project costs. - Use of AI or Blockchain Technologies:
Using advanced technologies like AI or blockchain requires special skills and more development time. This increases the overall cost. - Development Team Location and Expertise:
Developer costs vary by location and expertise. Skilled teams may charge more but can complete projects faster, saving time.
Budget Tips
Effective healthcare software product development depends on strategic planning to control costs and deliver value. Adopting the right approach early can prevent budget overruns and ensure the solution meets regulatory and user needs.
- Define Clear Requirements Upfront:
Establish detailed project goals and user needs from the start. This reduces the risk of costly changes later in development. - Start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP):
Build a basic version with essential features first. This allows testing in real environments and scaling based on feedback. - Choose Experienced Partners:
Work with development teams skilled in healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Their expertise helps ensure compliance and smooth project execution.
Role of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are driving significant advancements in healthcare information systems. They improve care delivery, data security, and patient outcomes through smarter, more connected solutions.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are improving healthcare by supporting diagnosis, patient interaction, and risk prediction.
- Diagnostic Aid: AI helps analyze medical images and detect abnormalities.
- Chatbots: Virtual assistants respond to patient queries and guide symptom checks.
- Predictive Models: ML identifies high-risk patients for early intervention.
These tools make care more accurate, accessible, and proactive.
2. Blockchain for Secure Data Management
Blockchain is transforming healthcare data management by securely storing and sharing patient information. Its decentralized system ensures records are tamper-proof, protecting data integrity and privacy.
- Secure, tamper-proof record keeping: Blockchain ensures that patient data cannot be altered or deleted without consensus, protecting sensitive information.
- Controlled sharing: It enables patients and providers to share health data securely and selectively, improving care coordination while maintaining privacy.
- Smart contracts: Automated contracts streamline processes such as insurance claims and payments, reducing administrative costs and errors.
3. The Use of IoT in Healthcare Applications
IoT technology is improving patient care through real-time monitoring and data sharing. Devices like wearables and smart equipment help track health conditions and enhance safety inside and outside hospitals.
- Wearables: Track vitals like heart rate, oxygen, and blood sugar, transmitting data automatically for continuous monitoring.
- Smart beds: Monitor patient movement and safety through built-in sensors, alerting staff to potential risks.
- Home health devices: Assist elderly and chronically ill patients in managing conditions independently, improving quality of life, and reducing hospital visits.
The adoption of these technologies offers a competitive edge for care providers.
Challenges and Risks in Healthcare Software Product Development
Healthcare software development faces unique challenges that require careful attention to security, cost, timelines, and usability. Navigating these risks effectively is critical to delivering compliant, efficient, and user-friendly solutions.
1. Ensuring Data Security and HIPAA Compliance
Strict adherence is required to avoid breaches.
- Implement role-based access controls.
- Use secure, encrypted data transfer channels.
- Conduct regular audits to cement trust.
2. Managing Development Costs and Timelines
Delay and overspending are common risks.
- Define milestones and scope at project start.
- Use agile project management to adapt to changes.
- Prioritize critical features for the earliest release.
3. Addressing User Experience and Accessibility Issues
Effective healthcare software prioritizes intuitive, accessible design to support diverse users and enhance clinical workflows.
- Design intuitive interfaces for busy clinicians.
- Include multilingual support and voice/UI options.
- Evaluate with real users, adapting for varying skills and needs.
4. Other Common Pitfalls
Beyond technical challenges, overlooked operational issues can derail the adoption and long-term success of healthcare software.
- Insufficient staff training leads to underused technology.
- Poor integration projects stall user adoption and data sharing.
- Lack of change management complicates transitions from legacy systems.
Proactive planning and testing help minimize these risks.
Best Practices for Successful Healthcare Software Product Development
Healthcare software product development demands a strategic approach that balances flexibility, quality, and user engagement to meet complex industry requirements effectively.
1. Adopting Agile Methodologies
Agile development breaks the work into short cycles, letting teams improve the software step-by-step based on user feedback. It also allows easy changes when healthcare rules or needs change.
2. Engaging Stakeholders Throughout Development
Engaging stakeholders throughout development involves scheduling regular review meetings and including end-users, compliance officers, and domain experts at every phase to ensure the product meets clinical, regulatory, and user needs.
3. Continuous Testing and Quality Assurance
Continuous testing and quality assurance involve automating functional, security, and regression testing pipelines to catch issues early. Running parallel user acceptance testing helps identify usability or performance problems before the software is deployed.
4. User Training and Support
Training should be customized for different users, like clinicians, administrators, and patients. Provide clear onboarding guides and e-learning resources. Keep support channels open to help with issues and updates.
Future Trends and Innovations in Healthcare Software Product Development
Healthcare software is rapidly evolving through advances like AI, wearables, and virtual reality, enabling more personalized, efficient, and connected patient care solutions. These innovations are shaping the future of healthcare delivery and management.
1. Personalized Medicine and Predictive Analytics
Personalized medicine uses genomics and AI to create treatments just for each person. It helps predict disease outbreaks and health risks. Real-time data also helps doctors prevent problems before they happen..
2. Integration of Virtual and Augmented Reality
Virtual reality (VR) offers immersive, risk-free surgical training that helps doctors practice and improve their skills. Augmented reality (AR) provides real-time guidance during surgeries, enhancing precision and safety.
3. Advancements in Health Monitoring Devices
Next-generation wearables gather more detailed health data such as ECG, blood oxygen levels, and sleep patterns. Continuous monitoring with these devices helps reduce emergency hospital visits. Their integration also supports telemedicine and at-home care for chronic conditions.
4. Interoperability and Open Platforms
Open APIs enable seamless sharing of patient data across different healthcare providers, making health information easily portable. This supports patient-centered health records that individuals can access throughout their lives, improving continuity of care.
5. Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics in healthcare, like automated dispensing and robotic surgeries, cut manual work, improve accuracy, and speed up recovery. The focus is now on safety, personalization, and better user experiences.
Healthcare technology will continue to push boundaries, focusing on safety, personalization, and seamless user experiences.
Practical Table: Types of Healthcare Software with Examples
| Software Type | Example Use | Key Technologies |
| EHR Systems | Manage patient records | HL7, FHIR, PostgreSQL |
| Telemedicine Apps | Virtual consultations | Twilio Video, Zoom SDK |
| HIS | Integrated hospital management | Django, Next.js, AWS |
| Practice Management | Billing, scheduling | Stripe, Zapier, PHP |
| AI Diagnostic Tools | Radiology support | OpenAI, Python |
| Remote Monitoring Devices | Chronic care at home | IoT, Bluetooth, Python |
| Patient Engagement Portals | Appointment reminders | Firebase, SMS APIs |
Evidence in Action: DEVtrust Case Studies
Case Study: Precina & DEVtrust
Precina faced challenges with medication adherence, fragmented systems, and low patient engagement. Partnering with DEVtrust, they developed a secure digital platform featuring automated medication reminders, real-time syncing between web and mobile apps, and OTP-based authentication to protect sensitive data.
The results were impressive: a 98% reduction in manual tasks, a 95% increase in user trust, and significant improvements in patient health outcomes. This solution enabled Precina to deliver efficient, patient-centred chronic disease management on a large scale.
Case Study: Must Motivate & DEVtrust
Must Motivate set out to improve mental health and physical well-being by building a supportive online community. The platform faced challenges, including a lack of compatibility with diverse health devices, the absence of real-time data integration, and limited user engagement features.
DEVtrust addressed these hurdles by integrating leading health monitoring devices, developing a unified data interface, and embedding tools for mental health assessment. A gamified system of challenges, habit-building, and rewards further boosted motivation and engagement. As a result, Must Motivate achieved a 98% reduction in manual tasks, a 95% increase in user trust, and a more vibrant, health-focused community experience.
Conclusion
Healthcare software development is the critical foundation enabling safe, effective, and data-driven medical care. Modern applications connect patients and providers, streamline workflows, and enhance clinical decisions. Emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain are transforming healthcare delivery, raising the standard of care worldwide.
At DEVtrust, we combine deep industry expertise with advanced technical skills and unwavering commitment to regulatory compliance to deliver robust, secure, and user-centric healthcare software solutions. As digital transformation accelerates, partnering with DEVtrust empowers your organization to stay ahead, driving superior healthcare outcomes and confidently navigating future challenges.
Ready to transform your healthcare software vision into reality?
Contact DEVtrust today to schedule a consultation with our experts and start building the future of medicine: digital, innovative, and patient-centered.
Comprehensive Guide to Healthcare Software Product Development
Accelerate your healthcare software product development with insights on key trends, compliance, and best practices. Click to transform your IT.
Contact Us