Cloud applications have become the ideal choice for companies seeking to deliver scalable, efficient, and accessible software solutions. These applications run on remote servers and are accessed via the internet, allowing you to scale with demand, lower operational costs, and reach users worldwide. Cloud web application development allows real-time collaboration, seamless integration, and cost-effective scaling, making it the preferred method among other platforms.
This how-to guide offers a step-by-step blueprint for developing a cloud application, from planning to maintenance. You will learn the basics of cloud apps, their advantages over traditional programs, the necessary expertise and tools, and an in-depth ten-step process to develop a stable and scalable application.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud Applications vs Traditional Software: Cloud applications run on external servers and are accessed through the internet. They offer advantages like easier scaling, greater flexibility, and less hands-on maintenance than software installed on local systems.
- Types of Cloud Applications: Cloud applications are primarily categorized into three service models: SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. Each model solves different business needs, providing varying levels of control and flexibility.
- Building a Cloud Application: The process involves defining clear goals, selecting the right cloud service model, choosing a suitable platform, designing a scalable architecture, and ensuring security. Utilizing tools such as APIs, databases, and containerization technologies will streamline development.
- Cloud Application Security: Security is crucial, requiring strategies like IAM for access control, frequent security audits, and data encryption to protect user data and ensure compliance with regulations.
What is a Cloud Application?
Cloud applications are software solutions hosted on remote servers and accessed online through browsers, mobile devices, or APIs. Since they depend on cloud computing to receive resources needed to execute the service, they are inherently different from traditional applications that rely on on-site hardware. Cloud applications utilize on-demand resources for computing power, storage, networking, and other key resources.
Cloud applications are perfect for businesses wanting to be efficient and scalable. Education about their architecture and types, as well as their many advantages, is essential for planning a successful cloud project.
Cloud applications power a wide range of use cases, each tailored to specific needs:
- Web Applications: Tools that run in a browser and aim to help the user fulfill parts of work, such as project management, data analytics, and customer relationship management tools, with the intention to be used in the cloud. Each web application provides users with the convenience of accessing tools on multiple devices.
- Mobile Applications: Apps that use cloud back-ends to handle data processing, user authentication, and real-time notifications, ensuring smooth mobile experiences.
- Enterprise Applications: Systems that help to manage complex operations, such as supply chain management systems, financial reporting systems, and office human resources systems, that support organizational efficiency.
- Collaborative Applications: Web conferencing interfaces that facilitate real-time work on the same document, such as video conferencing or shared document editing.By matching your app’s purpose to one of these types, you can more specifically define its scope and technical needs, laying the groundwork for solid development. Having a good grasp of cloud applications, let us contrast them with traditional software to underline their respective strengths.
Key Differences Between Cloud Applications and Traditional Software Applications
Choosing between cloud-based and traditional software comes down to understanding how they differ in critical areas, such as deployment, maintenance, cost, and usability. These differences directly impact how you approach development. While cloud applications offer greater flexibility and scalability, traditional software may still be suitable in tightly controlled or offline environments.
Here’s a breakdown:
Deployment and Setup
Traditional software typically requires installation on local machines or on-premise servers. This involves complex setup, hardware compatibility checks, and manual configuration. Cloud applications, on the other hand, are hosted on third-party servers and can be accessed via a browser or API almost instantly with no local installation or heavy setup required.
Accessibility
Cloud applications work on any device via the internet, making them ideal for remote teams and users in different locations. Traditional software is restricted to the device where it’s installed and often requires additional setup, such as VPNs or remote desktop tools, to extend access.
Maintenance and Updates
With cloud solutions, providers manage all maintenance, security patches, and updates in the background, allowing users to focus on their core business. This frees up internal IT teams to focus on product development. Traditional software places the responsibility on your team, often requiring scheduled downtime, manual updates, and more IT overhead.
Scalability
Cloud apps scale automatically to meet user demand. Whether usage spikes or drops, the underlying infrastructure adjusts accordingly. Legacy software is limited by on-premise hardware, and scaling often means buying and configuring new servers, a slow and costly process.
Cost Structure
Cloud services typically follow a subscription or pay-as-you-go model, enabling businesses to align costs with usage and avoid substantial upfront investments. Traditional software usually involves a hefty one-time licensing fee, hardware costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Collaboration
Cloud applications support real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to edit files or view live dashboards simultaneously. Traditional software often requires manual file sharing or the use of third-party tools, which can slow down workflows and complicate teamwork.
While cloud applications are often the better fit for modern businesses, traditional software still has value in specialized or high-security environments where external connectivity is restricted.
Types of Cloud Applications (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS)
Cloud applications are developed over three main service models: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Each has its own unique functionality, levels of control, and use cases, which influence how you develop. By understanding their use cases and trade-offs, you can select the one that best suits your project’s technical requirements, budget, and long-term objectives.
- SaaS: SaaS is a fully managed software via subscription, requiring no infrastructure management. Users access ready-to-use tools through a browser, ideal for quick deployment. However, customization is limited, making it best for standardized solutions like email or CRM platforms.
- PaaS: PaaS provides a development environment with pre-configured tools, servers, and databases, enabling you to focus on coding rather than managing hardware. It’s suited for custom app development, offering flexibility without the complexity of full infrastructure control.
- IaaS: IaaS refers to virtualized computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking. You have the most control over the environment with IaaS, making it ideal for complex, customized projects that require full configuration and maintenance by a technically capable user.
Your choice comes down to how much you want to control versus how much you want to delegate. SaaS is easy to use, with minimal implementation and no control. PaaS enables you to develop for the cloud while maintaining control, as well as flexibility and scalability to some extent. IaaS can create solutions tailored to your needs, but you will need technical and other expertise to configure and maintain them effectively.
Prerequisites for Building Cloud Applications
Developing a cloud application requires a robust set of skills, tools, and foundational knowledge to ensure success. This preparation involves mastering cloud-specific concepts, programming languages, and technologies, as well as setting up the right environment. By addressing these prerequisites, you can avoid common challenges and streamline your development process.
- Cloud Computing Fundamentals: Understand core concepts like virtualization (abstracting physical servers), distributed systems (coordinating data across multiple nodes), and elasticity (scaling resources dynamically). These principles guide efficient cloud app design and resource management.
- Programming Proficiency: Master languages like Python for data processing, JavaScript for web interfaces, or Java for enterprise systems. These languages are widely supported in cloud environments and offer extensive libraries for rapid development.
- Databases and Storage: Learn to work with SQL databases (e.g., PostgreSQL) for structured data or NoSQL databases (e.g., MongoDB) for flexibility. Familiarity with cloud storage solutions like AWS S3 or Azure Blob Storage is essential for managing large datasets.
- APIs and Microservices: Gain expertise in designing and integrating APIs (REST or GraphQL) to enable communication between app components. Building microservices ensures modularity, making your app easier to scale and update.
- Containerization Technologies: Use Docker to package applications into portable containers and Kubernetes to orchestrate deployments across multiple servers. These tools simplify scaling and ensure consistency across environments.
- Cloud Platform Account: Create an account with a provider like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to access their services, such as computing instances, databases, and monitoring tools. Start with free tiers to experiment cost-effectively.
- Security Knowledge: Study cloud security practices, including encryption (e.g., AES-256), access control via Identity and Access Management (IAM), and compliance standards like GDPR or HIPAA. This ensures your app protects user data and meets regulatory requirements.
Equipping yourself with these skills and tools prepares you for the technical demands of cloud development.
With these prerequisites covered, let us dive into the detailed steps to build your cloud application.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Cloud Applications
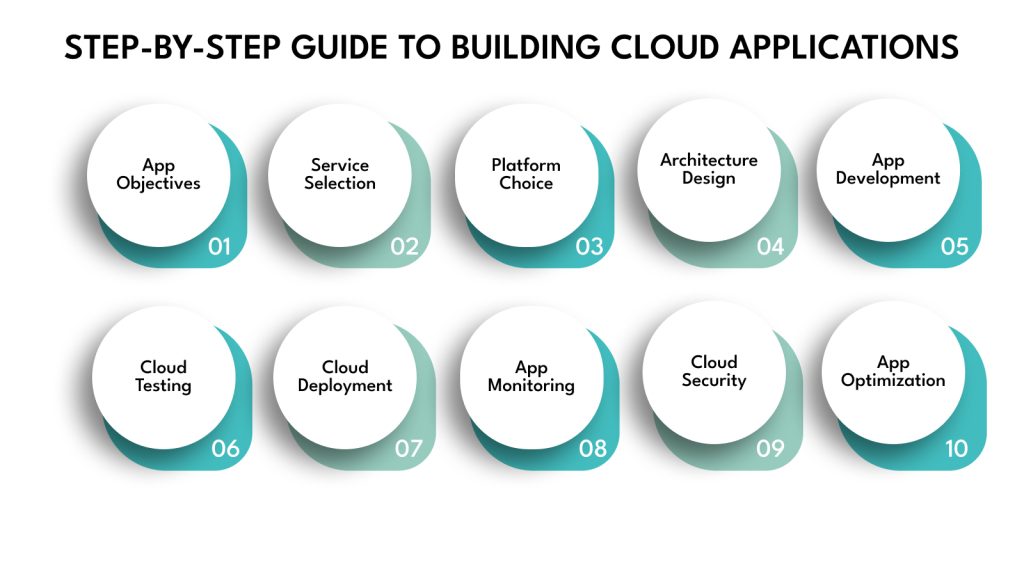
Creating a cloud application involves a structured, ten-step process that guides you from initial planning to ongoing maintenance. Each step addresses critical aspects of development, ensuring your app is scalable, reliable, and aligned with your goals. By following this roadmap, you can build a solution that fulfils current needs and adapts to future challenges.
Step 1: Set Clear Objectives for Your Cloud Application
The first step is to clarify your app’s purpose and objectives. Identify the specific problem it will solve, such as automating a business process or delivering a user-facing service. Set measurable goals, like achieving 99.9% uptime or supporting 5,000 concurrent users. Understanding your target audience’s needs, whether end-users, employees, or partners, shapes your app’s features and user experience. Conduct stakeholder interviews or market research to refine these goals, ensuring alignment with business priorities.
Step 2: Select the Right Cloud Service Model
Selecting the appropriate cloud service model (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) is critical to balancing control, complexity, and speed. SaaS is ideal for off-the-shelf solutions with minimal setup, PaaS suits custom development with managed infrastructure, and IaaS offers full control for complex projects. Assess your project’s technical requirements, team expertise, and timeline. For instance, a small team with limited DevOps skills might prefer PaaS to avoid server management, while a large enterprise might choose IaaS for custom configurations.
Step 3: Select the Cloud Platform
Choosing a cloud provider, such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or others, impacts your app’s capabilities and costs. AWS offers a vast service catalog, including EC2 for computing and RDS for databases. Azure excels in enterprise integrations and hybrid environments, while Google Cloud is strong in AI and data analytics. Evaluate factors like pricing (e.g., pay-as-you-go versus reserved instances), scalability options, global data center availability, and your team’s familiarity with the platform’s tools. Test platforms using free tiers to ensure compatibility before committing.
Step 4: Design the Cloud Application Architecture
A well-designed architecture ensures your app is scalable, resilient, and maintainable. Use APIs (e.g., REST or GraphQL) for component communication, select a database (e.g., MySQL for structured data or DynamoDB for NoSQL) based on data needs, and adopt microservices to break your app into independent, deployable units. Separating front-end (e.g., React) and back-end (e.g., Node.js) enhances flexibility. Plan for fault tolerance with load balancers and redundancy, and consider serverless options like AWS Lambda for cost-efficient scaling.
Step 5: Develop the Application
Set up a development environment with tools like Visual Studio Code, Git, and package managers like npm or pip. Choose languages and frameworks that suit your project: Python with Django for rapid backend development, or JavaScript with React for dynamic front-ends. Follow modular coding practices, document your code, and use linters to maintain quality. Integrate third-party APIs (e.g., Stripe for payments) early to test functionality, and collaborate with your team using Git branching strategies to manage changes.
Step 6: Test Your Cloud Application
Testing ensures your app is reliable, performant, and user-ready. Conduct unit tests to verify individual components (e.g., a login function), integration tests to check system interactions (e.g., API-database connectivity), and performance tests to simulate high user loads. Utilize cloud-specific tools, such as AWS Device Farm for mobile testing or Azure Test Plans for end-to-end validation. Incorporate stress testing to identify bottlenecks and security testing to catch vulnerabilities, ensuring your app handles real-world scenarios effectively.
Step 7: Deploy Your Cloud Application
Deployment brings your app to life. Utilize a PaaS platform like AWS Elastic Beanstalk for straightforward setups or containerized solutions with Docker and Kubernetes for more complex, scalable deployments. Implement CI/CD pipelines using Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Azure DevOps to automate builds, tests, and deployments, reducing errors and speeding up releases. Configure domain settings, SSL certificates, and load balancers to ensure accessibility and performance. Test the deployment in a staging environment before going live.
Step 8: Monitor and Maintain the Application
Ongoing monitoring and maintenance keep your app running smoothly. Use tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Google Stackdriver to track metrics like CPU usage, response times, and error rates. Set up alerts for anomalies, review logs regularly, and schedule updates to address bugs or add features. Implement disaster recovery plans and automated backups to minimize downtime. Regular maintenance ensures your app remains reliable and responsive to user needs.
Step 9: Ensuring Cloud Application Security
Security is non-negotiable for protecting user data and maintaining trust. Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control permissions, encrypt data at rest and in transit using protocols like TLS, and conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities. Use tools like AWS Shield or Azure Security Center to defend against attacks. Stay compliant with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, and train your team on security best practices to minimize risks.
Step 10: Iterating and Improving Your Cloud Application
Continuous improvement keeps your app relevant and efficient. Collect user feedback through surveys or analytics tools like Mixpanel to identify pain points. Monitor performance metrics to optimize speed or resource usage. Add features, scale infrastructure, or refactor code as needs evolve. Adopt an agile approach, releasing updates in small increments to maintain quality and responsiveness, ensuring your app grows with your business.
Conclusion
Building a cloud application is a strategic process that blends planning, technical expertise, and continuous refinement. By following these ten steps, you can create a scalable, secure, and efficient solution that aligns with your business goals and adapts to future demands. Each phase plays a vital role in delivering value to your users.
For expert support in developing your cloud application, partner with DEVtrust. Our experienced developers specialize in crafting custom software solutions designed for your needs, ensuring success at every step. Contact us today to explore how we can help you build a cloud app that drives growth and innovation.
How to Develop a Cloud Application Step-By-Step Guide
Learn how to develop a cloud application with this guide. From planning and designing architecture to deploying on AWS or Azure. Start now!
Contact Us Button