Despite the $151 billion market for financial software in 2024, most organizations continue to struggle with getting it right. The pressure to modernize, stay compliant, and build user trust while competition accelerates is relentless.
Financial software development offers a direct path forward. With the right architecture, security, and compliance strategy, technical leaders can build products that scale quickly without incurring long-term risks or rework.
This guide explains how to approach financial software development with clarity and control. It covers system design, infrastructure, security protocols, compliance standards, and the role of technologies such as AI and blockchain in reshaping the finance industry.
Key Takeaways
- Enhanced Security & Compliance: Ensuring data protection with reliable security measures and staying compliant with financial regulations, including GDPR and PCI-DSS, to prevent breaches.
- Scalability & Adaptability: Custom financial software solutions scale with your business, supporting growth without compromising performance, security, or compliance.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By automating processes like invoicing, payments, and reporting, custom financial software streamlines operations, reducing manual work and errors.
- Advanced Data Analytics: Financial software with built-in analytics helps businesses make data-driven decisions, track performance, and stay ahead of industry trends.
- Faster Time to Market: With agile development and modern frameworks, businesses can launch financial products faster, meeting market demands and staying competitive.
What Is Financial Software Development?
Financial software development is about building secure, high-performance systems that power how money moves, gets tracked, and stays compliant. That includes everything from mobile banking apps to automated trading platforms, handling billions in transactions with zero tolerance for downtime or data loss.
Financial software spans multiple product lines, each shaped by operational goals, compliance needs, and system behaviors.
- Banking Platforms: Core banking functions like account access, onboarding, and fraud controls with modern APIs.
- Investment & Wealth Systems: Includes robo-advisors, portfolio dashboards, and back-office tools, all operating under strict regulatory compliance.
- Insurance Technology: Supports quoting, underwriting, and claims workflows with automation and ML-driven decision-making.
- Popular FinTech Apps: Payment, investment, budgeting, lending, accounting, DeFi, cryptocurrency, and insurance apps.
As financial technology grows, these solutions are designed to meet industry demands while ensuring security, compliance, and scalability.
Also Read: Top Financial Advisory Apps for Budgeting and Planning 2025
Next, let’s explore how financial software development can drive meaningful improvements in your business operations.
Benefits of Financial Software Development
Financial software development provides businesses with a strategic advantage, enabling them to overcome challenges and capitalize on growth opportunities. Here’s why it’s critical for your business:
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Custom financial software development integrates various tools, from invoicing to expense management, into a seamless solution.
- Enhanced Control and Integration: Financial software development provides greater control over data by reducing reliance on paper-based records. Hence, there is seamless data flow across platforms, providing enhanced visibility for accurate financial reporting.
- Scalability and Adaptability: As business complexity increases, financial software can scale as needed. Custom solutions grow with your business, ensuring continued efficiency and flexibility.
- Improved Customer Experience: Investing in intuitive financial software boosts user satisfaction, whether for banking, financial reporting, or other services.
- Advanced Security and Risk Management: The financial industry demands robust data security. By incorporating features such as two-factor authentication and continuous threat monitoring, financial software development helps prevent security breaches and builds trust.
- Ongoing Support and Training: A well-implemented custom solution includes structured onboarding, documentation, and ongoing support. This helps your finance and operations teams adopt new workflows faster, reduces downtime when regulations or processes change, and keeps your platform aligned with how your business actually runs.
Strategic investment in financial software development results in streamlined operations and prepares your business to tackle the financial sector with confidence.
Ready to future-proof your financial operations? Partner with DEVtrust to create secure, scalable, and intuitive financial software that adapts to your growing business needs. Contact us today to start building your future-proof financial platform.
To experience these benefits, it’s essential to know the key features that make financial software systems both powerful and adaptable to your needs.
Key Features of Financial Software Systems
Financial software systems are designed to provide users with a range of powerful tools that enhance financial operations. Below are the must-have features for any financial software:
1. Secure Authentication and Authorization
Ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive financial data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric options (like fingerprint or facial recognition) enhance security, meeting industry standards and protecting against cyber threats.
2. Real-Time Updates and Notifications
Provides users with timely information about their financial status, including real-time transaction updates, alerts for unusual activities, and changes in account balances.
3. Customizable Dashboards and User Interfaces
Allows users to tailor their financial management experience. Personalized dashboards enable users to easily monitor accounts, track expenses, and manage investments within an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
4. Personalized Financial Management Tools
Offers tools for budgeting, saving, and tracking financial goals. Customizable financial management features cater to individual needs, enabling users to make informed financial decisions based on their unique circumstances.
5. Advanced Data Analytics and Reporting Capabilities
Includes built-in analytics for tracking expenses, income, and investments. Users can generate reports for financial planning, tax preparation, and performance tracking, enhancing decision-making capabilities.
6. Seamless Integration with Third-Party Financial Services
Integrates with services such as payment processors (e.g., Stripe, PayPal), investment platforms, and bank APIs, enabling seamless financial operations and ensuring data consistency across systems.
7. Automated Transaction Processing and Record-Keeping
Automates the recording of transactions, helping users maintain accurate financial records and reducing manual data entry errors. This feature supports efficient transaction management and ensures compliance with financial regulations.
8. Mobile-Friendly Design and Cross-Platform Compatibility
With a growing preference for mobile banking and financial services, financial software must be optimized for mobile devices. This feature enables users to manage their finances from anywhere, on any device, while maintaining the highest security standards.
The success of financial software depends on how effectively it can combine these features to create a seamless, secure, and scalable solution.
Features are your starting point, and they only take you so far. The real challenge is building the system around them. Let us walk through how that happens.
The Financial Software Development Process
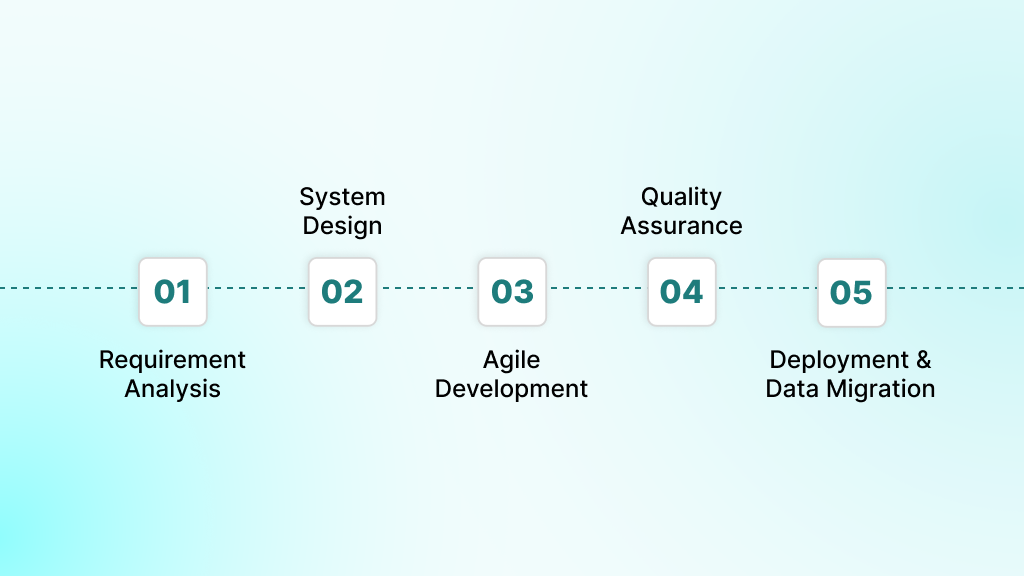
Financial software development follows a structured methodology that strikes a balance between rapid delivery and rigorous quality control. Each phase builds upon previous work while incorporating feedback loops that prevent costly late-stage discoveries.
Step 1: Discovery and Requirement Analysis
Clarity here prevents months of rework. Before building, understand key system requirements such as:
- High-volume transactions
- Data retention policies
- Compliance triggers
- User access flows
Stakeholder input is crucial, but not all requests can be translated into features. This phase involves mapping workflows, identifying constraints, and translating regulatory needs into informed decisions that shape the architecture. Rushing this step causes projects to drift.
Step 2: Architecture and System Design
Architecture influences every subsequent phase: speed, scalability, compliance, and data integrity. Key decisions include:
- Cloud-native environments: Offer flexibility and rapid scaling but require careful planning for data residency, sovereignty, and regional compliance so sensitive financial data stays in the right jurisdictions.
- Microservices: Provide autonomy but introduce complexity, particularly in service synchronization and security.
Designing the data layer, including tables, indexes, and permissions, impacts reporting and audit requirements. Security design covers identity management, access control, and encryption.
Step 3: Agile Development and DevOps Implementation
Financial software evolves with changing requirements, regulatory shifts, and integration needs. Agile methodology ensures adaptability:
- Sprint cycles: Focus on shipping features while addressing technical debt and security.
- CI/CD pipelines: Automate builds, validate commits, and perform security and performance checks early.
- DevOps practices: Infrastructure as code and containerization enable consistent, repeatable deployments.
Step 4: Multi-Layer Testing and Quality Assurance
Financial software relies on accuracy, speed, and security. Testing must catch issues early to avoid revenue, trust, or compliance risks:
- Unit tests: Verify core logic.
- Integration tests: Ensure smooth system communication.
- Security tests: Identify vulnerabilities in access, input, and data handling.
- Performance tests: Evaluate real-world system behavior.
Testing early and often helps maintain high velocity without sacrificing stability.
Step 5: Deployment, Data Migration, and Client Onboarding
Transition from staging to real-world use involves risk control:
- Blue-green and canary strategies: Gradual release methods for smooth rollouts and quick rollbacks.
- Data migration: Ensure financial records, timestamps, and mappings are verified to avoid compliance issues.
- User onboarding: Must be fast, secure, and compliant, including features like real-time ID verification and fraud detection.
At the end of the deployment, the system proves itself under real conditions. Everything that follows depends on getting this part right.
Don’t let outdated systems hold you back. DEVtrust’s proven development process has delivered compliant and scalable solutions for organizations ranging from startups to enterprises. Schedule a consultation to discuss your project.
You have seen the full process, from idea to execution. But what holds it all together? The tools. Knowing the right ones puts you a step ahead in every phase of development.
Technological Tools and Frameworks for Financial Software

Selecting the right tools and frameworks is crucial for building secure, scalable financial software. Here’s an overview of the key technologies we use to deliver high-performance solutions.
Backend Languages and Runtime Environments
Your backend tech stack determines how well your system performs under pressure, especially when handling real-time trades and sensitive data. Here is how some of the most trusted languages stack up in real financial builds:
- Java: Still the go-to for enterprise finance systems. It is stable, battle-tested, and backed by frameworks like Spring Boot that speed up delivery without cutting corners. Strong typing and mature tooling help prevent the kind of calculation errors that can not be afforded in production.
- Go: Great for high-throughput systems, real-time trading, payment engines, and anything with concurrency demands. It is fast, memory-efficient, and compiles lean binaries that are easy to deploy and manage at scale.
- Python: Ideal for analytics-heavy workflows, risk models, forecasting engines, and compliance reporting. Libraries like Pandas and NumPy make it the default for financial data science. It is also quick to prototype, which helps when you are validating new ideas under pressure.
- Node.js: Works well for I/O-Intensive apps, such as API gateways, dashboards, or microservices, that process a large number of concurrent requests. Additionally, using JavaScript on both the front end and back end reduces context switching for development teams and speeds up delivery.
Frontend Frameworks for Financial Interfaces
Financial applications need to surface live data, handle complex interaction flows, and stay responsive under load. The frontend stack you choose affects not only user experience, but also how fast your team can ship, iterate, and scale the product.
- React: Reliable and flexible for everything from dashboards to trading views. Its component-based model fits well with reusable, data-heavy interfaces. Add in libraries like Recharts or Victory, and you have the foundation for real-time charts and portfolio views that do not choke under load.
- Angular: This is best when you are building large, structured platforms with heavy logic on the front end, like insurance portals or admin consoles. TypeScript support and built-in tooling give you more control, and the framework’s opinionated setup keeps things consistent across teams.
- Vue.js: Lightweight but scalable. Easy to slot into legacy systems or prototypes, and still strong enough for full-scale applications. Its simplicity cuts down on ramp-up time, while Vuex and other state management tools help maintain UI stability in complex workflows.
Databases Optimized for Financial Loads
Financial systems move money, track history, and produce reports that auditors and regulators rely on. That means your database must handle high-volume transactions, ensure consistency, and still serve analytics without crashing.
- PostgreSQL: A relational database known for strong ACID compliance and reliability. It is ideal for core transaction processing, where integrity, accuracy, and auditability come first. Features like JSON support and custom data types enable you to model financial products without sacrificing structure.
- Redis: An in-memory data store built for speed. Use it as a caching layer to serve real-time balances, session tokens, or fraud-scoring results in microseconds. Its pub/sub features also make it useful for pushing live updates across distributed systems.
- Apache Cassandra: A distributed NoSQL database designed for high availability and massive scale. Best used for global financial platforms that can not afford downtime. While it sacrifices strict consistency for uptime, it is ideal for use cases such as logging, transaction metadata, or fraud event streams.
Third-party APIs and Financial Data Services
The right APIs let you plug into verified data sources, streamline onboarding, and launch features faster without compromising compliance. Below are some related tools to use:
- Plaid: An API service that connects apps to user bank accounts across thousands of institutions. Use it to handle account linking, balance checks, and transaction categorization without storing sensitive credentials yourself. Real-time webhooks enable you to trigger fraud checks or insights instantly.
- Stripe: A payment infrastructure platform with developer-first APIs. It handles everything from card payments and bank transfers to KYC, compliance, and fraud detection. Ideal for teams that need global payment coverage without building an entire billing engine in-house.
- Open Banking APIs: Standardized interfaces that let you access customer-permissioned data from banks and financial institutions. Use them to power budgeting apps, loan eligibility engines, or account aggregation tools while staying aligned with regulatory frameworks such as PSD2 in Europe or local central bank guidelines in markets like the UK, EU, or India.
DevOps and Observability Stack
DevOps tools enable the reliable deployment and monitoring of financial software systems. These tools provide the automation and visibility needed to maintain high availability and performance.
- Docker: A containerization tool that packages code and dependencies into isolated units. It ensures consistency across development, testing, and production environments, eliminating the “works on my machine” problems and enabling faster, safer rollouts.
- Kubernetes: An orchestration system that manages containers across clusters. It automates deployment, scaling, and recovery. Financial systems maintain high uptime while handling workload spikes and enforcing network security policies.
- Prometheus & Grafana: Prometheus collects real-time metrics, and Grafana turns them into actionable dashboards. Together, they help teams track everything from infrastructure health to transaction volumes so you spot issues before users do.
- Terraform: A tool for defining infrastructure as code. It consistently creates, updates, and tears down cloud environments. For regulated systems, it also provides a version history and audit trails every time a change occurs.
Utilizing advanced tools and frameworks ensures your financial software is secure, efficient, and scalable.
Even with the right technology foundation, financial software development presents unique challenges that require specialized expertise and proven solutions. Let’s go over them.
Challenges in Financial Software Development
Financial software development challenges are specific, technical, and often regulatory; solving them requires more than clean code or fast delivery.
1. Adapting to Constantly Changing Regulations
Compliance is a moving target. Requirements vary by region, shift quickly, and may sometimes be applied retroactively.
Why is it a challenge?
- Jurisdictions impose unique rules with short lead times.
- Legacy systems are hard to adapt under pressure.
- Compliance logic tied to core code slows response.
How to handle it:
- Isolate regulatory logic as a separate module or service.
- Use configuration-driven rule engines for faster updates.
- Embed audit trails directly into workflows.
2. Protecting Sensitive Financial Data
Data breaches in finance carry financial, legal, and operational consequences that extend far beyond downtime.
Why is it a challenge?
- Attack surfaces are large and constantly evolving.
- Insider threats and over-permissioned roles often go unnoticed.
- Storage location laws restrict cloud and infrastructure choices.
How to handle it:
- Adopt zero-trust access control from the start.
- Encrypt data across its full lifecycle
- Monitor user behavior and log all access activity.
3. Innovating While Staying Audit-Ready
Fast iteration must still meet strict oversight. Auditors require transparency at every level, particularly in systems driven by AI or automated logic.
Why is it a challenge?
- Machine learning models must provide explainable outputs.
- Every system change requires traceability.
- CI/CD pipelines risk introducing non-compliant changes.
How to handle it:
- Automate compliance checks into your build and deploy stages.
- Store model versions, parameters, and outputs for every update
- Log decision points clearly and consistently.
4. Untangling Legacy Systems
Older systems still run critical operations, but they were not built for today’s integration or scalability demands.
Why is it a challenge?
- Business logic is deeply embedded and poorly documented.
- Rewrites are costly and high-risk.
- Integration points can not handle modern loads.
How to handle it:
- Use APIs to wrap legacy systems instead of replacing them outright.
- Introduce microservices gradually for new features.
- Sync and monitor data across old and new systems with rollback paths.
5. Scaling Without Downtime or Compromise
Financial platforms must scale seamlessly without compromising compliance, data integrity, or user trust.
Why is it a challenge?
- Even short outages can trigger legal or financial consequences.
- Latency impacts transaction integrity and user confidence.
- Failure at one point can cascade across services.
How to handle it:
- Use active-active setups and automated failover.
- Load balance across zones with health checks in place
- Automate backups, replication, and disaster recovery testsAddressing these challenges with reliable solutions ensures your financial software remains secure, scalable, and aligned with industry standards.
How DEVtrust Helps You Ship Reliable, Compliant Financial Software
When you’re dealing with money, compliance, and real-time data, you can’t afford guesswork. DEVtrust acts as your specialist financial software development partner, handling architecture, security, and delivery end-to-end so your team can focus on strategy and growth.
Here’s what working with DEVtrust looks like for you:
- Domain-focused engineering: You work with teams who understand banking, lending, payments, insurance, and investment workflows, not generalists learning finance on the job.
- Compliance built into the architecture: HIPAA (where relevant), GDPR, PCI-DSS, SOC controls, audit trails, and logging are accounted for from the first design decision, not bolted on at the end.
- Secure-by-design systems: We implement zero-trust access, encryption in transit and at rest, secure API gateways, and continuous monitoring to ensure your platform withstands real-world threats.
- Scalable cloud-native infrastructure: Your core systems are designed for high-volume transactions, horizontal scaling, and low-latency performance across regions.
- Clean integrations with financial ecosystems: We build stable connections to core banking systems, payment gateways, KYC/AML providers, open banking APIs, and internal tools without creating brittle dependencies.
- Transparent delivery and handover: You get clear roadmaps, sprint updates, documentation, and knowledge transfer so you’re not locked into a “black box” implementation.
- Long-term partnership, not one-off builds: We stay with you post-launch for enhancements, regulatory updates, performance tuning, and new product lines as your platform grows.
If you need a financial software development company that treats security, compliance, and scale as non-negotiables, DEVtrust is built for exactly that.
Trends and Innovations
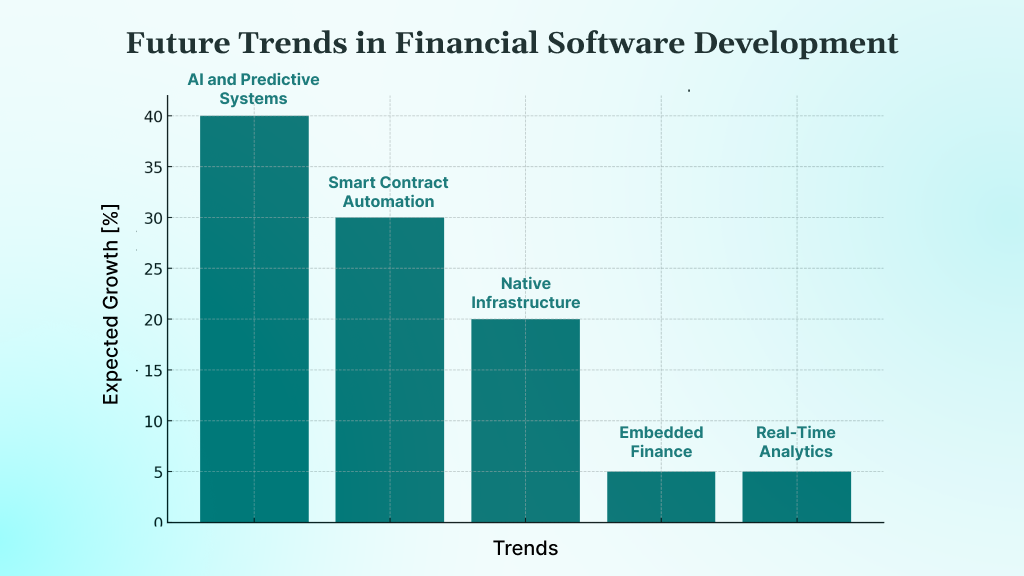
Financial technology continues advancing rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and cloud computing. Here’s a breakdown of the top trends in financial software development:
1. AI and Predictive Systems
AI models now drive fraud detection, credit scoring, and personalized financial experiences at scale. Real-time data processing and machine learning have replaced manual reviews in high-stakes decisions.
- Example: JPMorgan’s AI systems process billions of signals daily to cut fraud and automate document review, freeing up both time and capital.
2. Blockchain and Smart Contract Automation
Distributed ledgers bring transparency and eliminate the need for intermediaries. Use cases span everything from tokenized assets to automated loan agreements.
- Example: Ant Group’s blockchain handles over 100 million daily transactions across cross-border payments and supply chain finance, cutting costs and boosting speed.
3. Cloud-Native Infrastructure
Serverless and container-based architectures support elastic scaling, lower costs, and faster releases, all while meeting strict uptime and compliance standards.
- Example: Capital One runs entirely on AWS, scaling with demand and reducing infrastructure costs by 40%.
4. API-First and Embedded Finance
Open banking and BaaS platforms let fintechs and non-financial players offer regulated financial services through plug-and-play APIs.
- Example: Plaid connects 11,000+ banks to fintech apps, powering billions of secure API calls for apps like Robinhood and Chime.
5. Real-Time Analytics and Event-Driven Systems
Event-based systems allow financial platforms to react instantly to transactions, risks, or user behavior at scale.
- Example: Goldman Sachs processes over 50 billion market signals per day to power algorithmic trades and live risk monitoring.
Your success depends on translating innovation into practical solutions that meet both technical requirements and business objectives.
Conclusion
Building financial software means engineering for precision, scale, and compliance from day one. It is not just a technical challenge – it is a product, security, and regulatory challenge combined.
The companies that get it right are the ones that align product scope with system behaviour, design for audit readiness, and choose architectures that scale without needing to be rebuilt every two years. That’s where the right financial software development company makes the difference.
DEVtrust specialises in software development for financial services, with engineers who understand banking, wealth, payments, and insurance platforms in depth. Every system we deliver is built to perform under real-world load, pass regulatory scrutiny, and evolve with your roadmap, not fight it.
If you are planning a new platform or modernising a legacy system, we can help you move faster with less risk. Contact us today to discuss your financial software development needs and get a clear, actionable path forward.
Build Financial Software You Can Trust
Every transaction, report, and integration must be accurate, secure, and audit-ready. Partner with engineers who understand financial workflows, regulations, and the technical depth needed to ship platforms that scale without breaking.
Talk to a Financial Software Expert