Every growing enterprise runs on multiple systems: ERP, CRM, finance tools, cloud apps, and older software that still handles important work. Over time, these systems stop talking to each other cleanly. Data gets delayed, teams rely on manual updates, and small errors turn into daily operational problems.
As businesses scale faster and add more tools, this disconnect becomes harder to ignore. That’s why enterprise application integration has become a priority. In fact, the global enterprise application integration market is expected to reach $40.56 billion by 2029, showing how widespread this problem has become.
In this blog, we will discuss what enterprise application integration is, how it works, where it’s used, and why it matters for modern enterprises.
Overview
- Enterprise Application Integration enables seamless communication, data flow, and workflow automation across ERP, CRM, legacy, and cloud systems.
- EAI types include data-level, API-based, business process, and event-driven integrations, each suited to specific operational needs.
- Modern EAI architectures range from point-to-point and hub-and-spoke to ESB, API-led, microservices, and event-driven patterns for scalability and flexibility.
- Implementing EAI requires careful consideration of security, compliance, scalability, integration complexity, and long-term maintainability.
- Following best practices such as modular design, standardized APIs, centralized monitoring, and documentation ensures reliable, secure, and adaptable integrations.
What Is Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)?
Enterprise Application Integration is a disciplined integration approach that enables enterprise systems to communicate, coordinate, and execute workflows as a single operational fabric. It focuses on how data moves, how events trigger actions, and how processes span multiple applications without manual intervention.
In practice, EAI ensures that a single business event, such as an order submission, status update, or policy change. automatically propagates across ERP, CRM, finance, inventory, and operations systems in real time or near real time. This requires structured message flows, data mapping, orchestration logic, and error controls.
Now that you understand what EAI is, we can explore the specific challenges it addresses and how it keeps sprawling enterprise systems connected and reliable.
Also Read: Nearshore Software Development in 2026: What It Is and How It Works
What EAI Solves in Complex Enterprise Systems?
Inside complex enterprise environments, EAI solves the problem of system sprawl and operational disconnect. As organizations add ERPs, CRMs, SaaS tools, data platforms, and legacy systems, information flow becomes fragmented and fragile.
EAI addresses this by enabling:
- Consistent data movement across systems without manual exports or re-entry
- Event-driven process continuity, where actions in one application trigger workflows in others
- Controlled integration logic that survives application upgrades and schema changes
- Centralized monitoring and failure handling to detect, retry, and resolve integration issues
- Reduced operational risk by eliminating brittle scripts and unmanaged point connections
The result is a resilient integration layer that keeps enterprise systems aligned as complexity grows. Up next, let’s explore why integrating applications strategically is essential.
Why Enterprise Application Integration is Required for Modern Enterprises?
As enterprises scale, disconnected applications create operational drag, hidden risk, and decision blind spots. EAI acts as a core integration layer that governs how systems exchange data, trigger actions, and stay operationally aligned.
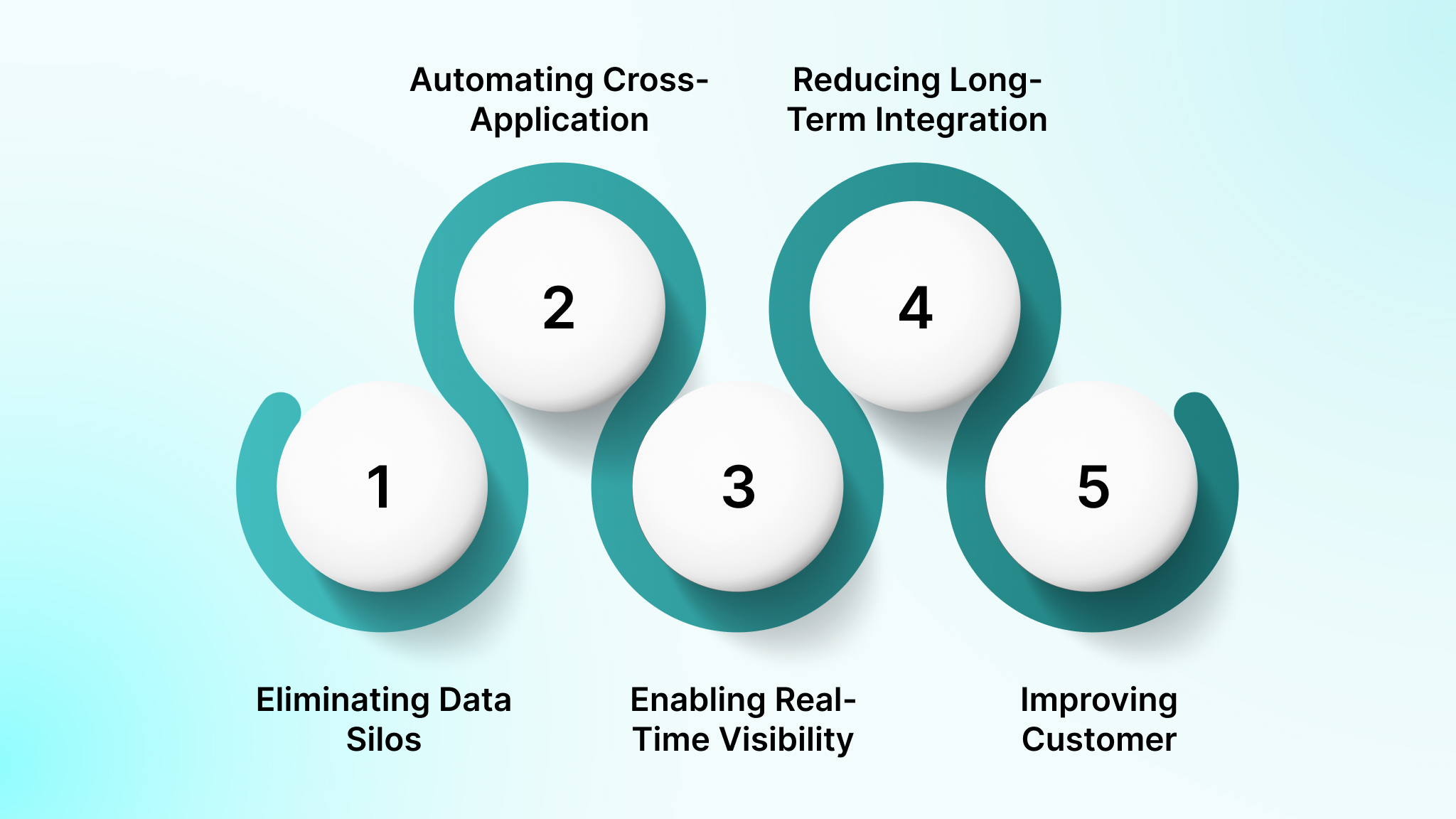
1. Eliminating Data Silos Across Disconnected Systems
EAI synchronizes records across ERP, CRM, finance, and analytics systems using governed data flows. It ensures updates in one system propagate consistently and prevents conflicting reports, duplicate entries, and reconciliation delays.
2. Automating Cross-Application Business Processes
EAI orchestrates multi-step workflows across applications, such as order fulfillment or customer onboarding, by triggering actions automatically between systems. This eliminates manual handoffs, approval bottlenecks, and operational dependency on individual teams.
3. Enabling Real-Time Visibility and Decision-Making
Through event-driven or near-real-time integrations, EAI ensures dashboards, alerts, and forecasts reflect live operational data. It enables leaders to act on current inventory, revenue, and service metrics instead of delayed batch updates.
4. Reducing Long-Term Integration and IT Costs
By replacing custom scripts with reusable integration logic, EAI lowers maintenance overhead, simplifies change management during system upgrades, and reduces the cumulative cost of managing fragmented point-to-point connections.
5. Improving Customer and Employee Experience
EAI ensures consistent data across customer-facing and internal systems, reducing errors, boosting response times, and allowing employees to focus on execution instead of manual reconciliation and system chasing.
Having discussed the benefits, the next step is understanding the different types of EAI and which integration approach suits specific operational needs.
Types of Enterprise Application Integration
Not all integrations serve the same purpose. Enterprises use different EAI types depending on data complexity, process depth, and timing requirements. Before choosing an architecture, it’s important to understand these core integration types.
1. Data-Level Integration
You use data-level integration when your priority is keeping systems aligned, not triggering actions. It moves records between databases on a schedule, which works well for reporting but breaks down when timing matters.
Example: Customer data synced overnight from your CRM into finance and analytics tools for consolidated reporting.
2. Application Interface (API-Based) Integration
API-based integration is what you turn to when systems must talk to each other instantly. One application requests data or validation from another at runtime, allowing EAI to enforce rules, retries, and response handling.
Example: Your billing flow calls an ERP API to confirm tax logic before completing a transaction.
3. Business Process Integration
You choose business process integration when a task spans multiple systems and cannot be reduced to simple data movement. EAI controls the order of steps, decision points, and system dependencies end-to-end.
Example: Onboarding a new hire triggers account creation, payroll setup, compliance checks, and access approvals automatically.
4. Message-Oriented and Event-Driven Integration
Event-driven integration fits when you need systems to react without being tightly coupled. Applications publish events, and downstream systems respond independently, improving resilience and scalability.
Example: An “order placed” event triggers inventory reservation, invoicing, and fulfillment without direct system calls.
Once you know the types, let’s look at practical EAI use cases where integration drives efficiency and keeps enterprise workflows running smoothly.
Common Enterprise Application Integration Use Cases
Modern enterprises manage diverse systems that must share data and workflows seamlessly. In this section, we explore key EAI use cases that drive operational efficiency and integration success.
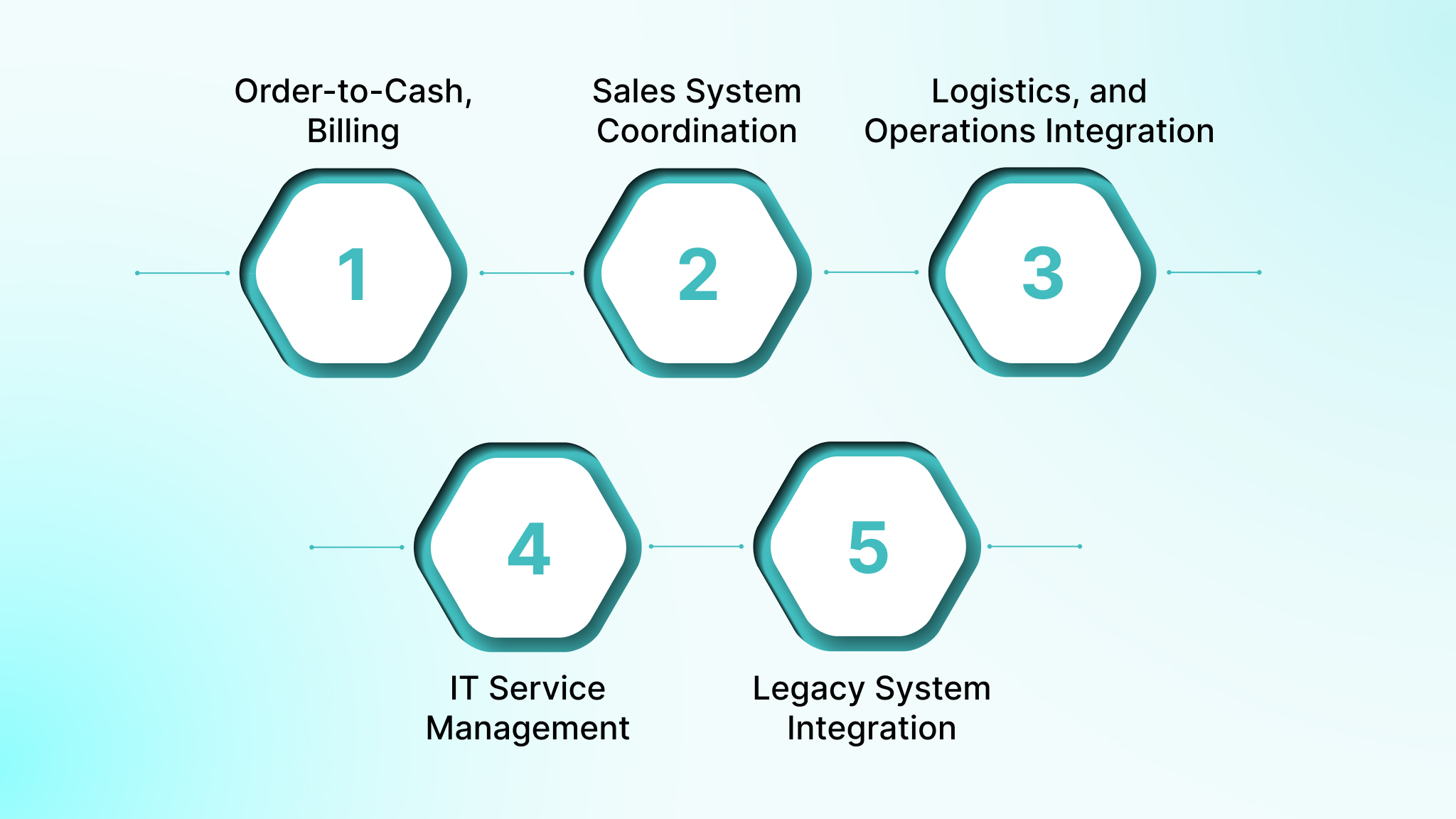
1. Order-to-Cash, Billing, and Financial Workflows
EAI keeps orders, invoices, payments, and accounting entries synchronized across ecommerce platforms, billing systems, ERPs, and finance tools. It prevents revenue leakage and eliminates manual reconciliation between financial systems.
2. Marketing, CRM, and Sales System Coordination
EAI connects marketing automation, CRM, and analytics platforms so lead activity, campaign engagement, and deal updates move seamlessly. This ensures sales teams act on accurate, current customer data.
3. Supply Chain, Logistics, and Operations Integration
Inventory levels, shipment status, supplier updates, and warehouse systems are integrated through EAI to maintain real-time operational alignment and reduce fulfillment delays and stock inaccuracies.
4. IT Service Management and Internal Tooling
EAI automates IT workflows by connecting ticketing systems, asset management, identity platforms, and monitoring tools, enabling faster incident resolution and consistent access control.
5. Legacy System Integration and Modernization
EAI exposes data and functions from legacy systems through controlled interfaces, allowing them to participate in modern workflows without risky, large-scale system replacements.
In practice, a company like DEVtrust helps enterprises implement integrations that simplify workflows. It helped AI-HDR optimize HDR blending and API testing, resulting in integration ease across the tech stack reaching 88%, while overall clarity and consistency across outputs achieved 87%. Check out the full case study here!
With real-world applications in mind, we can now examine the step-by-step mechanics of EAI, from data extraction to workflow orchestration and error handling.
Also Read: Understanding OCR and AI: Differences and Applications
How Enterprise Application Integration Works?
Effective enterprise integration requires a defined sequence that ensures data moves accurately, triggers the right actions, and maintains business continuity across systems. Here’s how EAI orchestrates this.
1. Application Discovery, Data Extraction, and Transformation
This is the first step in connecting systems. It identifies which applications to integrate, extracts the necessary data, and transforms it into a format that downstream systems can understand.
How to do it effectively:
- Inventory all source and target systems to understand data availability.
- Extract relevant records while respecting schema, validation, and data types.
- Transform data formats, units, or structures to match the receiving system.
- Enrich data where necessary (e.g., adding geolocation info to customer addresses).
2. Routing, Orchestration, and Workflow Execution
After the data is ready, it must be sent to the right system in the correct order. Orchestration manages dependencies and ensures workflows execute seamlessly across multiple applications.
How to do it effectively:
- Define routing rules to determine which system receives which data.
- Map out conditional paths and dependencies in workflows.
- Automate multi-step business processes like approvals, notifications, or billing updates.
- Use orchestration engines to coordinate actions across ERP, CRM, and analytics platforms.
3. Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Integration Flows
EAI supports both immediate (synchronous) and delayed (asynchronous) processing depending on business needs, balancing speed with scalability.
How to do it effectively:
- Use synchronous flows where instant feedback is required (e.g., payment validation).
- Employ asynchronous flows for batch updates, reporting, or large datasets.
- Monitor queues and message brokers to ensure data integrity in asynchronous processes.
- Combine both approaches where hybrid workflows require real-time alerts and deferred processing.
4. Error Handling, Monitoring, and Observability
Even with robust integrations, failures happen. A reliable EAI system detects issues quickly and enables fast recovery without disrupting operations.
How to do it effectively:
- Implement retry mechanisms for transient errors.
- Configure alerts for failed integrations or abnormal patterns.
- Maintain detailed logs for auditing and troubleshooting.
- Use dashboards for real-time monitoring of integration health across all connected systems.
After seeing how integrations operate, it’s important to understand the underlying architectures and patterns that make EAI scalable, resilient, and maintainable.
Enterprise Application Integration Architectures and Patterns
Choosing the right architecture is essential for scalable, resilient, and maintainable EAI. It defines how systems communicate, how workflows are orchestrated, and how your integrations adapt as your enterprise grows or changes.
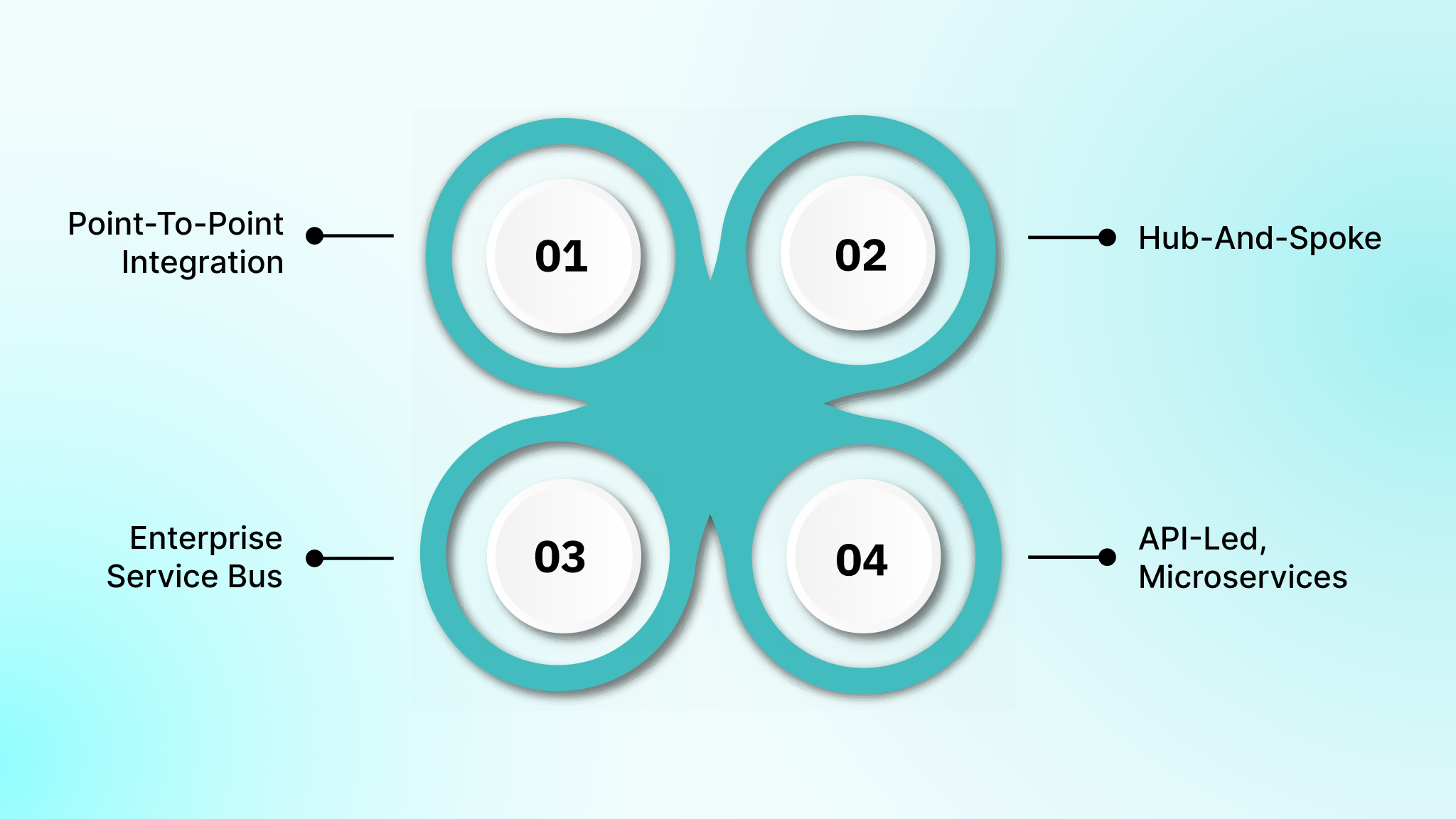
1. Point-to-point integration and its scaling limits
You connect applications through direct, one-to-one links, where each system communicates independently with another. This approach is simple to implement initially, but becomes difficult to maintain as systems increase, creating tight coupling and higher operational overhead.
2. Hub-and-spoke and broker-based architectures
A central hub manages all communication between applications, reducing connection complexity. It enables standardized data routing, conditional workflows, governance enforcement, and monitoring, offering a structured approach for growing enterprises with multiple interdependent systems.
3. Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architecture
ESBs standardize messaging, transformation, and routing across systems. They are ideal for complex enterprise integrations, providing centralized control, protocol translation, and operational monitoring, though disciplined governance is essential to prevent bottlenecks and maintain efficiency.
4. API-led, microservices, and event-driven integration
Modern enterprises use APIs, microservices, and event-driven models for decoupled, real-time integrations. This approach supports cloud-native environments, scalable workflows, and flexible adaptation of business processes without disrupting critical operations or legacy systems.
Having reviewed architectures, let’s clarify how EAI compares to related technologies like ESB, iPaaS, ERP, and EDI, and when each approach fits.
EAI vs ESB vs iPaaS vs ERP vs EDI: Learn the Difference
Enterprises often use multiple integration and automation technologies, but each serves a distinct purpose. Understanding their differences helps you design a cohesive integration strategy that avoids redundancy and maximizes efficiency:
| Technology | Primary Role | Scope | Examples | Key Difference |
| EAI | Strategy for connecting enterprise systems | Internal and cross-application workflows | Syncing CRM, ERP, and analytics for order-to-cash automation | Defines integration logic and orchestration, not a product |
| ESB | Middleware for standardized messaging and routing | Centralized communication hub | Routing invoices from ERP to billing, CRM, and warehouse | Provides the architecture and tools to implement EAI efficiently |
| iPaaS | Managed integration platform | Cloud-based, multi-system integrations | Connecting SaaS apps like Salesforce, Shopify, and HubSpot | Acts as a delivery layer for EAI; simplifies implementation |
| ERP | Internal process standardization | Enterprise-wide operational systems | SAP or Oracle ERP managing finance and HR | Focused on internal workflows, EAI extends ERP to other systems |
| EDI | Standardized B2B document exchange | Trading partners, suppliers, vendors | Sending purchase orders or invoices between companies | Handles external document exchange, EAI manages internal coordination |
Once you know the difference, it’s time to understand the challenges enterprises face when implementing EAI, from compliance to scalability and system complexity.
Key Challenges in Enterprise Application Integration
Even well-planned EAI initiatives face hurdles in complex US enterprises, where multiple systems, regulations, and high-volume operations create risks. Let’s understand these challenges now.
1. Security, Identity, and Compliance Challenges
Integrating systems exposes sensitive data to potential breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse. US regulations like HIPAA, SOX, GLBA, and CCPA add strict compliance requirements, making secure identity management, encryption, and auditing essential yet challenging to enforce consistently across platforms.
2. Scalability and Performance Challenges
Handling peak transaction volumes across multiple applications can overwhelm integration layers. Without careful design, latency, processing bottlenecks, and system failures occur, especially in real-time workflows, high-frequency transactions, and enterprise-scale cloud or hybrid deployments.
3. Integration Complexity and Long-Term Maintainability
Diverse systems, APIs, data formats, and legacy applications increase integration fragility. Updates or workflow changes can break multiple connections simultaneously, causing cascading failures. Maintaining these integrations over the years demands extensive documentation, standards, and governance.
4. Cost, Tooling, and Team Expertise Challenges
Limited budgets, suboptimal or incompatible integration tools, and a shortage of skilled US-based developers or architects can delay EAI deployments. It can also escalate maintenance costs and risk the sustainability of complex, enterprise-wide integration initiatives.
To solve these common obstacles, you must focus on proven best practices to design, govern, and maintain integrations that remain reliable and secure over time.
Also Read: Online Payment Gateway Integration: A Step-by-Step Guide for 2026
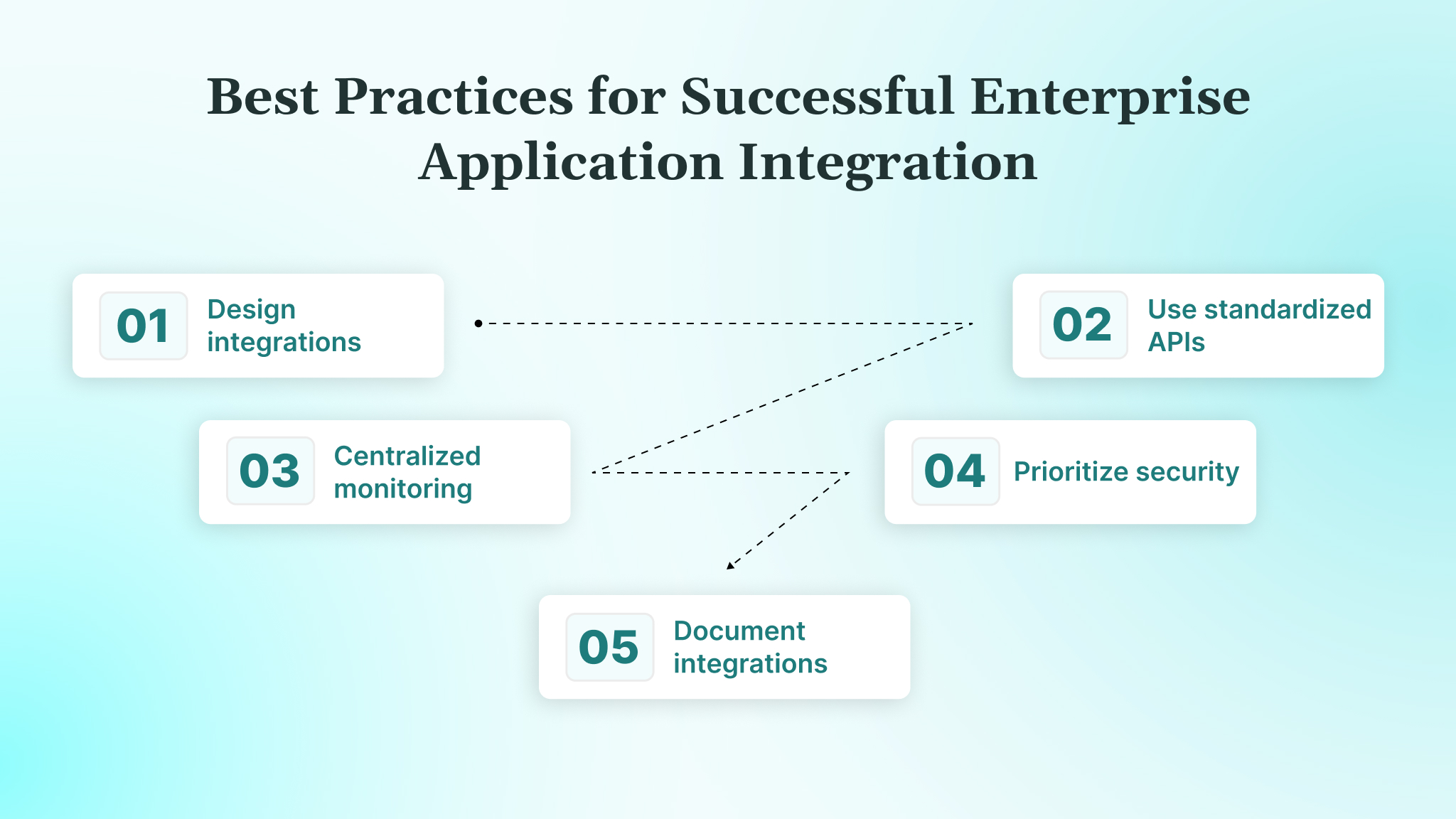
Best Practices for Successful Enterprise Application Integration
Effective EAI programs succeed when designed proactively, considering scale, compliance, and maintainability. Following these practices ensures integrations remain reliable, secure, and adaptable across evolving enterprise systems.
- Design integrations with scalability and change in mind: Plan for growing data volumes, new applications, and growing business processes using loosely coupled, modular integration patterns.
- Use standardized APIs and data models: Adopt consistent schemas and REST/GraphQL APIs to reduce transformation errors, simplify maintenance, and ensure interoperability across systems.
- Implement centralized monitoring and governance: Use dashboards, alerts, and logs to track integration health, detect failures early, and maintain operational visibility across all systems.
- Prioritize security, access control, and compliance: Enforce encryption, role-based access, and US regulations like HIPAA, SOX, and CCPA within integration workflows, not as an afterthought.
- Document integrations and plan for long-term ownership: Maintain versioned documentation, clear ownership, and governance processes to ensure continuity as teams, applications, and workflows scale.
With a framework of practices established, here’s how DEVtrust applies these principles to help enterprises implement secure, scalable, and AI-enhanced integrations across systems.
How DEVtrust Supports Enterprise Application Integration?
Enterprises often struggle with brittle integrations, inconsistent data flows, and the complexity of connecting ERPs, CRM tools, legacy systems, and cloud platforms in a secure, scalable way. These challenges impact real-time decision-making, compliance, and operational reliability.
DEVtrust helps enterprises implement robust integration strategies by combining secure API design, modular architectures, comprehensive testing, and cloud‑ready systems. Together, they help enable reliable data exchange and process coordination across systems.
Here’s what our offering includes:
- Custom API Development & Integration: Design and build REST/GraphQL APIs that connect core systems, third‑party services, and data stores with clean, documented interfaces.
- Modular, Scalable Architecture: Develop enterprise software with integration‑ready architecture, enabling smooth data flows between ERP, CRM, legacy, and cloud environments.
- Integration & System Testing: Validate API interactions, message flows, and microservice integrations using automated test suites embedded in CI/CD pipelines.
- Cloud Application & Migration Support: Migrate or build cloud‑native systems that scale securely with your enterprise workloads and maintain consistent data exchange.
- AI‑Enhanced Workflow Automation: Integrate AI models and agents to enrich data processing, contextual insights, and adaptive workflows where applicable.
With DEVtrust’s structured integration‑aware engineering approach, enterprises can unify data flows, reduce fragmentation, and increase confidence in end‑to‑end process orchestration across diverse applications.
Conclusion
Effective enterprise application integration connects disparate systems, eliminates data silos, automates workflows, and ensures real-time visibility. By using architectures like ESB, API-led, and microservices, organizations can simplify processes, reduce errors, and modernize legacy systems.
DEVtrust helps enterprises implement these integrations securely and at scale. With API-first design, modular architecture, AI-enhanced orchestration, and centralized monitoring, your applications communicate reliably, processes run smoothly, and data remains consistent across all platforms.
Book a demo with us to know how DEVtrust can help you unify systems, automate workflows, and achieve end-to-end operational efficiency.