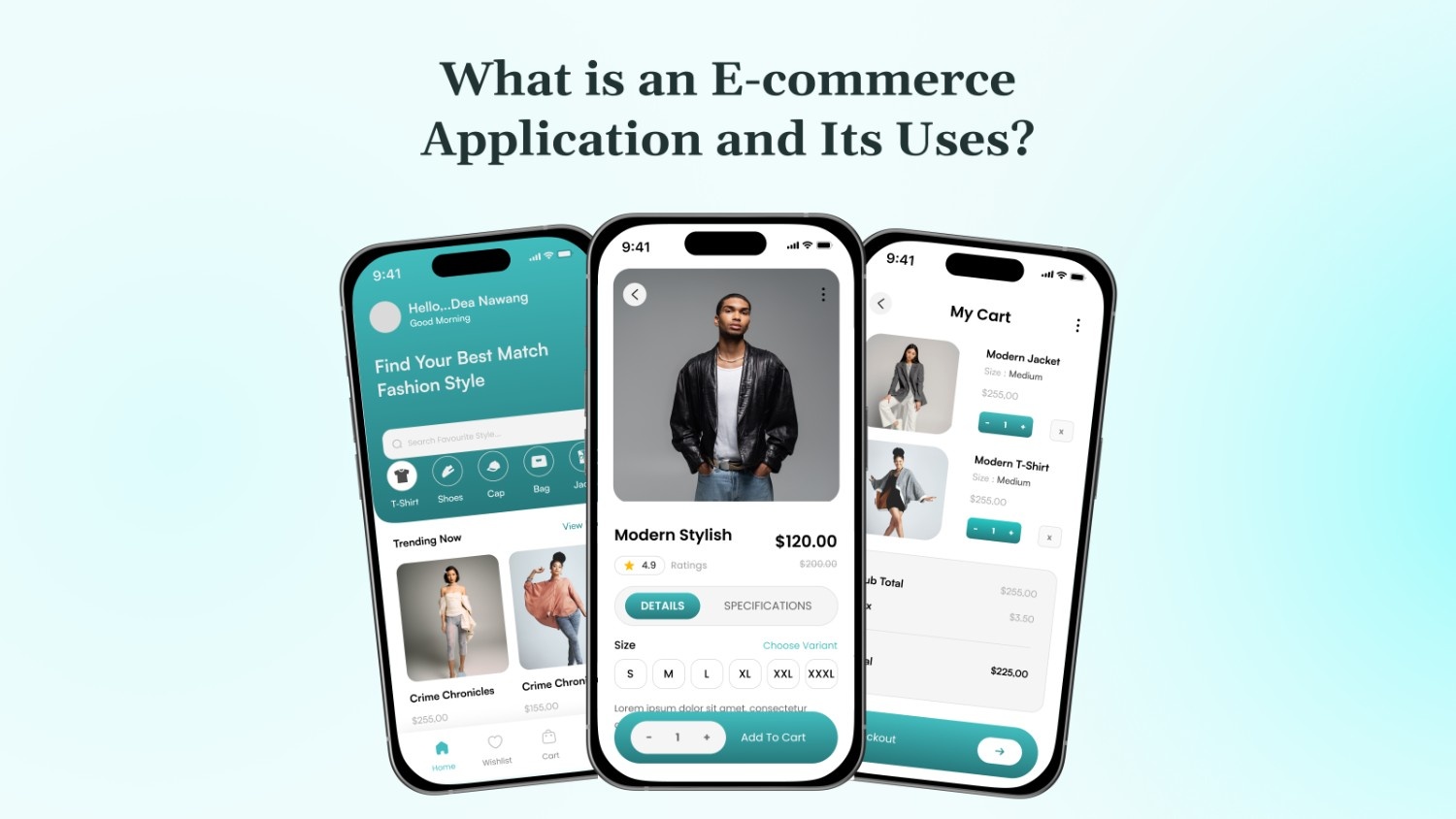
In 2024, global e-commerce sales reached an all-time high of $6.09 trillion, with over 2.14 billion digital buyers worldwide.
This rapid growth highlights a significant shift in consumer behavior; online shopping has become the norm rather than the exception. Whether it is purchasing daily essentials, luxury items, or services, e-commerce applications have revolutionized how we shop.
For businesses, this shift represents both a challenge and a massive opportunity. From giant corporations to small startups, everyone is utilizing e-commerce apps to reach global audiences, streamline operations, and enhance customer engagement.
This blog will explore what an e-commerce application is, its essential features, the various types, and how it benefits both businesses and consumers.
Key Takeaways
- E-commerce apps streamline online shopping, allowing businesses to reach customers worldwide with features like secure payments, real-time tracking, and inventory management.
- Various e-commerce models (B2C, B2B, C2C) offer flexibility, enabling businesses to choose the best structure for their operations and customer engagement.
- Future technologies like AI, AR, and blockchain are transforming e-commerce apps by enhancing personalization, security, and user experience.
- E-commerce apps boost business efficiency, offering benefits like lower operational costs, 24/7 availability, and data-driven insights for better decision-making.
What is an E-Commerce Application?
An e-commerce application is a platform that facilitates the online buying and selling of products or services. These applications provide a digital space where businesses can showcase their offerings, allowing customers to browse, select, and purchase goods or services conveniently from anywhere.
E-commerce apps typically include features like secure payment gateways, real-time inventory tracking, and personalized recommendations, all aimed at enhancing the shopping experience.
E-commerce Websites vs. E-commerce Applications (Mobile Apps)
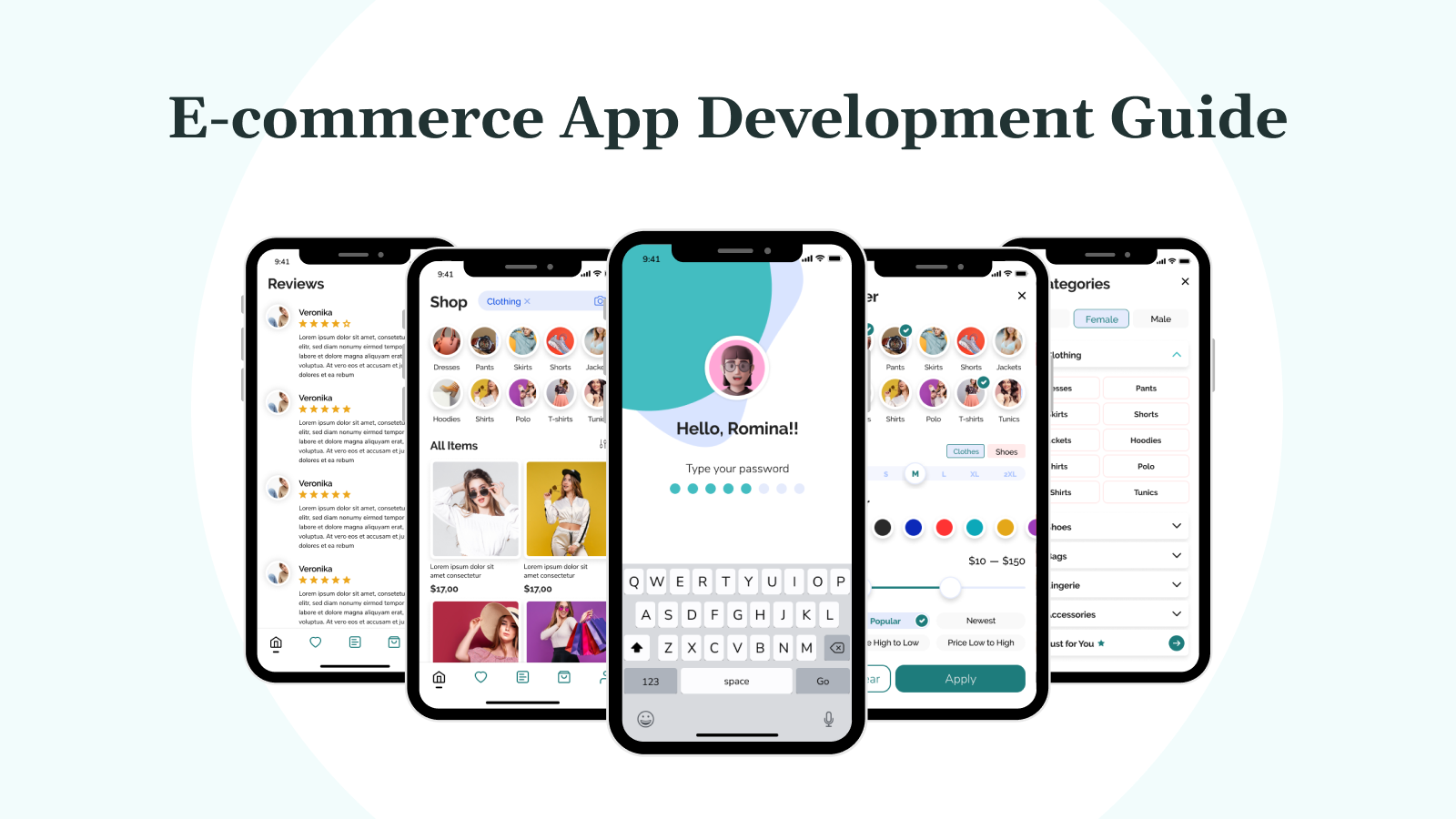
While both e-commerce websites and applications serve the same purpose of online buying and selling, there are distinct differences between the two.
- Web-based applications: These are accessed via browsers on desktops, laptops, or tablets. Customers can browse the product catalog, add items to their cart, make payments, and track orders from the comfort of their desktops.
- Mobile applications: Designed for smartphones and tablets, these apps offer the same functionality as web-based applications but are optimized for touch interfaces and mobile devices. With mobile apps, customers can make purchases on the go, receive push notifications for promotions, and track their orders in real time.
Businesses rely on these apps to create a seamless interaction with customers, whether they are selling physical products, digital goods, or offering services.
How Do E-commerce Applications Work?
E-commerce applications operate on a complex yet straightforward framework that facilitates the buying and selling of goods and services online.
While users interact with the front-end interface, a series of back-end processes ensures that the application functions smoothly, from browsing products to completing a purchase and fulfilling orders. Here is a look at the basic functioning of an e-commerce app:
1. User Browsing Products, Adding to Cart, and Proceeding to Checkout
The first step in an e-commerce journey involves the user browsing the application to explore available products or services. E-commerce apps typically offer product categories, a search bar, filters, and recommendations to help users find what they are looking for quickly and efficiently.
Once a user selects a product, they can add it to their virtual shopping cart, where they can review items, modify quantities, or remove products. The cart serves as a temporary storage area before the user proceeds to checkout.
2. Payment Processing and Order Fulfillment
After reviewing the cart, the user proceeds to the checkout process. At this stage, the e-commerce app collects necessary information, such as the shipping address, payment method, and any promo codes. The app integrates with secure payment gateways to facilitate transactions, ensuring that sensitive payment data is encrypted and handled safely.
Once the payment is successfully processed, the user receives an order confirmation. The app generates an order ID and sends an acknowledgment to both the user and the seller, initiating the order fulfillment process.
3. Back-End Processes (Inventory Management, Order Tracking, Customer Support, etc.)
Behind the scenes, several back-end processes work together to ensure a seamless experience for both users and sellers:
- Inventory Management: E-commerce applications connect with inventory systems to ensure real-time updates on stock availability. When a product is purchased, the inventory is automatically updated to reflect the new stock level, preventing overselling and stockouts.
- Order Tracking: E-commerce apps often integrate with logistics providers, enabling users to track their orders in real-time. From dispatch to delivery, customers are notified of their order’s status, keeping them informed and satisfied.
- Customer Support: A crucial part of the back-end system is customer service. Many e-commerce apps offer customer support features like live chat, FAQs, or ticketing systems, ensuring that users can get assistance with any issues during or after the purchase process.
Looking for a custom e-commerce app tailored to your business needs? At DEVtrust, we specialize in creating scalable and secure e-commerce solutions that are designed to drive growth. Contact us now to start building your e-commerce platform with our expert team.
Benefits of E-commerce Applications for Businesses
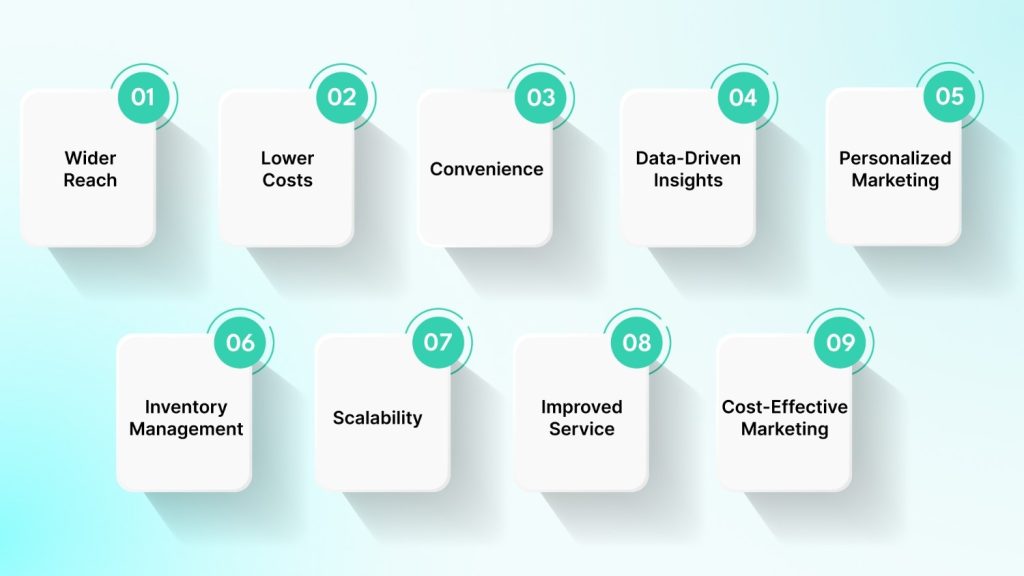
E-commerce applications offer several key benefits that can transform business operations:
- Wider Reach: E-commerce apps allow businesses to reach a global audience, breaking down geographical barriers and increasing brand visibility.
- Lower Operational Costs: With no physical storefront, businesses save on rent, utilities, and staff, reducing overall expenses.
- Convenience: E-commerce apps provide 24/7 shopping for customers and constant sales opportunities for businesses, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Data-Driven Insights: Integrated analytics help businesses understand customer behavior, enabling smarter marketing and inventory management.
- Personalized Marketing: Apps allow businesses to tailor offers and promotions based on customer preferences, increasing engagement and sales.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking and automated order processing streamline operations and reduce errors.
- Scalability: E-commerce apps grow with the business, adding new products and features without major system overhauls.
- Improved Customer Service: Direct support channels within the app enhance the customer experience and foster loyalty.
- Cost-Effective Marketing: Digital marketing through e-commerce apps is more affordable and measurable, improving ROI compared to traditional methods.
Build an e-commerce application that grows with your business. DEVtrust provides scalable cloud architecture solutions on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to support high traffic and ensure reliable performance. Get in touch to develop a robust, future-proof e-commerce app.
Key Features of E-commerce Applications
An effective e-commerce application must offer a range of essential features that not only enable transactions but also enhance the user experience. Below are the core features that define a successful e-commerce app.
1. Product Listings and Catalog Management
Product listings should include essential details such as high-quality images, detailed descriptions, pricing, and stock availability. A user-friendly catalog organization, with the ability to filter and search products, allows users to find exactly what they need quickly.
2. Shopping Cart and Checkout Process
A smooth, intuitive shopping cart is essential for any e-commerce app. Users should be able to add, remove, and modify items in their cart with ease. The checkout process should also be simple and efficient, offering various payment methods, including credit cards, digital wallets, and other online payment systems.
3. Payment Gateway Integration
E-commerce applications must securely handle transactions. Integration with multiple payment gateways (like PayPal, Stripe, or credit card processors) ensures users have various options to pay. The app should support secure, encrypted payment transactions to protect customer data and build trust.
4. Order Management and Tracking
After completing a purchase, users should be able to easily track their order status. The app should offer real-time updates on shipping status, including tracking numbers and delivery estimates. A reliable order management system also allows businesses to manage inventory, process returns, and handle customer inquiries effectively.
5. Customer Reviews and Ratings
User-generated reviews and ratings are vital for building trust and credibility. Consumers often rely on reviews to make informed purchasing decisions. E-commerce apps should allow customers to rate and review products, which not only helps other buyers but also provides valuable feedback for businesses.
6. Personalized User Experience
By using data analytics, e-commerce apps can offer personalized product recommendations, tailored discounts, and targeted marketing messages. Machine learning algorithms can analyze user behavior to provide more relevant content and suggestions, improving the overall shopping experience.
7. Customer Support Integration
An e-commerce app should offer various ways for customers to reach support, including live chat, email, or phone support. Efficient customer service integration can resolve issues quickly, enhancing user satisfaction and encouraging repeat business.
8. Mobile Optimization and Responsive Design
A responsive design adjusts to different screen sizes, providing an optimal shopping experience across smartphones and tablets. Mobile-friendly features like one-click purchases, easy navigation, and quick checkouts are essential.
9. Security Features
Security is a top priority in e-commerce. The app should include SSL encryption, two-factor authentication (2FA), and secure payment gateways to protect sensitive data. Implementing strong data protection measures ensures that customer information remains secure and builds trust in the platform.
Need secure payment integrations for your e-commerce application? DEVtrust offers seamless API integrations with Stripe, PayPal, and other gateways to ensure smooth, reliable transactions for your customers. Contact us today and enhance your app’s security.
Types of E-commerce Applications
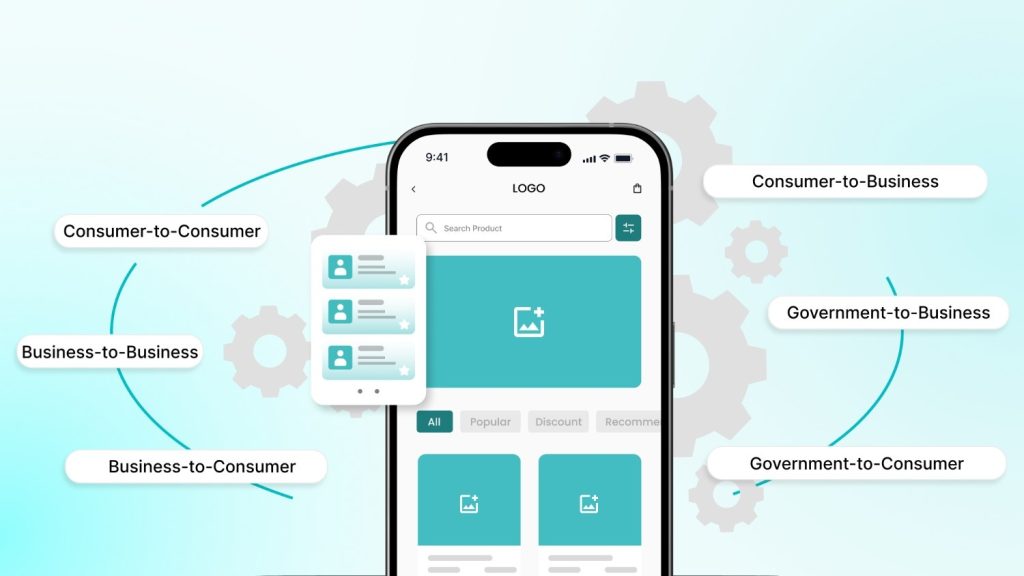
E-commerce applications come in various forms depending on the business model, the interaction between users, and the type of goods or services offered. Understanding these types can help businesses identify the right solution for their specific needs.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-commerce Applications
The B2C model allows businesses to sell products directly to consumers. They are typically what people think of when they hear “online shopping.”
Major examples include Amazon, Walmart, and Alibaba. B2C e-commerce applications enable businesses to manage product listings, process payments, handle customer inquiries, and manage logistics, all within the app.
Business-to-Business (B2B) E-commerce Applications
B2B applications cater to transactions between businesses, rather than between a business and a consumer. These platforms often deal with bulk orders, long-term contracts, or wholesale products.
Examples of B2B e-commerce apps include Alibaba and ThomasNet. These apps are tailored to meet the unique needs of large-scale transactions, including custom orders and recurring purchases.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) E-commerce Applications
C2C e-commerce apps facilitate transactions between individuals, often on a peer-to-peer (P2P) basis. These platforms allow users to sell products to one another, with the platform typically acting as a marketplace to enable the transaction.
Examples include eBay, Craigslist, and Facebook Marketplace. These platforms typically feature user-generated content, such as listings and reviews, and offer features like bidding, auctions, and direct messaging between buyers and sellers.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B) E-commerce Applications
The C2B model reverses the traditional e-commerce flow, where consumers offer products or services to businesses. This is often seen in freelance work, influencer marketing, and other service-based transactions.
Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr are great examples of C2B e-commerce applications. These apps allow businesses to tap into a broad range of independent contractors or service providers to meet their needs.
Government-to-Business (G2B) E-commerce Applications
G2B e-commerce platforms facilitate interactions between businesses and government agencies. Businesses can use these platforms to access government services, participate in bidding, or find information about government contracts.
Examples include government procurement websites and public sector portals.
Government-to-Consumer (G2C) E-commerce Applications
In the G2C model, government entities offer goods or services directly to consumers. These can include things like tax payments, public services, and more.
Examples include tax filing services and DMV license renewals. These platforms provide essential services to the public while streamlining government-citizen interactions.
Common E-commerce Applications
E-commerce applications serve various industries by enabling businesses to offer goods or services in a digital format. These apps cater to different customer needs, from retail purchases to subscription services, providing users with convenience and broad access.
Below are some common e-commerce applications, broken down by their specific business models:
| E-commerce Model | Examples | Description |
| Online Retail | Amazon, eBay, Etsy | These platforms allow businesses to sell products directly to consumers via a digital storefront. |
| Wholesale Platforms | Alibaba, Amazon Business | Wholesale platforms enable businesses to purchase goods in bulk, often at discounted rates. |
| Subscription Services | Dollar Shave Club, Netflix | Subscription-based apps provide regular deliveries of products or services to customers for a set period. |
| Online Booking | Booking.com, Airbnb | These apps allow users to book services such as accommodations, flights, and experiences online. |
How to Develop an E-commerce Application?
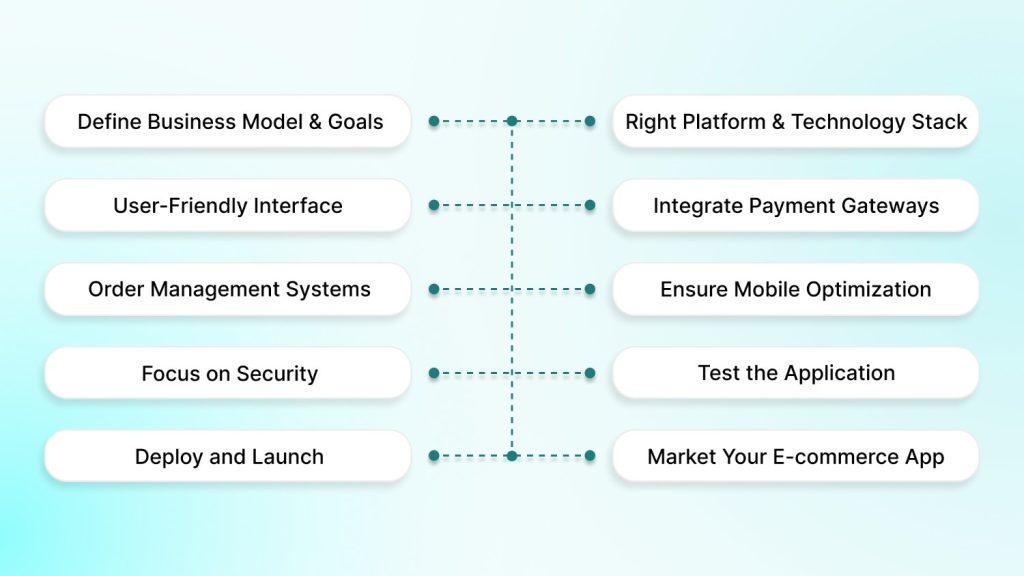
Developing a successful e-commerce application involves a systematic approach, from ideation to launch. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to go about building your e-commerce app.
1. Define Your Business Model and Goals
Start by identifying the type of e-commerce application you want to build. Whether it is B2C (Business to Consumer), B2B (Business to Business), C2C (Consumer to Consumer), or a hybrid model, defining your business model helps shape the app’s functionality.
Set clear goals, whether it is driving sales, expanding your customer base, or offering a unique product range, to guide your development process.
2. Choose the Right Platform and Technology Stack
Selecting the right technology is crucial for your app’s performance and scalability. If you want to use a pre-built solution, platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento may be good options. For a more custom-built solution, decide on your backend technologies (e.g., Node.js, Ruby on Rails, Django) and frontend frameworks (e.g., React, Angular).
Consider mobile responsiveness, user experience, and integration capabilities with third-party services like payment gateways, CRM systems, and marketing tools.
3. Design a User-Friendly Interface (UI/UX)
Your app should have an intuitive interface, with clear product categories, a smooth navigation structure, and easy access to shopping carts. A responsive design that works across mobile, tablet, and desktop is crucial, as many users shop on their mobile devices.
4. Integrate Payment Gateways
Payment processing is one of the core components of any e-commerce application. Ensure that your app integrates with secure and trusted payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or Square. Offer multiple payment options (credit/debit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers) to give customers flexibility.
Additionally, make sure that the payment system complies with industry security standards like PCI DSS to protect user data.
5. Set Up Inventory and Order Management Systems
To keep track of stock levels, set up an effective inventory management system within your app. This system should update in real-time as products are sold, ensuring customers only see products that are available for purchase.
6. Ensure Mobile Optimization
Mobile commerce (m-commerce) is rapidly growing, and optimizing your e-commerce app for mobile is crucial. Your app must load quickly, be responsive, and offer a streamlined experience on smaller screens.
7. Focus on Security
Protect sensitive customer data by implementing SSL certificates to encrypt transactions. Use multi-factor authentication and other secure methods for user login and account management. Regularly update your app and server to patch vulnerabilities, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
8. Test the Application
Before going live, conduct extensive testing across different devices, browsers, and operating systems to ensure the app’s functionality. Perform user acceptance testing (UAT) to see how real users interact with your app and identify any potential issues.
Test all features like payment systems, product search, cart management, and order fulfillment. Also, stress-test the app to ensure it can handle high traffic and large order volumes.
9. Deploy and Launch
Once the app is thoroughly tested, deploy it to your production environment. If you are launching a web-based e-commerce app, ensure that your web hosting provider can handle the expected traffic.
For mobile apps, submit them to the App Store and Google Play Store, ensuring they meet all guidelines and requirements. Launch your app with a solid marketing strategy to attract early users.
10. Market Your E-commerce App
After launch, focus on marketing your app. Use a combination of digital marketing strategies such as SEO (Search Engine Optimization), PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising, social media marketing, influencer partnerships, and email campaigns.
Challenges in E-commerce Application Development
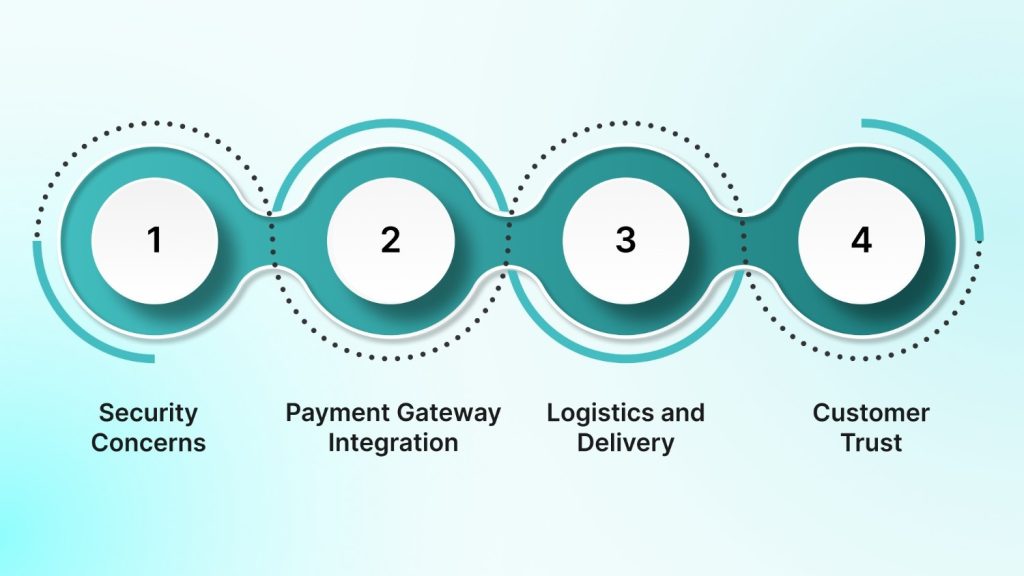
Developing an e-commerce application involves various technical and operational challenges. These issues must be addressed effectively to create a seamless, secure, and user-friendly platform. Below are some of the most common challenges faced during the development of e-commerce applications:
1. Security Concerns
E-commerce platforms handle sensitive customer data, making them prime targets for cyber threats. Protecting this data through strong encryption and secure payment systems is essential. Fraud prevention measures like two-factor authentication and secure login protocols are also crucial for safeguarding both the platform and its users.
2. Payment Gateway Integration
Handling multiple currencies and securing transactions across borders is a complex task for global e-commerce apps. It requires integrating reliable payment gateways that are secure and capable of handling a variety of payment options, ensuring that every transaction is processed safely and efficiently.
3. Logistics and Delivery
Managing an efficient supply chain is vital for timely delivery. E-commerce apps must integrate with logistics providers to ensure real-time inventory tracking, accurate order fulfillment, and fast shipping. Delays or issues in delivery can negatively impact customer satisfaction and business reputation.
4. Customer Trust
Building trust is essential for the long-term success of an e-commerce platform. Offering transparent product information, clear policies, and excellent customer service helps establish credibility. Fast response times, easy returns, and multiple communication channels are key to retaining customers and ensuring a positive shopping experience.
Future of E-commerce Applications
The future of e-commerce applications is shaping up to be more innovative and user-centric than ever before. With advances in technology, businesses are poised to provide smarter, more personalized, and seamless shopping experiences for consumers.
1. Artificial Intelligence & Personalization
AI is transforming e-commerce by offering personalized shopping experiences. Product recommendations driven by AI algorithms consider users’ browsing behavior and preferences. Chatbots, powered by AI, are also enhancing customer support by providing instant answers and personalized assistance.
2. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR are revolutionizing the shopping experience by enabling customers to try on products virtually. For example, furniture stores like IKEA use AR to let customers visualize how furniture will look in their homes. VR is also enhancing immersive shopping environments, where users can experience a store-like environment online.
3. Blockchain
Blockchain technology is enhancing transparency and security in e-commerce transactions. By providing a decentralized ledger, blockchain ensures that all transactions are secure, verifiable, and tamper-proof, reducing fraud and providing more trust in digital payments and transactions.
4. Voice Commerce
Voice commerce is on the rise as virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri make shopping more convenient. Customers can browse and purchase products simply by speaking, making the shopping experience hands-free and even more accessible, especially for those who prefer voice interactions over typing.
Conclusion
E-commerce applications have transformed the way businesses operate and consumers shop. With the rapid rise of mobile commerce, AI-driven personalization, and secure online transactions, the e-commerce industry is thriving and continues to evolve.
For businesses, creating a successful e-commerce app involves careful planning, a user-centric approach, and seamless integration of the latest technologies.
Whether you are a startup looking to create a custom e-commerce solution or an established business aiming to enhance your digital presence, having the right technology partner can make all the difference. At DEVtrust, we specialize in crafting secure, scalable, and feature-rich e-commerce applications that can help your business grow and adapt to ever-evolving market needs.Ready to build your own tailored e-commerce application? Get in touch with our expert team today and turn your ideas into a reality.
What is an E-commerce Application and Its Uses
Learn what an e-commerce application is, its uses, and how it benefits businesses and consumers. Discover essential features, types, and future trends.
Contact Us