Most e-commerce businesses still rely on mobile websites that underperform in terms of engagement and conversion. They struggle to retain users, collect actionable data, or communicate directly as third-party tracking becomes less effective.
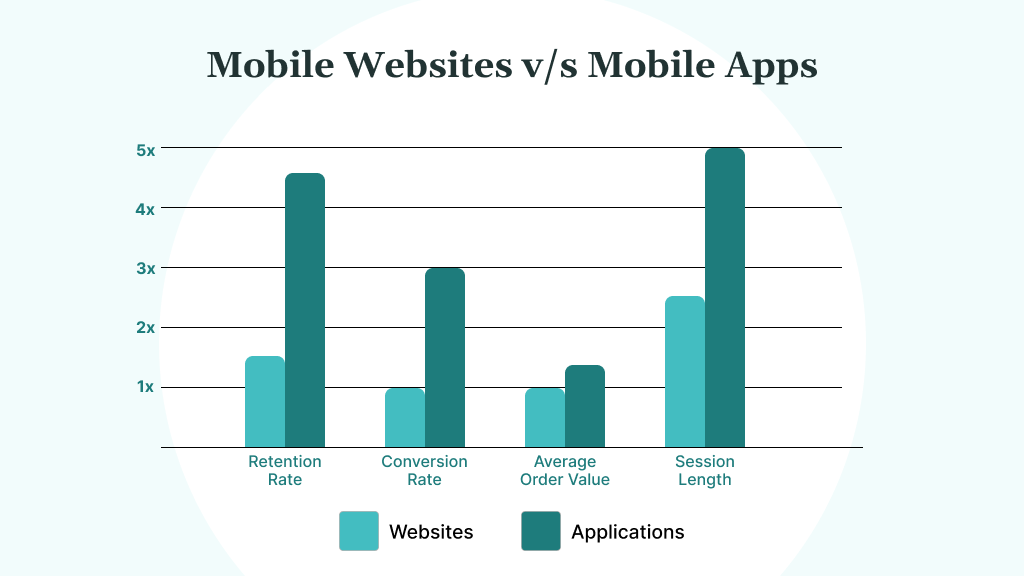
E-commerce mobile apps solve these challenges. They offer higher conversion rates, enable the collection of first-party data, and facilitate direct communication through push notifications. More importantly, they help build long-term customer relationships that drive repeat purchases and brand advocacy.
This guide covers every stage of e-commerce mobile app development, from market research and platform selection to launch, optimization, and scaling. It also outlines common pitfalls to avoid, highlights key features that impact revenue, and provides guidance on staying on track with your budget and timeline.
Key Takeaways
- Mobile apps typically achieve higher retention, conversion rates, and customer loyalty compared to mobile websites, mainly due to their enhanced capabilities and user engagement features.
- MVPs should focus on solving real user problems with minimal features that work well.
- Building in-house slows you down when speed and experience are non-negotiable.
- Testing, performance, and post-launch support are critical for long-term app success.
- Choosing the right tech stack and partner upfront prevents costly rebuilds later.
What is an E-commerce Mobile App?
An e-commerce mobile app is a shopping platform built specifically for smartphones and tablets. It allows users to browse products, make purchases, track orders, and receive updates, all within a dedicated app installed on their devices.
These apps perform faster and offer enhanced functionality compared to mobile websites by storing data locally, reducing loading times, and supporting features such as push notifications, camera use, and offline browsing, which results in higher user conversion rates.
The use case depends on the business model. For B2C brands, mobile apps facilitate interactive and personalized shopping experiences. For example, Nike’s SNKRS app releases limited-edition sneakers, while Sephora utilizes virtual try-on features to boost engagement. On the B2B side, Alibaba’s app helps retailers place bulk orders with custom pricing and account-level tools.
This shift toward mobile-first experiences reflects a change in user behavior. Shoppers who use apps tend to make more purchases, and they are more loyal, spending most of their mobile time within apps rather than browsers.
Why Should Your Business Invest in Mobile Apps Right Now?
If digital growth is a priority and your customer experience still relies on a mobile site or third-party platforms, you are falling behind. Mobile usage continues to evolve, particularly as Gen Z, comprising 40% of global consumers, expects mobile-first experiences by default. They grew up with smartphones, and brands that do not offer app-level speed, personalization, and control are already losing ground.
The question is not “Do apps perform better?” They do. The real question is: What specific signs in your business performance indicate it is time to build one?
Here are a few scenarios worth paying attention to:
- Users visit your store but rarely return. If repeat traffic or purchase frequency is dropping, it is likely that you lack a direct retention channel that keeps your brand top of mind between purchases.
- You are reaching the limits of third-party platforms. Depending solely on marketplaces or paid ads for growth means you do not fully own your customer journey or your margins.
- Your roadmap includes features that browsers can not support well. If your vision includes features such as subscription logic, offline use, reward systems, or custom product flows, these require a native app infrastructure.
If any of this reflects your current challenges, building an app becomes less about future readiness and more about solving what is already holding your growth back.
What Are the Latest Trends Shaping Mobile Commerce?
Practical shifts in user behavior, platform capabilities, and business demand will drive mobile commerce in 2025. Knowledge of these trends will help you build a stronger e-commerce mobile app and align it with what drives growth. Here is what is shaping the e-commerce market right now:
AI-Powered Personalization
Modern AI systems now analyze micro-behaviors, such as scroll speed, tap patterns, and time spent viewing specific product angles. Take Sephora’s new AI assistant integration, which creates personalized makeup tutorials based on your skin tone and preferred looks. Harvard Business Review reports that personalization can boost marketing ROI by as much as five to eight times when executed effectively.
Augmented Reality
AR features enable users to visualize products in their real-world environment using their phone’s camera. This feature started as a novelty but is now becoming a core part of many e-commerce mobile apps. A strong example is IKEA’s AR tool, which enables users to automatically measure spaces and generate complete room layouts directly on their phones. Beauty brands have also adopted virtual try-ons, resulting in fewer returns.
Voice Commerce
Voice ordering via mobile apps is growing annually, driven by the hands-free convenience it offers users during commutes and while multitasking. Companies like Domino’s are benefitting from this immensely. Its voice ordering system now supports complex customizations and recalls past orders, streamlining the entire experience.
Social Commerce
Social commerce is an emerging trend that has topped the charts over the past few years, and it is still gaining ground. It merges online shopping with social media, allowing users to discover, review, and purchase products without leaving platforms like Instagram or TikTok. Live-stream shopping events, where influencers showcase products in real-time, are now delivering 10x higher conversion rates than standard social posts.
Omnichannel
Omnichannel retail connects online and offline touchpoints to deliver a consistent customer experience across every interaction, app, website, or physical store. The trend has now moved past basic integration toward full unification. For example, Target’s app shows real-time inventory at nearby locations, supports mobile checkout in-store, and enables same-day returns for online orders. This consistent approach will lead to an increase in customer satisfaction and a reduction in support costs.
Which Type of E-commerce App Fits Your Business Model?
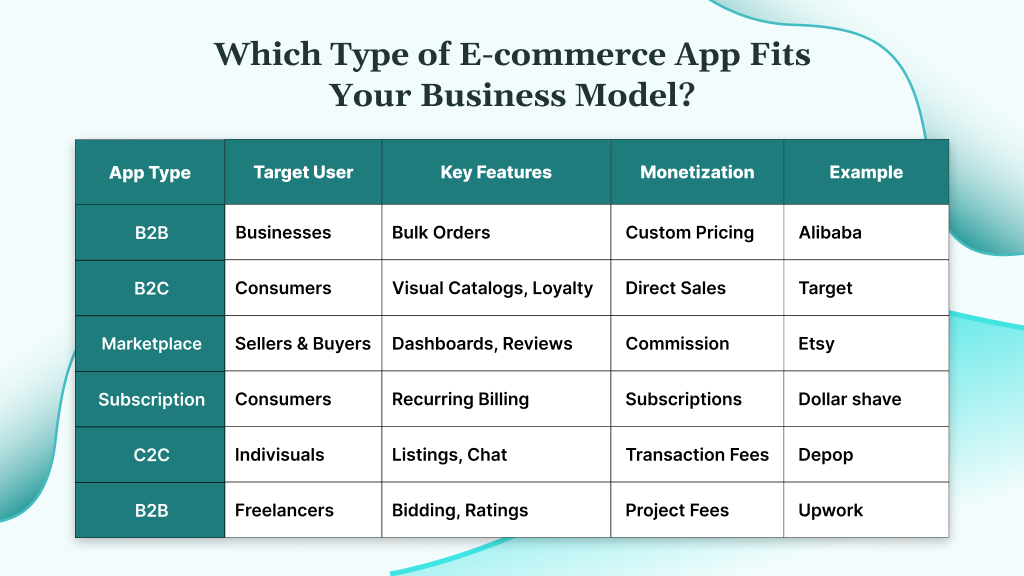
Your app category determines user expectations, technical requirements, and revenue models. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about features, design, and development approaches.
B2B Commerce Apps
B2B apps serve business customers with complex purchasing needs and approval processes. It includes features such as:
- Custom pricing tiers based on order volume and customer relationships
- Bulk ordering capabilities with quantity breaks and wholesale pricing
- Account management features for multiple users within organizations
- Integration requirements with ERP systems and procurement workflows
- Approval workflows for purchase orders and budget management
Example: Alibaba’s wholesale app enables manufacturers to sell directly to retailers with custom catalogs and negotiated pricing.
B2C Retail Apps
B2C apps focus on individual consumers with an emphasis on discovery and impulse purchases. Below are some examples of what it entails:
- Visual product catalogs with high-quality images and videos
- Personal recommendation engines based on browsing and purchase history
- Wishlist and favorites functionality for future purchases
- Social features like reviews, ratings, and product sharing
- Loyalty programs with points, rewards, and exclusive access
Example: Target’s app combines inventory checking, store maps, and exclusive mobile deals to drive both online and in-store purchases.
Multi-Vendor Marketplace Apps
Marketplace apps connect multiple sellers with buyers, requiring complex vendor management systems.
- Vendor dashboard for product management and sales analytics
- Commission and payout systems for seller compensation
- Review and rating systems for both buyers and sellers
- Dispute resolution mechanisms for transaction issues
- Advanced search and filtering across diverse product catalogs
Example: Etsy’s marketplace app enables independent sellers to reach global audiences while providing buyers with unique, handcrafted products.
Subscription E-commerce Apps
Subscription apps focus on recurring relationships with automated billing and delivery.
- Subscription management with pause, skip, and modification options
- Automated billing and renewal with payment failure handling
- Member-exclusive content and pricing tiers
- Delivery scheduling and frequency customization
- Retention features like loyalty rewards and referral programs
Example: Dollar Shave Club’s subscription app manages recurring deliveries while providing member-exclusive content and product customization.
C2C Commerce Apps
Consumer-to-consumer apps enable individuals to sell directly to other consumers.
- User verification systems for buyer and seller trust
- Listing management tools for product photos and descriptions
- Messaging systems for buyer-seller communication
- Payment protection for secure transactions
- Shipping integration with label printing and tracking
Example: Depop combines social media features with peer-to-peer selling, targeting Gen Z consumers who value unique, vintage items.
C2B Commerce Apps
Consumer-to-business apps allow individuals to sell services or products to companies.
- Profile and portfolio management for service providers
- Project bidding systems for competitive pricing
- Skill verification and rating systems
- Payment processing for project-based work
- Communication tools for client collaboration
Example: Upwork’s mobile app enables freelancers to find projects, communicate with clients, and manage their business relationships on the go.
What Should You Consider Before Starting Development?
Business objectives must align with technical decisions from day one. Define whether you are prioritizing customer acquisition, increasing purchase frequency, or expanding into new markets. These goals influence everything from feature prioritization to technology selection.
- Product Goals: Define what success looks like, user growth, revenue per user, and market expansion. Your goals drive core feature sets, user flows, and monetization models.
- Budget Planning: Go beyond development costs. Account for hosting, third-party services, compliance, app store fees, and ongoing maintenance. Set aside 15–20% of the build cost annually for updates and support.
- Team Capabilities: Assess internal bandwidth and expertise. Can your in-house team deliver on time? If not, external partners or dedicated teams may offer better speed and predictability.
- Scalability Readiness: Plan for user and data growth from the start. Architecture decisions should accommodate future catalog size, traffic spikes, and regional rollouts without expensive rework.
- Compliance and Security: Understand regulatory obligations early, PCI-DSS for payments, GDPR, or CCPA for data, and accessibility standards. Building with these in mind avoids legal risk and late-stage changes.
How Do You Develop an E-commerce Mobile Application: Step-by-Step?
This eight-step process transforms your concept into a market-ready application. Each step builds upon the previous one, creating a systematic approach that minimizes risks and maximizes success probability.
Step 1: Validate Your Idea and Goals
Market research prevents expensive mistakes by confirming demand before development begins. Conduct user interviews with potential customers to understand their pain points and shopping behaviors. Analyze competitor apps to identify gaps your solution can address.
Competitive analysis reveals market opportunities and threats. Study app store ratings, user reviews, and feature comparisons to understand what works and what does not. Look for consistent complaints about existing solutions that your app can solve better.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) provide measurable success criteria. Track metrics such as
- Customer acquisition cost
- Lifetime value
- Retention rates
- Conversion percentages.
The above metrics will guide your development decisions and measure progress toward business objectives. Moreover, user persona development creates clarity about your target audience. Define demographics, shopping behaviors, pain points, and preferences for your primary users. All this clarity will influence design decisions, feature prioritization, and marketing strategies.
Step 2: Choose the Right Platform and Technology Stack
Platform selection impacts development costs, user reach, and maintenance complexity. iOS users typically spend more per transaction, while Android provides a broader global reach. Cross-platform frameworks like React Native or Flutter reduce development costs while reaching both audiences.
Backend technology selection should support your growth plans rather than current trends. For example:
- Node.js excels in real-time features
- Python offers machine-learning capabilities
- NET provides enterprise-grade security.
Choose based on your specific requirements and team expertise. Another important factor is Integration planning, which ensures your app connects with existing business systems. Consider connections to inventory management, customer relationship management, and enterprise resource planning systems. Poor integration planning often requires expensive rebuilds later.
Third-party service evaluation covers payment processing, analytics, push notifications, and crash reporting. Select established providers with strong documentation and reliable uptime.
Step 3: Define Core Features and Plan Your MVP
Essential features form your app’s foundation and must work flawlessly before adding enhancements. Include user registration, product browsing, shopping cart functionality, secure checkout, and order management. These core features determine user satisfaction and app ratings.
Feature prioritization balances user needs with development resources. Use frameworks like MoSCoW (Must have, Should have, Could have) to categorize features. Focus on high-impact, low-complexity features for the initial release.
List of Game-Changing Features
Next-generation features create competitive advantages and drive user engagement beyond basic commerce functionality.
- Gamified Shopping Experiences incorporate challenges, achievements, and social competition. Users earn points for reviews, referrals, and purchase milestones. Gaming elements increase session duration by 67% and customer retention by 89%.
- Sustainability Scoring appeals to environmentally conscious consumers by rating products based on carbon footprint, ethical sourcing, and recyclability. Gen Z consumers pay 15% more for sustainable products, making this feature valuable for premium positioning.
- Virtual Personal Shopper uses AI to provide personalized recommendations based on budget, style preferences, and upcoming events. This feature increases average order value by 127% while improving customer satisfaction scores.
- Social Proof Integration displays real-time purchase activity, friend recommendations, and location-based popularity. Features like “3 people in your area bought this today” increase conversion rates by 34%.
Step 4: Design UI/UX for Maximum Conversion
Create a visual hierarchy that guides users toward purchase decisions through the strategic use of colors, typography, and spacing. Product images should dominate screens while maintaining clear navigation paths.
User experience optimization reduces friction at every step. Minimize the number of taps required for common actions, enable guest checkout options, and provide clear error messages. Every additional step in the purchase process increases abandonment rates.
Mobile-first design principles account for smaller screens and touch interactions. Design for thumb-friendly navigation, readable text sizes, and accessible color contrasts. Test designs on various device sizes to ensure a consistent user experience.
Performance optimization ensures fast loading times and smooth interactions. Optimize images, implement lazy loading, and minimize API calls. Users abandon apps that take more than 3 seconds to load, making performance a critical conversion factor.
Step 5: Develop Your MVP Using Agile Methodology
Agile development uses iterative sprints to deliver working software incrementally. Two-week sprints enable the incorporation of rapid feedback and facilitate course corrections. This approach reduces risks and improves final product quality through continuous refinement.
Sprint planning involves breaking features into manageable tasks and estimating completion times. Include buffer time for testing, bug fixes, and unexpected complications. Regular sprint reviews ensure alignment between development progress and business objectives.
Stakeholder involvement throughout development prevents miscommunication and scope creep. Schedule regular demonstrations of working features and gather feedback from potential users. This involvement ensures the final product meets market expectations.
Quality assurance testing occurs throughout development rather than only at the end. Test each feature as it is completed to identify issues early when they are less expensive to fix. Automated testing catches regressions and ensures consistent quality.
Step 6: Build Scalable Backend Architecture
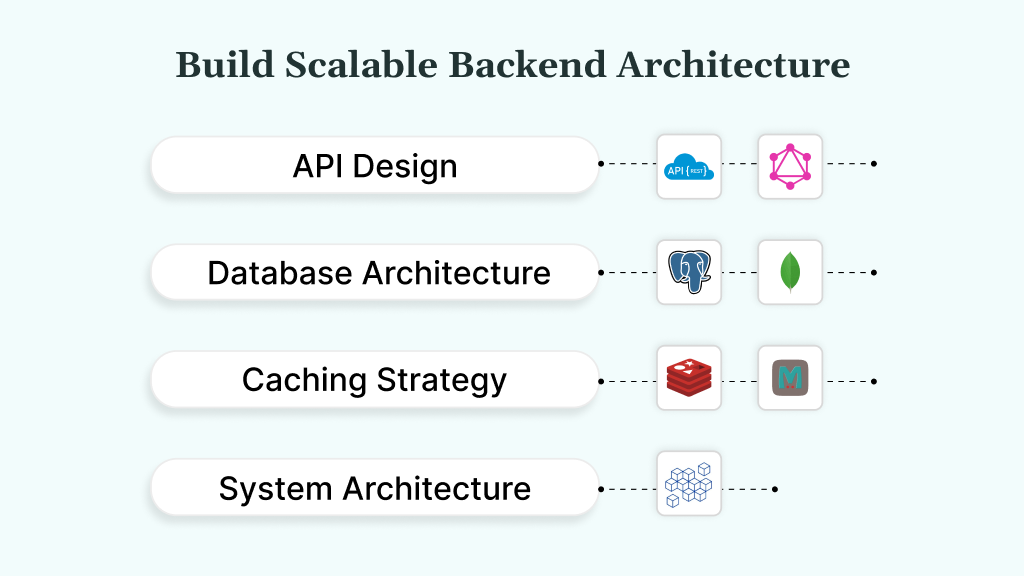
A strong backend ensures your app performs reliably as users and data grow. From APIs to databases and architecture patterns, every choice should support long-term scalability without overengineering upfront. Here is what to focus on:
1. API Design and Communication
- Choose the right API approach for your app. REST is a standard protocol using predictable endpoints, best for straightforward data flows. GraphQL is a query language that lets clients request only the data they need.
- Use REST when building fast with standard endpoints. Choose GraphQL for complex, client-driven apps where bandwidth optimization matters.
2. Database Architecture
- Build a schema that can support long-term growth, including an increase in users, products, and transactions. Avoid hardcoded structures or designs that break under scale.
- Use relational databases, such as PostgreSQL, for structured data and strong consistency, or MongoDB if you need schema flexibility for evolving product types.
3. Caching Strategy
- Caching improves performance by storing frequently accessed data in memory.
- Tools like Redis (an in-memory key-value store) and Memcached (a lightweight caching layer) help reduce direct database hits.
- Use Redis for session data, product lists, and user preferences. Set TTL (time-to-live) to balance freshness with speed.
4. System Architecture: Monolith vs Microservices
- A monolithic architecture packages all services in one deployable unit, ideal for early-stage builds with tight timelines.
- Microservices separate services into independent modules that can scale and deploy individually, best used once specific parts of your system (e.g., checkout, search) outgrow the monolith.
- Start monolithic to reduce initial complexity. Move to microservices gradually as you identify performance bottlenecks.
Step 7: Implement Secure Payment Processing
Payment gateway selection affects user experience and transaction costs. Below are some non-negotiable details to cover:
- Choose the Right Payment Gateway: Pick a gateway that fits your market and scale. Stripe works well for global apps, while tools like Razorpay are better suited for specific regions.
- Support Multiple Payment Methods: Offer cards, wallets, UPI, and BNPL to reduce cart abandonment and meet user preferences.
- Prioritize Security Basics: Use encryption, tokenization, and secure login flows to protect sensitive data and avoid trust issues.
- Understand Compliance Requirements: Be aware of key regulations like PCI DSS and GDPR. Handling payments comes with legal obligations, so plan for them early.
- Add Basic Fraud Protection: Use built-in tools or service provider features to block suspicious transactions and reduce chargebacks.
Step 8: Test, Optimize, and Launch
Before launch, your app needs to be stable, fast, secure, and user-friendly. Testing and validation ensure you catch critical issues early and deliver a polished experience.
- Start with Comprehensive Testing: Cover all key areas, functionality, performance, security, and usability. Use both automated tests (to catch regressions quickly) and manual testing (to surface UX issues that automation misses). Run tests across devices, OS versions, and network types to uncover edge-case bugs.
- Validate Performance Under Load: Run load testing to simulate peak traffic and stress conditions. This helps identify bottlenecks and fix them before launch, preventing downtime, crashes, or slow response times that frustrate users and hurt retention.
- Run a Targeted Beta Test: Internal QA can not catch everything. Open your app to a small group of real users from your target market. Observe how they interact, where they hesitate, and what breaks their stride. These insights often reveal usability gaps you may have overlooked.
- Plan Launch Logistics in Parallel: While testing wraps up, Study app ratings, user reviews, and feature comparisons to identify effective features and consistent complaints that your app can address.
Planning to build your app? This is the right time to bring in experienced hands. Book a call, share your idea, and get clear insights on what will work, what will not, and how to move forward with a practical development roadmap.
What Challenges Will You Face During Development?
Some common obstacles might be a hindrance while you are building an e-commerce mobile app, and knowing them in advance will allow you to stay one step ahead of your competitors. We have compiled a list of challenges and tips on how you can overcome them below:
Unclear Scope and Expanding Requirements
We have seen apps stall for months because priorities kept shifting. Teams kept adding new features mid-sprint without adjusting timelines, which delayed core functionality and caused friction between stakeholders.
- How to solve: Finalize the scope early and document it well. Use user stories to define what matters and apply prioritization frameworks like MoSCoW to stay focused. Add new features only after assessing the impact on delivery.
Backend Performance Bottlenecks Under Load
Apps that functioned well in staging crashed under real user traffic post-launch. Poor API design and unoptimized databases led to timeouts, slow load times, and abandoned sessions, especially during promotions or peak hours.
- How to solve: Design with scale in mind. Use efficient data models, implement caching early, and simulate real-world usage with load tests before going live.
Security and Compliance Gaps
The problem arises when businesses launch quickly but tend to overlook security layers. Weak encryption and unverified user flows exposed customer data, leading to urgent fixes, lost trust, and, in one case, temporary removal from the app store.
- How to solve: Build security into your development cycle from day one. Use proven frameworks, apply encryption standards, and conduct regular audits. Stay ahead of compliance requirements like PCI DSS and GDPR to avoid penalties.
Third-Party Integration Failures
Several projects hit setbacks because payment or shipping APIs failed unexpectedly or changed specs mid-development. In one case, an app’s checkout flow broke during a high-volume sale because the gateway integration lacked fallback logic.
- How to solve: Choose service providers with stable APIs and strong documentation. Build modular integration layers, handle failures gracefully, and test what happens when third-party services go down.
Inconsistent Experience Across Platforms
Apps that looked polished on Android often felt off on iOS, with mismatched layouts, broken navigation, or missing behaviors. These inconsistencies led to negative reviews and increased support tickets from confused users.
- How to solve: Build from a shared design system and test early on real devices. Respect native UX patterns and ensure parity between platforms without forcing one-size-fits-all layouts.
Incomplete Testing Before Launch
Most of the time, startups push to launch under pressure and skip proper QA. The result: critical bugs in production, poor app store ratings, and immediate churn. Fixing post-launch costs more than preventing issues upfront.
- How to solve: Plan testing as a core phase, not a checkbox. Combine automated tests with real-user scenarios. Run user acceptance testing (UAT) and block releases with unresolved critical bugs.
No Post-Launch Support Plan
Some apps get launched and then left behind. Without a plan for updates or bug fixes, users drop off, ratings fall, and the product slowly dies. One team came back a year later, only to find they needed a full rebuild.
- How to solve: Budget for maintenance and feature evolution. Set performance benchmarks, collect user feedback, and schedule regular updates to keep the app aligned with expectations.
Should You Build In-House or Partner with Experts?
The development approach you choose significantly impacts your project’s timeline, quality, and long-term success. Planning to build an e-commerce mobile app in 2025 is a bold move and a necessary one if your business wants to keep pace with evolving consumer demands. But developing something from the ground up means juggling tight timelines, complex tech decisions, and the pressure to launch with zero room for failure.
On paper, building in-house gives you more control, but in practice, it often costs you momentum. Hiring takes months. You will need to build workflows, align teams, and manage a learning curve that slows you down at the exact moment the speed matters most.
For CTOs and PMs in growing companies, the real question is not Can you build internally, It is Should you?
In this scenario, partnering with a team that has already solved the challenges you are about to face often proves faster, cleaner, and more cost-efficient. So, what are the pros of partnering? Let us have a look:
- Execution-ready teams: You get immediate access to vetted engineers, designers, and PMs with deep experience in e-commerce and mobile.
- Faster delivery: Ready to launch production-grade apps in less time, including architecture, design, QA, and integrations.
- Predictable outcomes: Proven workflows, cross-industry experience, and real-time collaboration keep progress transparent and on schedule.
- Shared responsibility: Risk is distributed, and the team will bring solutions to known scaling, performance, and security challenges.
And if you choose to partner, the next decision is even more critical: how do you find a team that understands both your product vision and the business outcomes behind it? Let us jump on.
How Do You Choose the Right Development Partner?
Technical expertise alone does not guarantee project success. Look for partners who understand business strategy, user experience design, and industry-specific challenges. The best partners act as strategic advisors, not just implementers.
At DEVtrust, we are a team of deeply experienced engineers, designers, and strategists who build for outcomes. Our services span full-cycle product development, from backend architecture to mobile apps, SaaS platforms, APIs, and integrations. We have delivered solutions for clients across FinTech, HealthTech, Real Estate, EdTech, and more, always aligning our execution with your business objectives, not just the tech stack.
We focus on results that are measurable, scalable, and guaranteed through our delivery standards. When companies work with DEVtrust, they gain a partner invested in long-term success.
Take TAPPIT, for example, a SaaS platform that helps small and mid-size businesses launch branded mobile apps to automate operations and simplify customer interactions. DEVtrust built the platform end-to-end, enabling clients to launch fast, serve better, and grow without technical bottlenecks.
Are you still concerned about choosing the wrong development approach? Schedule a strategy session with DEVtrust to explore your options and receive expert guidance on the best path forward for your specific situation.
Conclusion
Mobile commerce continues to reshape how businesses reach customers and generate revenue. Apps provide superior user experiences, higher conversion rates, and stronger customer relationships compared to traditional web platforms. Companies that invest strategically in e-commerce mobile app development will capture a disproportionate market share as consumer behaviors continue evolving.
Success requires more than technical execution; you need partners who understand the intersection of technology, user experience, and business strategy. Focus on partners who understand your industry, have proven track records, and can provide ongoing support after launch. The decisions you make now will impact your business for years to come.
DEVtrust specializes in handling exactly these kinds of requirements. Share your goals, and we will deliver. If you are still on the fence about building your e-commerce mobile app, you are already falling behind. The market is moving fast, and your competitors are not waiting.
It is now or never.
Get on a call with us today and take the first step toward launching an app that drives real results.
Ecommerce Mobile App Development Guide and Steps
Drive sales with an ecommerce mobile app! Conduct market research, define goals, and design intuitive UI. Start development now!
Contact Us