The healthcare software market is growing steadily, expected to reach USD 38.5 billion in 2025 and expand significantly by 2034. This growth results from the adoption of digital health tools such as telemedicine, AI-enabled platforms, cloud computing, and wearable devices.
Artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things are improving data sharing, predictive analytics, and automation in healthcare. Telemedicine is expanding rapidly, with the market expected to reach nearly USD 380 billion by 2030. At the same time, AI-driven applications play a growing role in diagnostics and patient management.
Healthcare software development transforms these technologies into scalable, tailored solutions for providers and patients. This guide covers the key trends, challenges, and opportunities shaping healthcare software in 2025.
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare software is vital for improving patient care, streamlining operations, and ensuring compliance. Solutions like EHRs, telemedicine platforms, and AI-driven tools are at the forefront.
- The market is booming, and global healthcare software is expected to surpass $1 trillion by 2034, driven by demand for efficiency, better outcomes, and regulatory changes.
- Key trends include personalized medicine, predictive analytics, cloud and IoT integration, and a focus on interoperability and data privacy.
- Custom solutions enable seamless integration, better care coordination, reduced costs, and data-driven decision-making.
What Is Healthcare Software Product Development?
Healthcare software development involves designing and building customized digital tools that enhance clinical accuracy, streamline workflows, and support better patient care within healthcare organizations.
These solutions enable healthcare professionals to efficiently manage patient records, schedule and track appointments, access diagnostic information, and coordinate care teams.
From the patient’s perspective, such software offers convenient features like easy appointment scheduling, secure communication with providers, safe sharing of medical data, and quick access to personalized health updates. Together, these capabilities help create a more connected and efficient healthcare experience for both providers and patients.
The Current Landscape: Digital Healthcare’s New Era
The healthcare software market is expanding rapidly, valued at $420 billion in 2025 and projected to exceed $1 trillion by 2034. Key drivers include:
- Patient-centered care: Increasing demand for personalized, accessible services.
- Regulatory evolution: Updates to HIPAA, GDPR, and the 21st Century Cures Act.
- Technological innovation: AI, cloud, and IoT are enabling scalable, integrated applications.
- Operational efficiency: Software reduces administrative overhead and improves coordination.
Persistent Challenges
Despite progress, healthcare faces significant challenges:
- Data fragmentation: Siloed systems hinder care continuity.
- Security risks: Healthcare is a top target for cyberattacks.
- Administrative burden: Physicians now spend nearly as much time on paperwork and documentation as they do on direct patient care, making it a major challenge in healthcare.
- Integration gaps: Lack of interoperability causes delays and errors.
- Medical errors: In the U.S., medical errors contribute to an estimated 98,000 deaths annually.
Global Perspective
A Statista survey found that dissatisfaction with healthcare systems is widespread: 63% of respondents in Poland, 52% in Italy, and 33% in the U.S. felt their systems were falling short. Software solutions that automate tasks, enhance data access, and improve communication can play a crucial role in overcoming these challenges.
Why Invest in Healthcare Software Development?
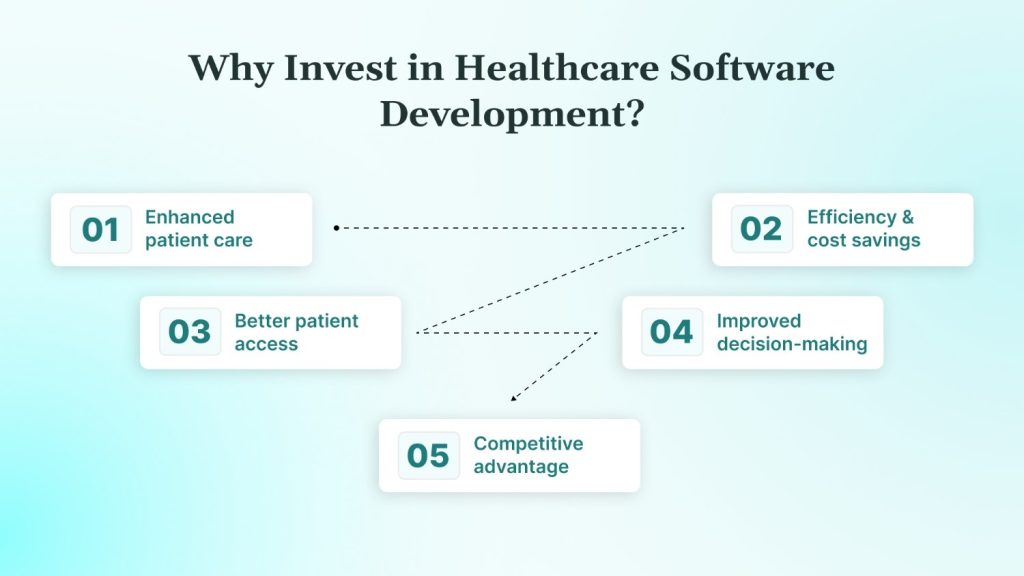
Custom healthcare software delivers measurable benefits:
- Enhanced patient care: Streamlined processes, fewer data entry errors, and personalized treatment.
- Efficiency and cost savings: Automation reduces manual work and administrative costs.
- Better patient access: Patient portals and mobile apps empower patients to manage appointments, records, and communication.
- Improved decision-making: Integrated data and analytics support evidence-based care.
- Competitive advantage: Modern, transparent, and personalized services help build lasting patient trust, exactly what DEVtrust delivers through its custom healthcare platforms.
Types of Healthcare Software Solutions
Healthcare software solutions vary widely, with each type developed to address distinct requirements across clinical, administrative, or operational domains. A strong healthcare software ecosystem effectively links these diverse components together, enabling smooth and complete care delivery.
| Software Type | Purpose / Benefit |
| Electronic Health Records (EHR) / Electronic Medical Records (EMR) | Centralized digital records of patient health data, including history, diagnoses, medications, and lab results. Enables authorized providers to access and update patient information in real time. |
| Patient Management Systems | Tools for scheduling appointments, tracking patient progress, managing communication, and streamlining front-desk operations. Improves patient flow and administrative efficiency. |
| Telemedicine Platforms | Enable virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and follow-ups. Expand access to care, especially for rural or underserved populations. |
| Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) | Collects real-time health data from wearables and IoT devices. Supports chronic disease management and reduces hospital readmissions. |
| Pharmacy Management Systems | Manage medication inventory, prescriptions, refills, and patient safety. Helps prevent medication errors and supports regulatory compliance. |
| Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) | Manage lab workflows, including test ordering, specimen tracking, results reporting, and quality control. Ensures accuracy and efficiency in diagnostics. |
| Radiology Information Systems (RIS) | Handle imaging workflows, including patient scheduling, image storage (PACS integration), AI-powered analysis, and report generation. |
| Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) | Provide evidence-based recommendations and alerts to assist healthcare providers in making accurate, timely decisions. Reduces diagnostic errors. |
| Billing & Invoicing Modules | Automate patient billing, insurance claims, co-payments, and financial reporting. Improves revenue cycle management and reduces claim denials. |
| Hospital Management Systems (HMS) | Integrate administrative, clinical, financial, and operational functions across departments. Streamline workflows and improve resource allocation. |
| Drug Discovery Systems | Support research and development of new pharmaceuticals using AI, big data, and simulation tools. Accelerate time-to-market for new drugs. |
| AI-Powered Chatbots & Virtual Assistants | Offer 24/7 support for appointment booking, symptom checking, FAQs, and triage. Enhance patient engagement and reduce staff workload. |
A strong digital infrastructure integrates these modules for seamless, end-to-end healthcare delivery.
Key Features of Modern Healthcare Software
To maximize impact, healthcare software should include:
- Patient registration and profile management
- Appointment scheduling and reminders
- E-prescription management and pharmacy integration
- Health history and EHR access
- Predictive analytics for outcomes and resource planning
- AI-powered chatbots for 24/7 support
- Automated alerts for critical events
- Quantitative imaging analysis
- Operating theater and inventory management
- Billing, invoicing, and insurance fraud detection
- Mobile access and responsive design
- Secure authentication and role-based permissions
These features support both clinical excellence and operational efficiency.
The Healthcare Software Development Process
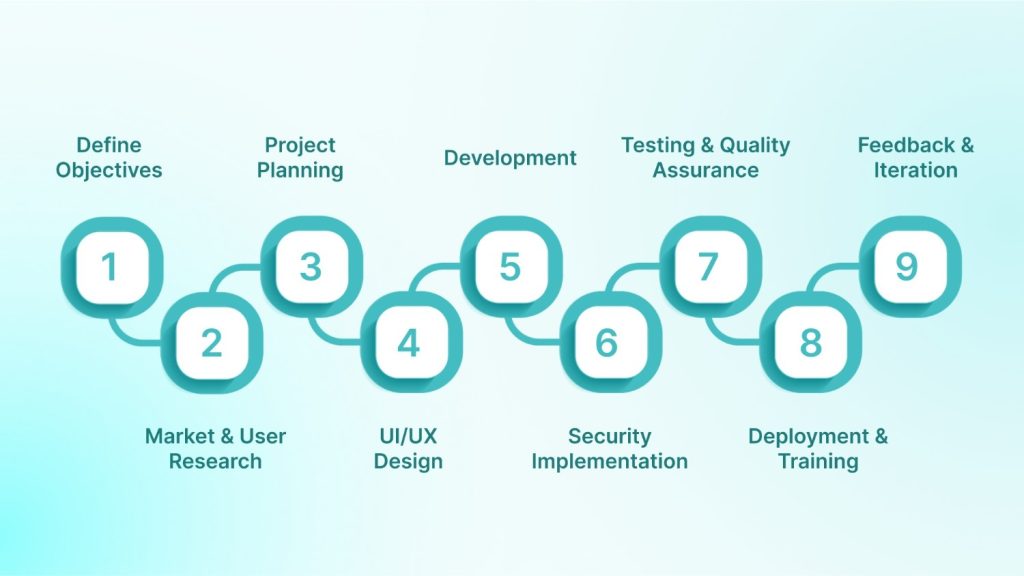
Developing healthcare software is a complex, multi-phase journey that requires careful planning, cross-disciplinary collaboration, and a strong focus on security and compliance.
1. Define Objectives and Requirements
Every successful healthcare software project begins with a precise understanding of its goals and constraints.
- Clarify the Problem and Purpose: Is the software for EHR management, telemedicine, billing, remote monitoring, or another function? Define the specific pain points it will address.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve clinicians, nurses, administrators, IT staff, and even patients early in the process. Their input ensures the software reflects real-world workflows and user needs.
- Regulatory Mapping: Identify all relevant compliance requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, HL7, DICOM, local health regulations). This step is critical, as overlooking a regulation can result in costly delays or legal issues.
- Success Metrics: Establish clear KPIs, such as improved patient outcomes, reduced administrative time, or increased data accuracy, to measure project impact.
2. Market and User Research
Understanding the competitive landscape and user expectations is vital for building a relevant product.
- Competitive Analysis: Study existing solutions to identify their strengths, weaknesses, and unique features. This helps avoid reinventing the wheel and reveals market gaps.
- User Research: Conduct interviews, focus groups, and surveys with end-users (doctors, nurses, patients, administrative staff). Gather insights on pain points, feature requests, and usability concerns.
- Personas and Use Cases: Develop detailed user personas and map out typical user journeys. This ensures the software is tailored to its intended audience.
3. Project Planning
A robust plan sets the stage for smooth execution.
- Scope Definition: Clearly outline what the project will and will not include. This prevents scope creep and keeps the team focused.
- Milestones and Deliverables: Break the project into phases with specific goals, requirements gathering, design, MVP development, testing, etc.
- Budgeting: Estimate costs for development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. Factor in compliance and security expenses.
- Resource Allocation: Assemble a cross-functional team with expertise in healthcare, software engineering, UI/UX, security, and compliance.
- Technology Stack Selection: Choose technologies that meet performance, scalability, and security needs. For example, React or Angular for the front-end, Python or Node.js for the back-end, and AWS or Azure for cloud infrastructure.
4. UI/UX Design
User experience is especially critical in healthcare, where usability can impact patient safety and compliance.
- Accessibility: Ensure the interface adheres to accessibility standards (WCAG), making it usable for people with disabilities.
- Wireframes and Prototypes: Create detailed wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize workflows and gather early feedback.
- Iterative Design: Use feedback from stakeholders to refine designs before development begins.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent look and feel across modules to reduce user confusion and training time.
5. Development
This is where the vision becomes reality, and best practices are crucial.
- Agile Methodology: Adopt an agile approach to enable iterative development, frequent feedback, and rapid adaptation to changing requirements.
- Front-End Development: Build responsive, user-friendly interfaces for web and mobile access. Prioritize performance and security.
- Back-End Development: Develop robust APIs, ensure secure data storage, and implement business logic. Integrate with existing systems (EHRs, labs, billing) using industry standards like HL7 or FHIR.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Automate building, testing, and deployment to catch issues early and accelerate delivery.
6. Security Implementation
Security is non-negotiable in healthcare due to the sensitivity of patient data.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt all data at rest and in transit using industry-standard protocols.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement multi-factor authentication and role-based access control to restrict sensitive operations.
- Audit Trails: Log all access and changes to patient data for compliance and forensic analysis.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Regularly scan for security vulnerabilities and patch promptly.
7. Testing and Quality Assurance
Rigorous testing ensures reliability, safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Unit Testing: Test individual components for correctness.
- Integration Testing: Validate that modules work together as intended.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve real end-users to ensure the software meets their needs and is intuitive to use.
- Performance Testing: Simulate high-load scenarios to ensure the system remains responsive.
- Compliance Testing: Verify that the software adheres to all relevant healthcare regulations and standards.
- Automated and Manual Testing: Combine both approaches for thorough coverage, especially for critical workflows.
8. Deployment and Training
Successful deployment and user adoption are as important as the software itself.
- Deployment Planning: Choose the right environment (cloud, on-premises, or hybrid) based on security, scalability, and compliance needs.
- Go-Live Checklist: Ensure all systems are configured, data is migrated, and backups are in place.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training for all user groups, including clinicians, administrative staff, and IT support. Use a mix of documentation, video tutorials, and live sessions.
- Support Resources: Set up a helpdesk and user support channels for post-launch troubleshooting.
9. Feedback and Iteration
Continuous improvement is key to long-term success.
- Monitoring: Track usage, performance, and error logs in real-time.
- User Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback through surveys, interviews, and analytics.
- Iterative Updates: Use feedback and monitoring data to prioritize bug fixes, new features, and usability enhancements.
- Regulatory Evolution: Continuously monitor shifts in healthcare legislation and adapt software promptly to ensure ongoing adherence to compliance standards.
Technical and Regulatory Considerations
Building healthcare software demands strict attention to technical standards and regulatory requirements. Ensuring security, compliance, and seamless integration is essential for safe and reliable digital health solutions.
Compliance and Security
- HIPAA (U.S.), GDPR (EU), HL7, DICOM, ISO 27001, HITRUST: Adherence is mandatory for handling patient data.
- Data protection: Encryption, secure authentication, audit logs, and regular security audits are essential.
- Interoperability: Standards like FHIR and HL7 enable seamless data exchange, which DEVtrust prioritizes to ensure smooth integration with existing systems.
- Scalability: The Architecture must support future growth and new features.
- Mobile and web access: Responsive design or hybrid apps (PWAs) ensure accessibility.
Integration and Usability
- EHR integration: Enables comprehensive patient records.
- Analytics: Actionable insights for providers and administrators.
- User-centric design: Interfaces must be intuitive for both clinicians and patients; usability is a key success factor.
Development Methodologies and Best Practices
- Agile development: Enables rapid iteration and adaptation to changing requirements.
- DevOps: Supports continuous integration, delivery, and deployment.
- Collaborative teams: Cross-functional groups (developers, clinicians, QA, UI/UX designers) ensure relevance and quality.
- MVP approach: Launching a minimum viable product allows for early feedback and iterative improvement.
Challenges in Healthcare Software Development
- Regulatory complexity: Navigating global and local requirements is time-consuming.
- Data security: Healthcare is a prime target for cyberattacks; robust measures are non-negotiable.
- Integration with legacy systems: Varying standards and formats complicate interoperability.
- High development costs: Advanced features and compliance increase project budgets.
- User adoption: Training and support are critical for successful rollout.
- Complex, unstructured data: Requires experienced developers and advanced analytics.
How DEVtrust Transforms Healthcare Through Software
Real-world results speak louder than theory. Here are two examples of how DEVtrust has helped healthcare clients solve complex problems with innovative, secure, and scalable software solutions.
Case Study 1: Precina – Simplifying Medication Management
Precina partnered with DEVtrust to develop a digital platform addressing medication adherence for chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Challenges:
- Ensuring patients take medications on time
- Lack of integration between web and mobile apps
- Low patient engagement and data access
- Data security concerns
Solutions:
- Reminder notifications for medication
- Real-time syncing between platforms
- Health-based alerts for vital signs
- OTP-based secure login
Results:
- 98% reduction in manual efforts
- 95% increase in user trust
- 97% improved document handling
- 92% boost in agent productivity
Case Study 2: Spero Institute – Enhancing Therapy Management
DEVtrust created a detailed app for Spero Institute to improve clinician-patient communication, progress tracking, and scheduling.
Challenges:
- Lack of secure login
- Inefficient document management
- Poor visual progress tracking
- Difficult scheduling and messaging
Solutions:
- Role-based secure authentication
- Streamlined document handling
- Intuitive DBT progress tracker
- Integrated scheduling with video calls and messaging
Results:
- Improved data security and access
- Faster document retrieval
- Clear therapy progress insights
- Seamless communication and scheduling
Future Trends and Innovations
Emerging technologies are transforming healthcare software, enabling smarter diagnostics, personalized care, and enhanced connectivity. Staying ahead of these trends is vital for providers and organizations seeking to deliver advanced, responsive healthcare solutions.
- AI and machine learning: Deeper integration for diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine.
- IoT and wearables: Real-time monitoring, proactive care, and patient engagement.
- Cloud and edge computing: Scalable, secure, and responsive infrastructure.
- 5G connectivity: Enables high-speed, low-latency data transfer for telemedicine and remote surgery.
- Quantum computing: Promises breakthroughs in data analysis and drug discovery.
- Digital twins and simulation: Advanced modeling for patient-specific treatment planning.
- Continuous updates: Software must evolve with new regulations, technologies, and user needs.
Conclusion
Healthcare software development in 2025 is redefining how care is delivered, managed, and experienced. With technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing becoming integral to healthcare systems, organizations have the opportunity to enhance patient results, optimize workflows, and boost patient engagement. However, success depends on more than just innovation; it requires secure, user-friendly, and compliant solutions built around real-world needs.
At DEVtrust, we partner with healthcare organizations to deliver secure, scalable software that meets today’s challenges and tomorrow’s needs. As healthcare evolves, thoughtful technology solutions will be essential for long-term success. We are committed to supporting that transformation every step of the way.
Book a short call and get expert feedback on your healthcare software approach!
Complete Guide to Healthcare Software Development
Discover essential trends in healthcare software development for 2025. Integrate AI, ensure compliance, and learn key methodologies now. Click to innovate!
Contact Us