Frequent app crashes, inconsistent performance, and device-specific bugs slow releases and frustrate users. Manual testing struggles to efficiently cover multiple devices, OS versions, and complex user scenarios.
Mobile app automation testing solves these challenges by automatically validating functionality, performance, and stability across all target devices. Automated tests reduce repetitive manual work, minimize errors, and provide faster, reliable feedback for every code change.
This approach ensures apps perform consistently, regressions are caught early, and release quality remains high. In this blog, we cover the key benefits of mobile app automation testing, top frameworks and tools, common challenges, and best practices for scalable, efficient testing programs.
Key Takeaways
- Manual testing doesn’t scale as device counts grow and release cycles accelerate; automation lowers cost per release while expanding test coverage.
- Native frameworks like Espresso and XCUITest run faster but require separate solutions, while cross-platform tools like Appium unify testing at the cost of slower speeds.
- Open-source frameworks save on licensing costs but require setup time and expertise; commercial platforms offer faster onboarding at higher annual fees.
- Real device clouds eliminate hardware investment but are expensive; combining emulators with targeted real-device testing optimizes budgets.
- Long-term success depends on test maintenance; page object models and stable locators prevent failures when the UI changes.
Why Manual Testing Alone Fails at Scale and When Should You Invest in Automation Testing?
Manual testing can support early-stage mobile apps with limited features and small user bases. However, as products scale across more devices, operating systems, and release cycles, manual testing quickly becomes a bottleneck, slowing deployment and increasing risk.
In this context, automation testing refers to a layered approach that combines UI automation with backend validations such as API and integration tests, ensuring coverage scales without relying solely on fragile UI scripts.
Your QA team can test five devices today. Tomorrow, you need coverage across 50 device models, three OS versions, and multiple screen sizes. Manual testing cannot keep pace with this complexity. Each new feature exponentially increases testing requirements, creating bottlenecks that delay releases and frustrate stakeholders.
Here is the real cause of failure:
- Repetitive regression testing exhausts teams: Running the same test scenarios after every code change wastes skilled QA time on mechanical tasks rather than exploratory testing that finds complex issues.
- Human error compounds over time: Fatigue, distraction, and inconsistent test execution lead to missed bugs that automated scripts reliably catch every time.
- Device coverage remains incomplete: Testing on even a dozen physical devices consumes hours per release. Manually covering the market’s device diversity is financially and logistically impossible.
- Feedback loops slow innovation: Waiting days for manual test results delays bug fixes and feature iterations, extending your time-to-market while competitors move faster.
When to invest in automation testing:
- Rapid release cycles: If you deploy weekly, bi-weekly, or practice continuous delivery, automation testing becomes essential infrastructure rather than optional tooling.
- Multi-device support: Apps targeting diverse device ecosystems need automated cross-device testing to ensure consistent experiences without ballooning QA headcount.
- Compliance-sensitive apps: HealthTech, FinTech, and other regulated industries require documented, repeatable testing processes that manual approaches cannot reliably provide at scale.
- Growing user base: As your user count increases, so do usage patterns and edge cases. Automation helps validate these scenarios continuously without incurring disproportionate costs.
Suggested Read: Python vs Java: Key Features, Differences, and Use Cases
Business Benefits of Mobile App Automation Testing
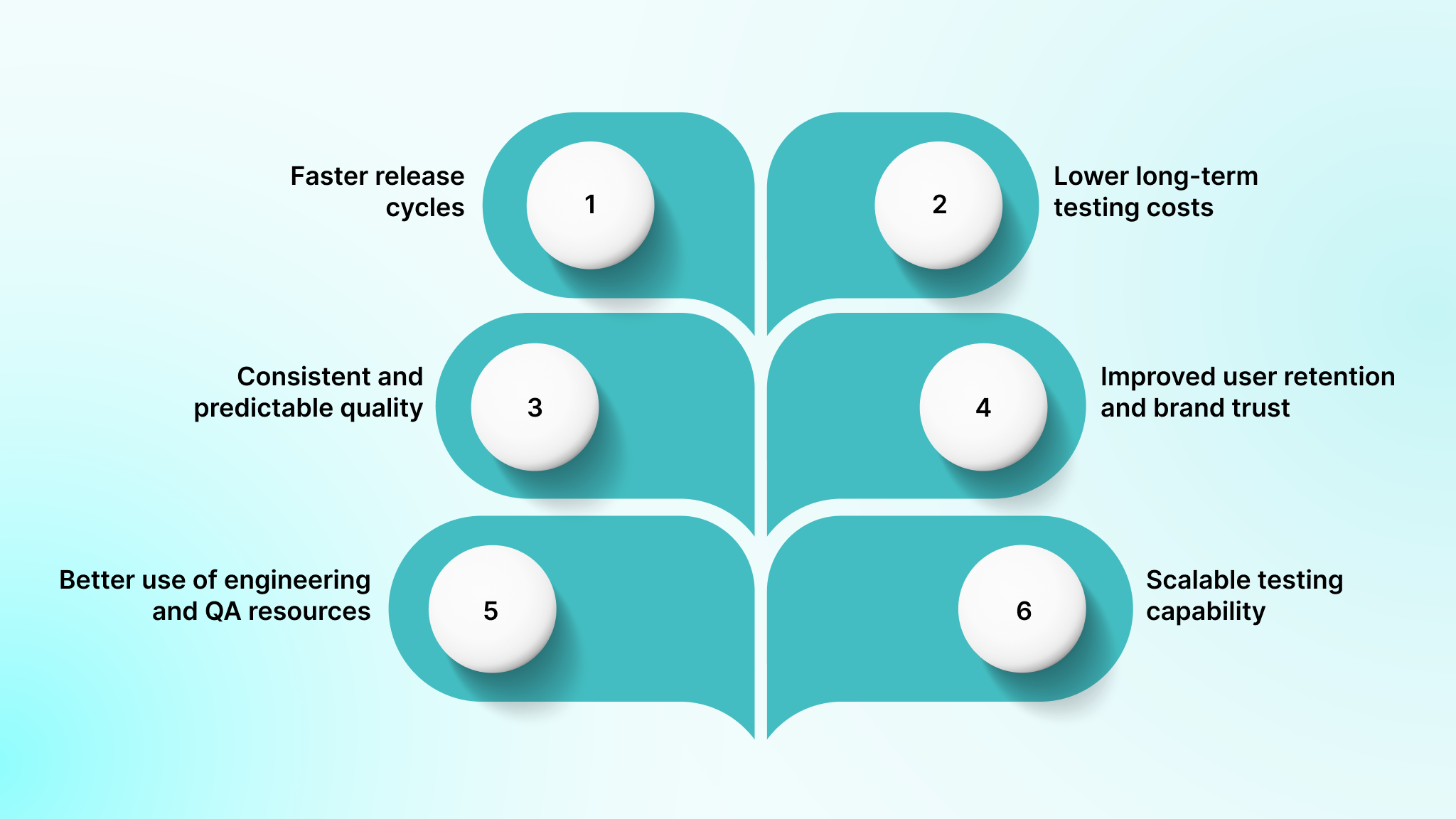
Mobile app automation testing delivers measurable business value beyond faster test execution. As products scale and release cycles shorten, automation becomes a strategic enabler that improves delivery predictability, cost efficiency, and user trust.
Key business benefits include:
- Faster release cycles: Automated test suites run in hours instead of days, removing QA as a release bottleneck. Teams ship features when they are ready, enabling more frequent and predictable releases without sacrificing quality.
- Lower long-term testing costs: Although automation requires upfront investment, it significantly reduces the cost per release over time. Reusable automated tests replace hundreds of hours of repetitive manual effort across future builds, increasing coverage without proportional cost growth.
- Consistent and predictable quality: Automated tests execute the same way every time, eliminating variability caused by human factors. Release decisions are based on objective results rather than subjective confidence, improving reliability across environments and devices.
- Improved user retention and brand trust: Fewer production defects lead to better user experiences. Consistent app performance across updates and devices increases engagement, reduces churn, and protects acquisition spend.
- Better use of engineering and QA resources: Automation handles repetitive validation, allowing QA engineers to focus on exploratory testing, edge cases, and usability scenarios that require human judgment. This improves productivity and team satisfaction.
- Scalable testing capability: Once frameworks and infrastructure are in place, expanding test coverage or device support requires minimal incremental effort. Testing capacity grows alongside product complexity without linear increases in team size or cost.
At large, teams that rely on automation can scale confidently without turning testing into a delivery constraint.
Core Mobile App Automation Testing Tools and Frameworks
Selecting the right automation tools determines whether your testing program succeeds or fails. Each framework offers distinct capabilities, learning curves, and ecosystem support that align differently with various project requirements and team structures.
Let’s look at all four categories in detail:
A. Native Mobile UI Frameworks
Native frameworks provide the fastest execution speed and highest stability by integrating directly with platform-specific automation APIs. These tools require maintaining separate test suites for iOS and Android, but eliminate cross-platform abstraction layers that introduce timing issues and debugging complexity.
1. Espresso

Espresso is Google’s native Android testing framework that integrates tightly with Android Studio and automatically synchronizes with the UI thread to eliminate timing-related flakiness. The framework operates within the same process as the application under test, providing direct access to app components.
Features
- Automatic synchronization with the app UI thread prevents flaky tests.
- Support for testing activities, fragments, and complex view hierarchies.
- The idling resources mechanism handles asynchronous operations gracefully.
- Espresso Intents for verifying and stubbing intent-based interactions.
- Comprehensive assertion library for validating UI state.
Pros
- Reliable synchronization eliminates timing-related test failures.
- Google’s official support and documentation.
Cons
- An Android-only framework requires a separate iOS testing solution.
- Limited cross-app testing capabilities compared to broader frameworks.
- Requires app source code access, unsuitable for black-box testing.
2. XCUITest

XCUITest is Apple’s official UI testing framework that integrates with Xcode and enables developers to write tests in Swift or Objective-C using familiar iOS development patterns. The framework executes tests in a separate process from the application, communicating through accessibility interfaces.
Key capabilities
- Parallel execution across simulators.
- Built-in screenshots, video capture, and code coverage.
- Accessibility identifiers for stable element location.
- Tight integration with Xcode Test Plans and Xcode Cloud.
Strengths
- Best-in-class stability for iOS.
- Immediate support for new iOS versions.
- Smooth fit with iOS development workflows.
Limitations
- iOS-only.
- Requires macOS and iOS development expertise.
3. EarlGrey

EarlGrey is Google’s iOS testing framework that brings robust synchronization and white-box testing capabilities to native app development. The synchronization engine tracks multiple aspects of application state, including network requests, animations, and dispatch queue operations.
Features
- Advanced synchronization automatically tracks dispatch queues, network requests, and animations.
- White-box access enables testing the internal app state and behavior of private methods.
- Accessibility validation built directly into the assertion library catches compliance issues during tests.
- Detailed failure messages include view hierarchy dumps and synchronization state for debugging.
- CocoaPods and Swift Package Manager integration simplifies project setup.
- Custom matchers support domain-specific assertions beyond standard UI validation.
- Screenshot comparison testing detects visual regressions across test runs.
Strengths
- Excellent flake resistance.
- Deep internal testing capabilities.
- Strong Google backing (via EarlGrey 2.0 branch).
Limitations
- iOS-only.
- Requires app source access.
- Steeper learning curve for non-developers.
- No longer actively maintained; prioritize XCUITest for new projects to ensure iOS version compatibility.
Please Note: EarlGrey 1.0 is deprecated by Google (since 2021); use EarlGrey 2.0 or migrate to XCUITest for active support.
B. Cross-Platform Mobile UI Automation
Cross-platform frameworks allow teams to maintain a single test codebase for both platforms. This reduces duplication and can accelerate initial adoption, but introduces abstraction layers that must translate commands into platform-specific actions.
Operational reality: Cross-platform automation succeeds or fails based on discipline. Without strict locator strategies, synchronization rules, and framework conventions, teams often experience increasing flakiness as test suites scale.
Use when: You want one automation approach across platforms and language flexibility.
Tradeoff: Slower execution and higher stability risk without strong engineering standards.
1. Appium

Appium is an open-source framework built on the W3C WebDriver specification. Test scripts communicate with an Appium server, which translates commands to XCUITest on iOS and UIAutomator2 on Android.
- No app modification or SDK integration required.
- Broad language support and an extensive plugin ecosystem.
- Compatible with local devices and cloud device labs.
Limitations: Slower than native frameworks and requires experienced engineers to diagnose failures across multiple layers (test code, Appium server, platform driver).
C. Real Device Clouds
Device cloud platforms eliminate the need to maintain physical device labs by providing remote access to real devices. These services handle device procurement, maintenance, and management while offering integration with popular test frameworks.
1. Kobiton

Kobiton provides a web-based interface for manual testing sessions and API access for automated test execution. Session recordings capture complete interactions, including device logs and network traffic.
Features
- Real device cloud with broad device coverage spanning major manufacturers and OS versions
- Manual and automated testing on an identical platform enables seamless workflow transitions.
- Session recordings capture complete test execution, including device interaction logs.
- Performance profiling monitors CPU, memory, and battery usage during test runs.
- Scriptless automation builder enables test creation without coding expertise.
- Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest integration supports preferred test frameworks.
Limitations
- Subscription costs scale with usage.
- Less control than self-hosted labs.
- Performance depends on network quality.
2. Perfecto

Perfecto combines real device access with intelligent test orchestration and in-depth reporting. Network virtualization capabilities allow testing under various connection conditions without requiring physical network infrastructure.
Features
- Enterprise device lab with extensive device, OS, and browser combinations.
- AI-powered analytics identify failure patterns and suggest remediation strategies.
- Network virtualization simulates various connection conditions, including 3G, 4G, 5G, and WiFi.
- Visual testing capabilities detect UI regression across releases and devices.
- Single sign-on and role-based access control support enterprise security requirements.
- Integration with major CI/CD platforms, including Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and GitLab.
- Executive dashboards track quality metrics, test coverage, and release readiness.
Cons
- Premium pricing reflects the enterprise target market.
- Vendor dependency for critical testing infrastructure.
- Learning curve for maximizing platform capabilities.
- It may include features that smaller teams do not require.
D. Mobile Web Testing
Mobile web testing tools focus on validating responsive websites and progressive web applications accessed through mobile browsers. These frameworks do not support native iOS or Android applications. Use them only for responsive websites or progressive web apps accessed via mobile browsers.
1. Cypress

Cypress executes test code in the same run loop as the application, running directly in the browser rather than using WebDriver. It can test responsive mobile web views and PWAs, but cannot test native mobile apps.
Features
- Real-time test execution with automatic reloading on code changes.
- Time-travel debugging allows inspection of past application states.
- Automatic waiting eliminates the need for manual sleep commands.
- Built-in screenshot and video capture for failure analysis.
- Network traffic control and stubbing for isolated testing.
- Developer-friendly error messages with actionable debugging hints.
- Modern JavaScript framework support, including React and Vue.
Limitations
- No native app support.
- Limited mobile gesture and device feature testing.
- Parallel execution requires paid plans at scale.
Enterprise Platforms and Support Tools for Mobile Automation
These tools are most valuable in organizations that need to standardize testing across teams with varying skill levels. It typically bundles execution engines, reporting, device access, and test management into a single ecosystem. The tradeoff is reduced flexibility and higher cost compared to open-source frameworks.
1. TestComplete

SmartBear’s TestComplete combines visual test recording with AI-powered object recognition to reduce maintenance overhead when applications evolve. The platform includes device cloud access, cross-browser testing, and integration with popular development tools.
Key capabilities
- Visual record-and-playback test creation.
- AI-driven object recognition that adapts to UI changes.
- Multi-language scripting support (JavaScript, Python, VBScript, C++Script, keyword-driven).
- Built-in access to real devices and cross-browser environments.
- Data-driven testing with external data sources.
- Native integration with CI/CD tools and defect-tracking systems.
Strengths
- Lower barrier to entry for teams new to automation.
- Reduced maintenance effort through intelligent object handling.
- Commercial support with regular updates and documentation.
- Unified platform reduces tool sprawl.
Limitations
- Licensing costs increase as teams scale.
- Proprietary abstractions limit fine-grained control.
- Heavier runtime footprint than lightweight frameworks.
2. Ranorex

Ranorex targets enterprises that need to standardize automation across teams with mixed technical expertise. It combines codeless test creation, advanced object recognition, and reusable test modules.
Features
- Codeless test creation through a visual drag-and-drop interface.
- Object recognition uses multiple identification strategies with automatic fallback.
- Mobile device management built into the platform eliminates the need for separate tooling.
- Reusable test modules create maintainable test libraries across projects.
- Selenium WebDriver integration enables a hybrid approach combining Ranorex with open-source tools.
- Data binding connects tests to external data sources for parameterized execution.
- Executive dashboards provide high-level quality metrics and trend analysis.
Pros
- Accessible to non-technical team members through a visual interface.
- Strong vendor support and training resources.
- Comprehensive documentation and knowledge base.
- Enterprise features, including role-based access control.
Cons
- Premium pricing targets enterprise budgets.
- Proprietary platform limits customization options.
- Heavier resource requirements compared to lightweight frameworks.
- Learning curve for advanced scenarios requiring code.
Ultimately, enterprise automation platforms are a strong fit when governance, support, and ease of adoption outweigh the need for lightweight, highly customizable frameworks.
Key Challenges in Mobile App Automation (and How to Avoid Them)
Mobile app automation delivers significant value, but unprepared teams often encounter avoidable obstacles that slow releases and erode confidence in test results. Unlike web automation, mobile environments introduce additional complexity, including device fragmentation, platform-specific behavior, and infrastructure overhead.
The following challenges are among the most common, along with practical ways teams can address each one.
1. Device Fragmentation Complexity
What begins as a manageable device list can quickly expand into hundreds of Android models and multiple iOS versions, making comprehensive testing difficult to sustain.
Recommended approach:
- Use analytics data to identify the devices most commonly used by real users.
- Focus on high-impact devices rather than attempting full market coverage.
- Gradually expand coverage as automation maturity improves.
2. Flaky Tests That Erode Trust
Few issues damage confidence in automation more than tests that fail inconsistently. Teams often spend hours investigating failures that disappear on reruns, creating noise in CI pipelines and delaying releases.
To reduce instability, teams should replace static waits with condition-based synchronization, standardize locator strategies around accessibility identifiers, and actively refactor unstable tests instead of allowing technical debt to accumulate.
3. High Test Maintenance Overhead
Even small UI changes can cause dozens of tests to fail when automation lacks structure. Over time, constant fixes slow feature development and discourage further investment in automation.
What works in practice:
- Centralize UI interactions using Page Object or Screen Object models.
- Separate test intent from implementation details.
- Apply the same review and quality standards to test code as production code.
4. Limited Visibility Into Test Failures
When tests fail on specific devices or OS versions, teams frequently lack the context needed to diagnose the issue. Without logs, screenshots, or recordings, debugging becomes guesswork.
Practical ways to reduce risk:
- Enable detailed logging during test execution.
- Automatically capture screenshots on failure.
- Use video recordings to investigate complex or intermittent issues.
5. CI/CD Integration Friction
Integrating mobile tests into CI pipelines often introduces longer build times and slower feedback. Running complete test suites on every commit can create tension between speed and confidence.
Instead of testing everything at once, teams can run lightweight smoke tests on each commit, schedule complete regression suites nightly or on demand, and rely on parallel execution to keep overall test duration manageable.
Suggested Read: Machine Learning App Development: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Practices for Scalable Mobile App Automation Testing
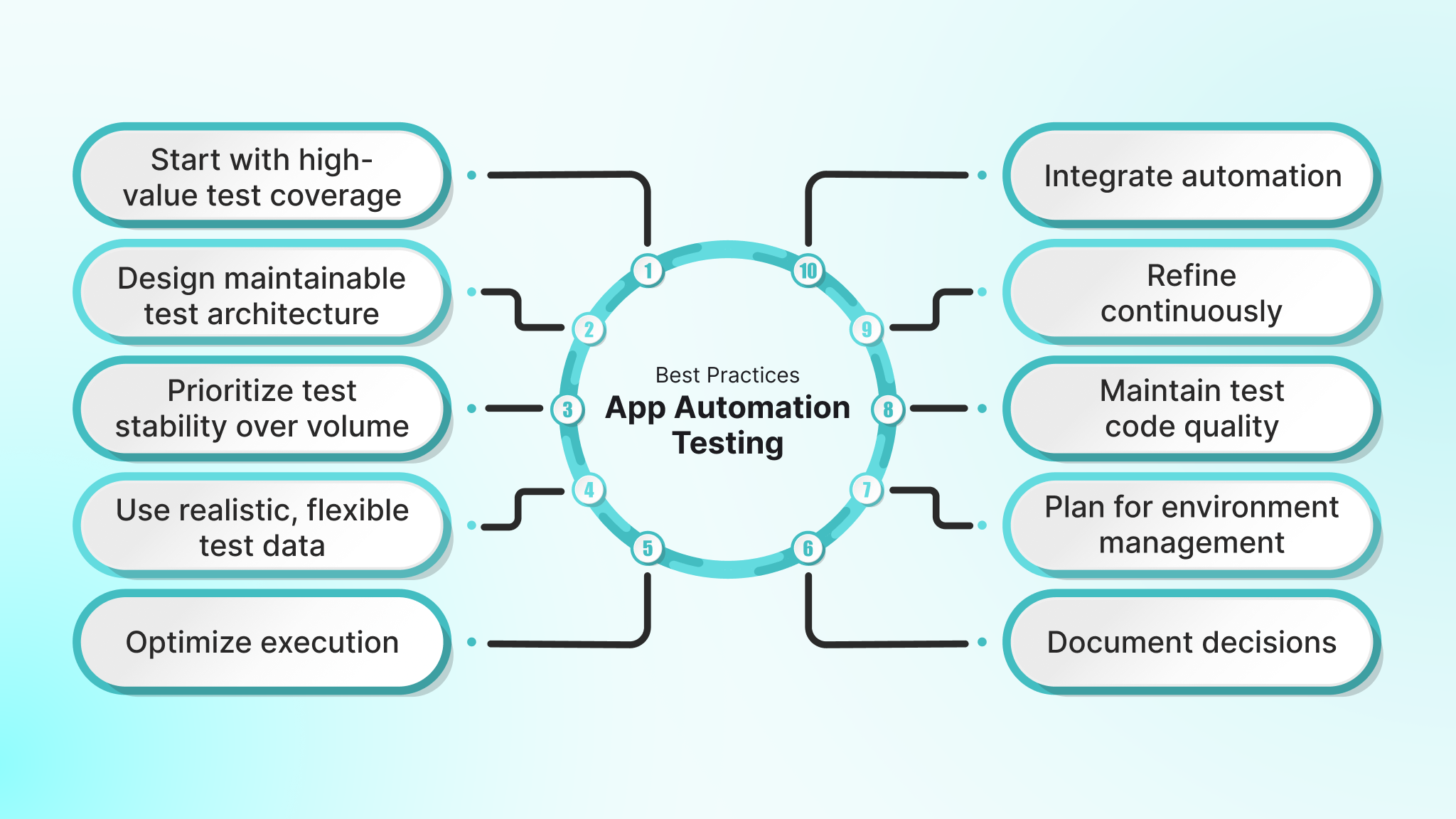
Successful automation programs are built on disciplined execution, not just tool selection. These best practices focus on sustainability, reliability, and long-term maintainability as test suites grow.
- Start with high-value test coverage: Automate critical user journeys and core workflows first. A small set of reliable smoke tests provides more value than an extensive suite of unstable tests that teams hesitate to trust.
- Design maintainable test architecture: Use patterns such as the Page Object or Screen Object Model to separate test logic from UI implementation details. This structure reduces maintenance effort when interfaces change.
- Prioritize test stability over volume: Reliable tests are more valuable than extensive but flaky coverage. Invest time in synchronization, locator strategy, and cleanup before expanding the suite.
- Use realistic, flexible test data: Avoid hardcoding values that break easily. Generate or manage test data that reflects real-world usage while keeping tests independent and repeatable.
- Optimize execution through parallelization: As test suites grow, sequential execution slows feedback. Run tests in parallel across devices and environments to maintain fast feedback cycles.
- Integrate automation early into CI/CD pipelines: Do not wait for perfect coverage. Integrate stable tests as soon as they are ready and expand incrementally within existing pipelines.
- Monitor and refine continuously: Track execution time, pass rates, and failure patterns. Metrics reveal which tests provide value and which introduce noise or maintenance burden.
- Maintain test code quality: Apply the same review, refactoring, and quality standards to test code as production code. Neglected test suites accumulate technical debt quickly.
- Plan for environment management: Establish transparent processes for managing emulators, physical devices, or cloud labs. Consistent environments reduce flaky behavior and onboarding friction.
- Document decisions and standards: Capture why specific frameworks, patterns, and conventions were chosen. Clear documentation prevents rework and supports team scalability.
Suggested Read: Jenkins: What Is It?
How DEVtrust Helps Teams Succeed with Mobile App Automation Testing?
Mobile automation fails when it is bolted on late, built with the wrong tools, or executed without a clear device and CI strategy. Teams often end up with slow, flaky test suites, limited device coverage, and automation that breaks whenever the UI changes, reducing trust in test results.
DEVtrust helps teams operationalize mobile automation as an engineering discipline, not a checkbox activity. We design automation systems that fit native mobile architectures, scale across devices, and run reliably inside modern CI pipelines.
Here is what we deliver:
- Mobile UI automation foundations: We set up reliable automation frameworks using Appium or native stacks (e.g., Espresso for Android, XCUITest for iOS) tailored to your product and team structure. This includes locator strategies, synchronization rules, test architecture patterns, and standards that minimize flakiness and rework.
- CI execution that stays fast and reliable: Automation is integrated directly into CI/CD with a clear execution model: lightweight smoke suites on pull requests, scheduled regression runs, parallel execution, and reporting designed to reduce reruns and triage noise.
- Device strategy that balances speed and confidence: We define a layered device approach: emulators and simulators for fast feedback, followed by a curated real-device matrix or device cloud execution for release validation. This ensures meaningful coverage without exploding runtime or cost.
- Automation maintainability systems: To prevent test suite decay, we implement screen/page object models, test data strategies, and code review standards for test code. Automation evolves alongside the app, even as UI and workflows change.
- Release readiness and quality visibility: Our reporting focuses on what matters for release decisions, flaky test tracking, failure clustering, risk-based insights, and clear go/no-go signals, so stakeholders trust the automation rather than bypass it.
When mobile quality directly impacts user trust, ratings, and retention, automation must be purpose-built for native platforms and engineered for long-term reliability. DEVtrust helps teams ship mobile apps with confidence by making automation fast, stable, and release-ready.
Conclusion
Mobile app automation testing delivers real value when it is treated as an engineering system, not a last-minute QA activity. Success depends on selecting the right framework for your app type, building stable locators and test architecture, and running automation in CI with a device strategy that balances speed with real-world confidence.
If your automation suite is flaky, slow, or difficult to maintain, DEVtrust can help you rebuild it with a clean framework setup, a reliable CI execution model, and a device coverage plan that supports consistent, confident releases. Book a call to get the help you need.