In 2025, a growing number of organizations are making the shift from off-the-shelf learning platforms due to growing priorities and detailed requirements. According to Gartner, about 42% of businesses are dissatisfied with their current LMS tool because of limited functionality, while another 15% complain about inefficiency.
A custom LMS is a solution delivers them with complete flexibility, aligning with their branding, workflows, integration needs, and compliance standards.
Today’s learners expect personalized experiences that match their schedules and learning styles. Trends like microlearning, AI-driven analytics, and seamless collaboration require a system built to your specific needs.
This guide walks you through what custom LMS development involves, why it outperforms pre-built solutions, and how to build, launch, and grow a platform that truly supports your strategy. We shall begin by exploring what custom LMS software development is.
Key Takeaways
- Custom LMS gives you full control over features, branding, and compliance.
- It outperforms off-the-shelf tools when user experience, integrations, or analytics are key.
- Development follows a clear roadmap, from discovery to ongoing support.
- Tech decisions (cloud, database, frameworks, security) shape cost and scalability.
- Choosing the right partner ensures quality, ROI, and long-term alignment.
What Is Custom LMS Software Development?
The global LMS market stands at about $27.09 billion in 2025, all set to grow to $82 billion in 2032. Businesses and learning professionals are increasingly adopting new technologies and software to keep up with this market. Custom LMS software is a leading innovation that ensures personalized learning.
Custom LMS software development means creating a learning platform designed specifically for an organization’s unique needs. It’s about building a system shaped around workflows, content formats, user roles, and integration points that matter most to your business. The goal is to have an LMS that fits like a glove, rather than shoehorning your processes into pre-made software.
Development of a custom LMS involves multiple stages. It usually starts with understanding what learners and admins need. Then it moves into crafting a tailored architecture, designing intuitive interfaces, coding back-end and front-end systems, and testing to ensure everything works seamlessly.
Compliance requirements, such as GDPR or industry-specific standards, are built into the system from the ground up, rather than added as afterthoughts.
What sets custom development apart is its flexibility. In contrast to out-of-the-box platforms, a custom LMS is designed with full control and ownership. You choose how users log in, how data flows, how reporting works, and even how the system scales. Custom LMS solutions also have certain types.
Types Of Custom LMS Solutions
Custom LMS solutions vary widely to fit different organizational needs and deployment strategies. Deciding which type suits you best requires understanding both the depth of functionality needed and the infrastructure model preferred.
By Functional Complexity
Custom LMS platforms can range from delivering basic course content to powering advanced learning ecosystems. At the simplest level, they focus on delivering structured lessons, managing users, and tracking progress.
As complexity grows, so does capability. Advanced systems may include adaptive learning paths, AI-driven content recommendations, certification workflows, and comprehensive analytics dashboards.
By Deployment Model
Equally important is choosing the right deployment infrastructure. A cloud-based model delivers flexibility and ease: the LMS is hosted off-site and managed by your team or an external provider.
On-premise deployment gives you total control over data and system architecture, which is often critical for organizations with strict security or compliance needs. Hybrid models blend the benefits of both, allowing sensitive data to stay in-house while other components run in the cloud.
By Learning Scenario
This classification looks at the context in which the LMS will operate. An internal training LMS focuses on employee onboarding, upskilling, or compliance-based learning. These systems often align with the HR or operations ecosystem of a company.
Meanwhile, an extended enterprise LMS is built to train users outside the organization, like partners, customers, or franchises. There are also academic LMS systems, commonly used by educational institutions, with unique needs for grading, assessments, and curriculum planning.
Choosing the right type, based on functional demands and hosting architecture, is a strategic decision. DEVtrust helps clients balance these factors.
Both high-powered training platforms and secure on-premise environments require aligning the design with the operational context. This ensures your LMS is built for both current goals and future growth. Moving on, we have some key features in a custom LMS.
Key Features of Custom LMS
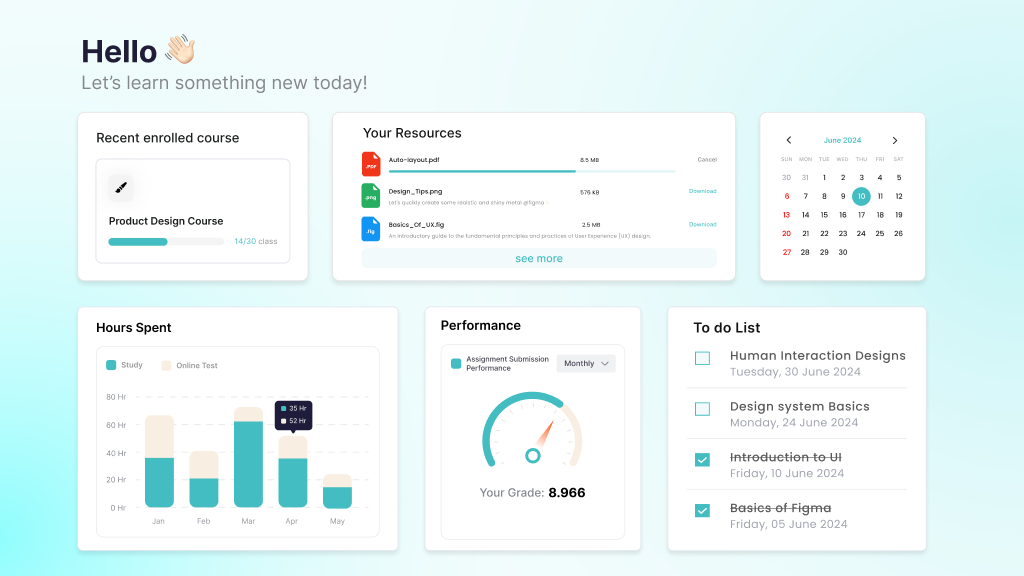
Custom LMS platforms are powerful when built to serve specific learning goals. These systems deliver key features that ensure engagement, compliance, and data-driven insights. Let’s explore the core capabilities that make a tailored LMS truly effective.
Course Management
A strong custom LMS enables smooth creation, organization, and delivery of content. This means structuring courses into modules, tracking progress, and managing enrollments.
Administrators and learners benefit greatly from intuitive content management and role-based access controls. When the onset clearly reflects an organization’s structure, usage increases, and efficiency improves.
Analytics & Reporting
Real insight comes from understanding how users engage and perform. Learning analytics frameworks combine human-centered design with visual dashboards to improve decision-making.
Custom reporting features help measure progress, identify knowledge gaps, and monitor completion trends. Powerful analytics make your LMS a tool for ongoing improvement.
Content Editing
An effective LMS must include internal tools that simplify content creation and updates. Administrators or instructional designers can edit text blocks, quiz questions, and multimedia without coding. A user-friendly WYSIWYG editor saves time and enables fast updates, keeping learning materials fresh and accurate.
Multi-format Content Support
Users consume learning in many forms. A custom LMS accommodates text, video, audio, SCORM packages, and interactive modules. Diverse formats serve different learning styles and enrich engagement. Being able to embed quizzes, podcasts, and documents in a single platform enhances flexibility.
Learning Object Repository
A centralized library of reusable content items adds scalability and consistency. Learning Objects are tagged and stored in a repository for easy reuse across courses. This modularity reduces duplication and simplifies updates. When an object is updated, the change applies wherever it appears.
Content Access
Ease of access boosts completion rates. Learners expect consistent availability across devices and offline access when the internet fails. Mobile-friendly interfaces and synchronized progress across platforms ensure uninterrupted learning. Secure access control enables content delivery per role or group.
By designing these key features, custom LMS platforms become more than just content hubs. They transform into dynamic ecosystems that adapt to learner needs, integrate with enterprise systems, and offer measurable outcomes.
DEVtrust leverages these capabilities to create platforms tailored to both immersive learning experiences and organizational strategy. Let us move on to know about the essential integrations for Custom LMS.
Core Integrations For Custom LMS
A custom Learning Management System (LMS) becomes far more capable when it connects seamlessly with other enterprise platforms. Integrations drive automation, personalize learning, and deliver strong ROI. Below are four critical integrations to consider.
HR Software
Integrating HR systems allows learner data to flow automatically into your LMS. When a new employee is added, their training account can be created instantly. Changes in role or status require them to update their learning assignments accordingly. This synchronization cuts manual tasks and keeps training aligned with job needs.
CRM
Connecting your LMS with a CRM lets you align sales or customer service training with real-world outcomes. Course completion, certifications, and learning paths can be tied to opportunity pipelines and customer segments. This dual visibility helps managers assign targeted training and track business impact.
CMS
A CMS integration makes content management simple and centralized. Training modules, documents, and media files are stored on one platform. The LMS can pull updated content automatically. This reduces duplication and ensures learners access the latest materials.
Social Media
Social integrations promote community and engagement. Learners can share badges or achievements on social networks. Discussion forums or comment threads within the LMS can link to enterprise collaboration platforms. This fosters peer learning, recognition, and real-time interaction.
Video Conferencing
Live sessions and virtual classrooms are standard features that many learners expect. Linking your LMS with tools like Zoom, Teams, or Webex allows scheduled, recorded, and interactive sessions. Real-time chat, polls, and breakout rooms promote engagement while attendance tracking ensures accountability.
By integrating HR software, CRM systems, CMS platforms, video conferencing, and social media tools, your custom LMS becomes a central hub. It becomes smarter, more streamlined, and better at driving retention and performance.
So, how does one implement custom LMS software development? Let us find out next.
Custom LMS Software Development Roadmap
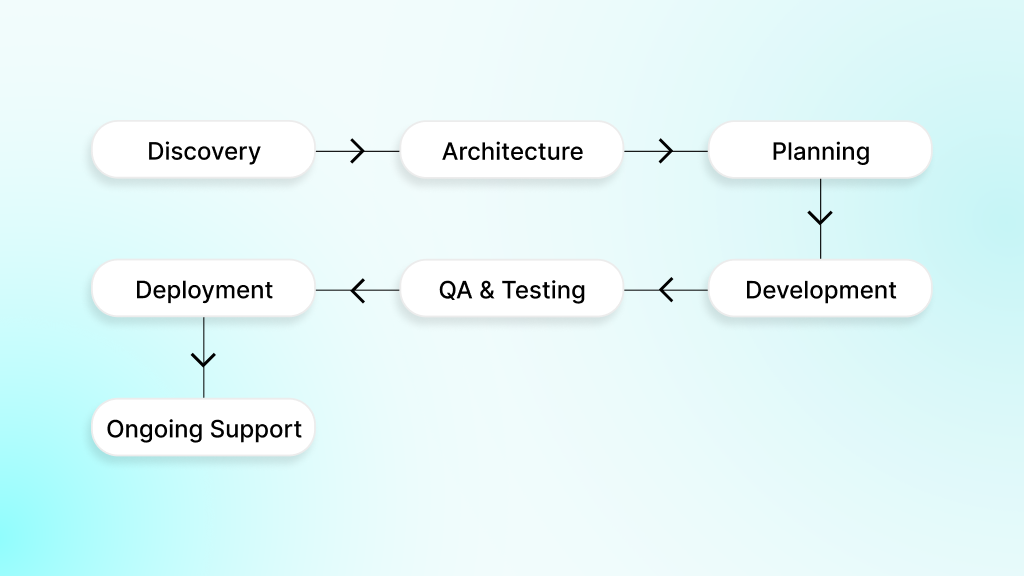
Building a custom LMS demands careful planning and a structured approach. A well-defined roadmap guides your project from initial discovery through deployment and ongoing support. Following a phased plan ensures alignment with business goals and delivers a system that users love.
1. Discovery & Requirements
Every successful LMS begins with a clear understanding of stakeholder needs. You start by defining objectives, conducting user and needs analysis, and documenting functional requirements in detail.
Defining clear goals and understanding your current capabilities provides a strong foundation for project scope and design. This phase also engages key stakeholders so everyone is aligned before development begins.
2. Architecture & Design
With requirements in hand, you move on to designing both the technical and visual structure of the LMS. Technical architects choose the tech stack, deployment model, and database schema. UX designers create wireframes, prototypes, and flows that match user expectations.
This dual effort ensures that the system is both structurally sound and intuitive to use. There is also great importance in designing architecture early on to support performance, scalability, and usability.
3. Planning & Backlog
Once the design is approved, it’s time to create a development plan. This includes breaking down features into user stories, estimating effort, and setting milestones.
Key tasks are assigned to sprints, with priorities set based on impact and risk. Establishing clear timelines and responsibilities here helps manage scope and ensures accountability throughout the process.
4. Front-end / Back-end Development
This phase brings the LMS to life, building both the user-facing interface and the server-side infrastructure. Front-end developers work on responsive dashboards, course interfaces, and user flows.
Back-end engineers implement authentication, content management, integrations, reporting, and data handling. It’s essential to maintain collaboration between both sides to ensure seamless end-to-end functionality.
5. QA & Testing
Quality assurance validates that front-end and back-end components perform as expected. Manual testing covers areas like usability, data flow, and compliance. Automated tests, such as unit, integration, and regression, catch bugs early.
Running a pilot or beta release gathers real user feedback before full launch. Best practices call for layered testing to avoid defects slipping into production.
6. Deployment & Training
During deployment, the LMS moves from staging to production environments. This often includes setting up CI/CD pipelines for smooth transitions.
Once live, user training begins. Admins, instructors, and learners receive guidance through workshops, documentation, and support channels. Successful onboarding relies on clear roles, tutorials, and accessible support.
7. Ongoing Support
Post-launch, continuous maintenance, updates, and performance monitoring are essential. This phase also includes periodic reviews and iterative improvements based on user feedback.
A strong support team addresses bugs, adds new features, and ensures the platform scales with user needs. Comprehensive support means the LMS grows alongside your organization.
A clearly defined development roadmap helps manage expectations and resources effectively. Each phase builds on the last, creating a reliable path from concept to a fully supported custom LMS that evolves with your needs.
Meanwhile, behold some technical considerations and know the tech stack for custom LMS software development.
Technical Considerations & Tech Stack For Custom LMS Software Development
Choosing the right technology foundation is crucial for building a custom LMS that can grow with your organization. Your decisions around hosting, data storage, frameworks, and security determine performance, reliability, and user trust. Let’s explore each consideration in depth.
Cloud Choices
Modern LMS platforms often leverage cloud services for flexibility and scalability. Cloud-hosted systems allow teams to easily adjust resources as user demand rises. Platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud support auto-scaling, load balancing, and global content delivery networks (CDNs).
Research into cloud database usage, such as the Taurus system, shows how modern architectures use separate compute and storage layers to enhance performance and availability. These design strategies make a cloud-based LMS resilient under heavy loads and ready for expansion.
Database Strategies
Selecting the right database is critical to efficiently managing user data, course content, and analytics. Common options include relational systems like MySQL or PostgreSQL and NoSQL databases like MongoDB.
A scalable LMS must support both structured and unstructured data, with features like regular backups, disaster recovery, and row- or schema-level data separation for multi-tenant systems.
For secure multi-tenant setups, MySQL offers isolation methods such as separate schemas and row filtering. These strategies help you find the right balance between performance, security, and maintainability.
Front-end & Back-end Frameworks
The front end of a custom LMS should be intuitive and responsive. React, Angular, or Vue are excellent choices for building interactive user interfaces.
For server-side logic, back-end frameworks such as Django, Laravel, Ruby on Rails, or Node.js help manage authentication, content workflows, and dynamic reporting.
Using mainstream, well-supported technologies ensures access to strong developer communities and up-to-date resources. Your framework selection affects the speed of development, system consistency, and ease of future updates.
A thoughtful tech stack balances user experience with performance, security, and future growth. It supports clean code, strong developer support, and adaptability.
This is where DEVtrust shines, by matching technical setup to your needs and building efficient, future-ready LMS platforms. Users shall also keep an eye for challenges and risks associated with custom LMS software development.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Custom LMS Software Development
Building a custom LMS is an exciting opportunity, but it comes with its share of challenges. Knowing what lies ahead can help you navigate the project smoothly. Below, we explore the primary risks you should prepare for.
Complexity
Custom LMS projects involve balancing many moving parts. Every role, permission level, learning path, and integration adds complexity.
LMS environments are inherently complex techno-social systems, requiring detailed governance and policy design to function effectively. Failing to account for this upfront invites feature creep and structural misalignment.
Timelines
A custom LMS timeline can stretch quickly without clear control points. Studies emphasize that projects lacking formal stakeholder involvement and milestone checks often fall behind.
Delays often stem from late stakeholder feedback or unclear dependencies across modules. It’s essential to build in buffer time and clear review cycles early on.
Adoption Hurdles
Even well-built LMS platforms can fail if users don’t engage. Studies from Egyptian universities highlight that LMS adoption often stalls due to poor user acceptance and limited training.
Resistance often stems from unfamiliarity, low ICT confidence, or misaligned workflows. Addressing this requires early planning for training, change management, and ongoing support.
By anticipating these areas, you position your project for success. DEVtrust helps clients navigate these precisely, ensuring thorough planning, user engagement, and robust integration strategies. But what drives the cost of custom LMS software development?
Custom LMS Software Development Cost Drivers
A custom LMS project’s budget isn’t determined just by development hours. It’s shaped by key decision points that define the system’s scope, requirements, and long-term strategy. Understanding these drivers helps you make informed choices and avoid surprises.
Feature Scope
The range and depth of features you include directly influence effort and cost. A core LMS might offer user management and progress tracking.
As you add adaptive learning paths, AI recommendations, or advanced certification workflows, the scope grows.
Market research indicates that expanding the feature set is one of the strongest predictors of project effort. Each added capability not only requires development time but also impacts testing, documentation, and maintenance.
Integrations
A custom LMS often needs to communicate with external systems like HR platforms, CRMs, e-commerce tools, or authentication services. Each integration adds complexity.
Aligning data models, managing API changes, and maintaining secure connections take time and expertise. Reports consistently flag third-party integration as a major cost driver because each interface requires mapping, testing, and ongoing monitoring.
Compliance
For industries like healthcare, finance, and corporate training, compliance isn’t optional. You might need to support GDPR, HIPAA, or data residency rules. This means adding features for encryption, audit trails, and role-based permissions.
Compliance-related development adds upfront effort and requires specialist knowledge. Case studies in regulated LMS environments consistently highlight compliance as a significant contributor to cost.
Deployment
Where and how you host your LMS shapes the cost as well. Cloud deployment offers flexibility and easier scaling, but comes with usage-based fees.
On-premise installations shift costs into internal infrastructure, security, and dedicated IT management. Hybrid models, offering both centralized and localized control, compound these costs. Market forecasts show that the deployment strategy has a direct impact on total project investment.
Here is a table showing typical cost ranges associated with each driver based on real-world LMS projects:
| Cost Driver | Impact on Budget | Estimated Range (USD) |
| Feature Scope | 30 %–50 % | $75,000–$250,000 (features vary widely) |
| Integrations | 20 %–30 % | $50,000–$150,000 (API mapping + testing) |
| Compliance | 10 %–20 % | $25,000–$100,000 (encryption, audit, policies) |
| Deployment | 10 %–20 % | $25,000–$150,000 (cloud, on‑prem, hybrid) |
By recognizing how these drivers elevate scope and cost, you gain visibility into where your investment is going. This enables a modular, phased approach. DEVtrust advises users to prioritize these drivers early to set realistic budgets and timelines. Let us move on to know the custom LMS software development methodologies.
Custom LMS Software Development Methodologies
Choosing the right methodology for your custom LMS project sets the tone for success. It shapes collaboration, iteration cycles, and the ability to adapt over time. There are two proven methodologies that align well with modern LMS needs.
Agile methodologies include Scrum, Kanban, and Lean.. They encourage flexibility and collaboration. They break work into manageable chunks, often called sprints. This structure allows continuous feedback from learners, instructors, and admins.
Agile approaches improve team communication, responsiveness, and software quality. Agile frameworks fit LMS projects well because they support frequent adjustments based on real user feedback.
Lean software development offers another layer of efficiency. It focuses on eliminating unnecessary steps and empowering teams to innovate.
In a custom LMS context, this might mean prioritizing only essential learning features first and releasing quickly. Teams then refine the system based on user habits and needs. Lean thinking ensures the final product is valuable without waste.
Maintenance, Scaling, & Upgrades For Custom LMS Software Development
Launching a custom LMS is the beginning of a continuous journey. Post-launch maintenance, scaling, and iterative upgrades ensure your platform remains valuable over time.
Maintenance includes regular bug fixes, security patches, and compatibility checks with browser or system updates.
Without a maintenance plan, even small issues can disrupt learning experiences. This phase also includes periodic performance testing and cleanup to prevent technical debt from slowing the system.
As your user base grows, you’ll need efficient scaling. This could mean optimizing database queries, adding caching layers, or increasing server capacity.
Often, cloud architectures enable smooth resource scaling without downtime. Monitoring tools then help you identify performance bottlenecks and plan upgrades proactively.
Beyond stability, upgrades become vital to stay current. You may need to add new modules, adjust compliance features, or integrate third-party tools.
An effective practice is to bundle upgrades into manageable releases, informed by user behavior and feedback. A combined strategy with built-in maintenance, capacity planning, and scheduled enhancements ensures your LMS remains responsive and future-ready.
How To Choose The Right Custom LMS Software Development Partner
Selecting a development partner is one of the most important decisions in a custom LMS project. Your choice affects the quality of features, the reliability of the system, and the future adaptability of your investment. The partner you select will shape not only the initial build but the ongoing experience of both admins and learners.
LMS Experience
Experience matters when it comes to LMS development. The best partners have built multiple learning platforms. This experience gives them insight into feature choices, compliance challenges, and user needs.
Experienced teams are needed to understand stakeholder roles, workflows, and pain points early on. Choosing a partner with this background increases your chance of launching a system that meets real-world needs.
DEVtrust holds profound experience in the EdTech sector. From having formulated online quiz platforms for autistic learners and e-learning systems with AI enhancements, we understand the current LMS demands to the core.
Tech Skills
It’s not enough to say someone writes clean code. Look for partners who can design scalable architectures, handle security, and manage integrations.
High-quality software teams built trust, coordinated expertise, and assimilated technical insight, making them more likely to deliver performant systems. Ask potential partners how they design for scale, encryption, and long-term maintenance.
E-Learning UX Sense
A custom LMS must be intuitive for learners and admins alike. The partner should demonstrate strong UX credibility.
They need to know how to design flows for course creators, instructors, and multiple user types. A partner with instructional design or e-learning experience will help drive engagement and satisfaction.
Stakeholder Alignment
Successful LMS projects keep users, instructors, IT, and compliance stakeholders in sync. Studies show that stakeholder analysis is essential in avoiding misalignment and adoption issues.
A good partner will involve these groups early and often, use workshops, and validate progress through demos.
Ongoing Support
Custom platforms require long-term care. After launch, there will be bug fixes, hosting issues, and evolving needs. Your partner should offer clear support tiers and fast responses.
Ask about maintenance practices, patch schedules, and what support looks like six months out. A true partner stays engaged throughout your LMS’s lifecycle.
By evaluating these five areas, you’re better positioned to choose a partner who will help your custom LMS sustain at launch and beyond.
Conclusion
Custom LMS development offers the flexibility and control that standardized platforms simply cannot match. From feature design and tech choices to integrations and ongoing support, every decision shapes the significance of your investment.
By following a clear roadmap, anticipating challenges, and selecting the right development partner, you ensure your LMS is tailored to your learners’ needs, your organizational goals, and future growth.
Ready to explore your options in custom LMS software development? Talk to DEVtrust to explore how a custom LMS can transform learning in your organization.
A Complete Guide To Custom LMS Software Development In 2025
Explore Custom LMS software development for 2025. Compare options, explore key features, roadmap, tech tips, and choose the right partner for long-term success.
Contact Us


