Modern applications are rarely standalone. They often consist of microservices, serverless functions, and SaaS integrations. AWS offers a powerful suite of services to connect these components, eliminating the need for custom middleware.
We understand that navigating the complexity of integrating diverse components can feel overwhelming and daunting, especially when aiming for scalable and resilient architectures.
With the right AWS integration approach, you can improve system resilience, accelerate feature delivery, and simplify operations. This blog walks you through the available strategies, key services, and best practices. You will leave with a clear roadmap to move towards seamless connectivity. But first, let us understand what AWS integration services are.
Key Takeaways
- AWS integration services enable scalable, decoupled communication without custom code.
- Select between API-driven, event-driven, or orchestration strategies based on use case.
- Core services, like API Gateway, SNS/SQS, EventBridge, Step Functions, and Lambda, address distinct integration patterns.
- Follow best practices: decoupling, security, managed services, and observability.
What Are AWS Integration Services?
When architects build modern applications, they often use multiple, decoupled components like microservices, serverless functions, and external SaaS platforms. AWS Integration Services form the glue that connects these parts. These fully managed services ensure that each component can communicate reliably, without needing custom code or middleware. By using AWS’s managed tools, teams focus on core business logic instead of building and maintaining integration layers.
AWS itself outlines this clearly on its product page. It explains that integration services let distributed systems and serverless apps communicate with minimal custom code.
They preserve flexibility through components that can evolve independently without affecting the entire system. In essence, AWS Integration Services simplify coordination among services, handle failure scenarios automatically, and reduce manual deployment and scaling tasks.
Beyond simplifying logic, these services also provide operational advantages. AWS-managed integrations automatically scale to accommodate traffic changes. They store messages across availability zones to ensure reliability. This lets teams confidently design resilient systems without worrying about message loss or manual failover.
The end result is clear: faster development cycles, improved fault tolerance, and reduced operational load, all critical in today’s distributed application context. Now, why do AWS integration services matter?
Why AWS Integration Services Matter
Choosing the right integration method is fundamental for modern, decoupled systems. The right strategy ensures your services can grow, adapt, and perform reliably. Below, we highlight two critical impact areas.
Enabling Service Communication At Scale
AWS integration services are designed to allow services to interact without being tightly linked. When one part of the system fails or spikes in usage, the rest continues working smoothly.
According to AWS documentation, these services support automatic scaling and cross-zone resilience, giving developers the confidence that their systems will not collapse under load.
In practice, this means teams can design architectures that respond to variable demand, such as flash sales or global launches, without custom middleware or heavy operational effort.
Improves Release Velocity And Maintainability
Integration via AWS reduces manual integration labor. You no longer need to write and maintain custom code just to connect systems. AWS states that application integration “[reduces] code that may be repeated in your microservices and functions.
This saves time on debugging and deployment. Teams can push updates faster, often with less risk. In our experience, professional AWS integration drives cleaner code structure and smoother change management.
When architectures follow these patterns, teams can innovate confidently and release features more rapidly.
Meanwhile, it is important to choose the right AWS integration strategy.
Choosing The Right AWS Integration Strategy
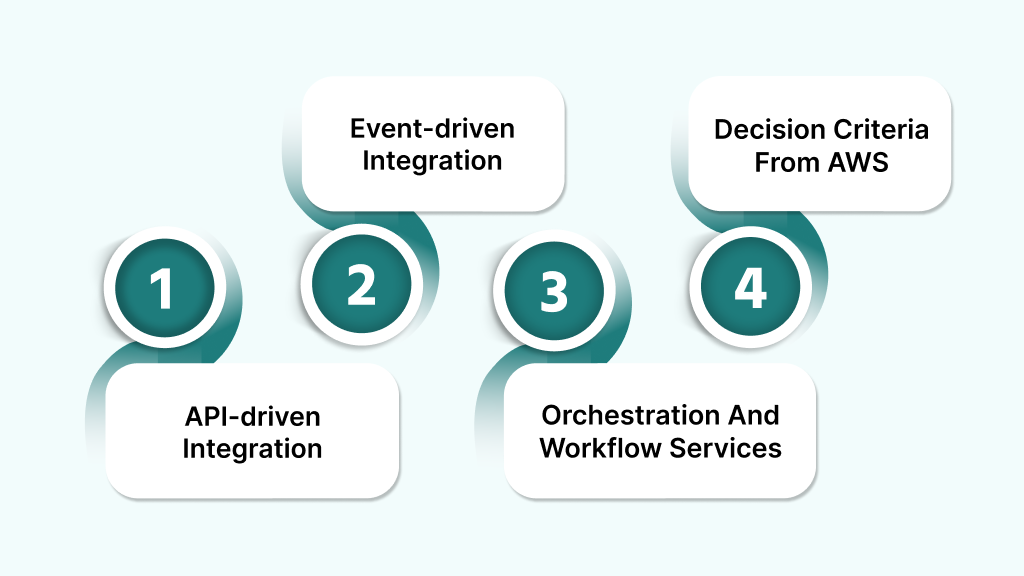
Integrating distributed systems on AWS requires choosing the right pattern based on your architecture and requirements. Each strategy offers distinct benefits and trade-offs. Selecting wisely ensures reliability, performance, and simplicity.
API-driven Integration
API-driven integration is ideal when you need synchronous interactions between services. Tools like Amazon API Gateway, AWS AppSync, or AppFlow provide REST or GraphQL interfaces. These services abstract the complexity of exposing endpoints, handling authentication, and managing rate limits.
From an expert standpoint, this strategy suits applications with real-time user interactions or CRUD operations. Fine-grained control over API monitoring and governance adds transparency to system behavior.
Event-driven Integration
Event-driven integration allows components to react to changes through messages. Services publish events to solutions such as SNS, SQS, or EventBridge. Consumers process these events without blocking. AWS defines event-driven architecture as using events to trigger and communicate between decoupled services, which enhances resilience by isolating failures and supports independent scaling through asynchronous processing.
In practice, this model excels in distributed systems where upstream and downstream systems must stay loosely coupled yet responsive. It fits well for order processing, notifications, and asynchronous workflows.
Orchestration And Workflow Services
Orchestration works best when coordination across multiple steps is needed. AWS Step Functions models multi-step processes with branching, retries, and error handling.
A workflow can include API calls, Lambda functions, or other service invocations. Experts prefer this for complex business logic that requires state management and visibility. It offers a clear visual representation of flows and makes debugging easier.
AWS also supports orchestration through pub/sub patterns, often a companion to event-driven integration. Using orchestration, you can structure critical processes for clarity and resilience, while still benefiting from decentralization.
Decision Criteria From AWS
To choose the right model, AWS recommends analyzing these key factors:
- Latency and interaction style: Will your components need instant response, or can they process information asynchronously?
- Event volume and scaling: Do you need to handle sudden bursts or regular traffic patterns?
- Workflow complexity: Does your process require multiple steps, state tracking, or retries?
- Error handling: How important is coordination in recovery or rollback?
- Design visibility: Do you need dashboarded flows versus simple messaging?
AWS’s official decision guide outlines these criteria, helping you map requirements to integration patterns. From an expert perspective, following such guidance early helps avoid costly refactors and misses in system reliability.
By partnering where architectural clarity matters, like at DEVtrust, you gain assurance that integration choices align with your business needs. Moving on, there are some key AWS services one should know about.
Key AWS Services For Integration

Selecting the right AWS service for your integration needs is crucial. Each service in the AWS application integration suite plays a specific role. They let you build reliable, scalable, and maintainable systems with clear responsibilities.
Amazon API Gateway & AWS AppSync
Amazon API Gateway and AppSync provide managed entry points for APIs. API Gateway supports REST, WebSocket, or HTTP endpoints. It handles routing, authentication, throttling, and monitoring.
You can integrate it directly with downstream services like SQS or Step Functions, bypassing custom middleware. AppSync offers real-time GraphQL APIs, connecting to databases and microservices without custom resolvers. These tools provide consistency and ease when managing API-based communication.
Amazon SNS & SQS
SNS and SQS are core to message-based integration. SNS delivers messages to multiple subscribers instantly. It supports use cases like alerts or notifications.
SQS provides durable queues for reliable, decoupled delivery across services. SNS can also forward messages to SQS, Step Functions, or EventBridge. Together, they enable scalable, resilient, and decoupled messaging architectures.
AWS EventBridge
EventBridge offers advanced event bus features. It can receive events from AWS services, your own applications, or SaaS providers.
With sophisticated routing rules, it sends events to targets like Lambda, SNS, or Step Functions. This enables event-driven architectures that scale without custom routing. EventBridge reflects AWS’s evolution toward managed, serverless integration.
AWS Step Functions
Step Functions provide visual workflow orchestration. They can coordinate APIs, Lambdas, service integrations, and SDK calls for over 200 AWS services.
With branching, retries, and state tracking, Step Functions are ideal for complex processes. They reduce custom state management and simplify modern distributed logic.
AWS Lambda
Lambda offers serverless compute triggered by other services. It plays an essential role in integration workflows. You can invoke Lambda from API Gateway, SNS, SQS, EventBridge, or directly from Step Functions.
Lambda handles data transformation, enrichment, and orchestration steps. It is the glue for connecting different services and systems while keeping infrastructure minimal and responsive.
Here is a tabulation of these AWS services and how they apply in real time:
| AWS Service | Primary Use Case | Capabilities |
| API Gateway & AppSync | Real-time API communication | REST/HTTP endpoints, authentication, throttling, monitoring, and GraphQL support |
| SNS & SQS | Pub/sub messaging and queue-based decoupling | Topic-based delivery, durable queues, cross-service integration |
| EventBridge | Event routing across services and SaaS integrations | Schema-based routing, SaaS support, scalable event buses |
| Step Functions | Workflow orchestration across AWS services | Visual workflows, state tracking, retries, AWS SDK actions |
| Lambda | Serverless compute for transformation and triggers | Event-driven execution, lightweight compute, seamless AWS integration |
This tabular overview helps you match each AWS service to specific integration scenarios. No matter if you need synchronous APIs, asynchronous messaging, event routing, or workflow orchestration, AWS offers managed tools to simplify architecture. So, how to get started with application integration on AWS?
Getting Started With AWS Integration: Steps of Application Integration on AWS
Every successful AWS integration project begins with a structured, expert-led process. From understanding your system to deploying the integration and validating workflows, these steps ensure a reliable, scalable architecture. Here is a framework aligned with AWS’s official guidance:
Analyzing Your Existing Applications
Start with a deep dive into the architecture and behavior of the apps you plan to integrate. Determine what parts rely on APIs, what legacy constraints exist, and where potential bottlenecks lie.
AWS encourages this initial assessment to uncover operational responsibilities and highlight areas best suited for managed integration services versus self-hosted solutions. This analysis lays the foundation for choosing the right tools and patterns.
Defining Integration Goals and Requirements
Once you have a clear view of your system, outline your integration goals. This could include improving uptime, handling high event volume, or simplifying workflows.
AWS recommends documenting latency tolerance, error recovery needs, and the volume of exchange in business terms. Establishing these targets early aligns your architecture with real-world priorities and avoids scope creep during implementation.
Designing the Integration Architecture
In this phase, architects sketch how components will communicate. You will decide whether to use API Gateway, SNS, EventBridge, Step Functions, or a combination.
AWS suggests mapping data flows, handling transformations, and planning security and scaling for high availability. A well-designed integration blueprint translates directly into faster development and clearer hand-offs between teams.
Implementing and Testing
Next comes the build phase. Implement API endpoints, set up event buses or queues, and deploy orchestration workflows. AWS stresses the importance of complete observability, which includes enabling CloudWatch logs, tracing, and metrics from day one.
Then, test thoroughly: simulate spikes, validate failover scenarios, and confirm end-to-end message handling. This step ensures your integration layer is both resilient and efficient.
Launching and Measuring Success
After deployment, shift focus to monitoring performance and validating goals. Track error rates, latency, delivery times, and business KPIs linked to integration, like order fulfillment time or data sync accuracy.
AWS encourages setting up metrics aligned with your defined goals. At this stage, you may plan improvements, such as adding retry policies, refining routing rules, or introducing new services as use cases grow.
This five-step method provides an expert-level approach to applying AWS integration services correctly. It is a framework that enables teams to build reliable, scalable, and future-ready systems.
When paired with technical oversight, like that offered by DEVtrust, organizations gain confidence in execution and clarity in outcomes.
Know more about how DEVtrust helped Moveit4U gain supply‑chain visibility, thanks to tailored API orchestration and full traceability. In the process, do not lose sight of some best practices for AWS integration.
Best Practices For AWS Integration
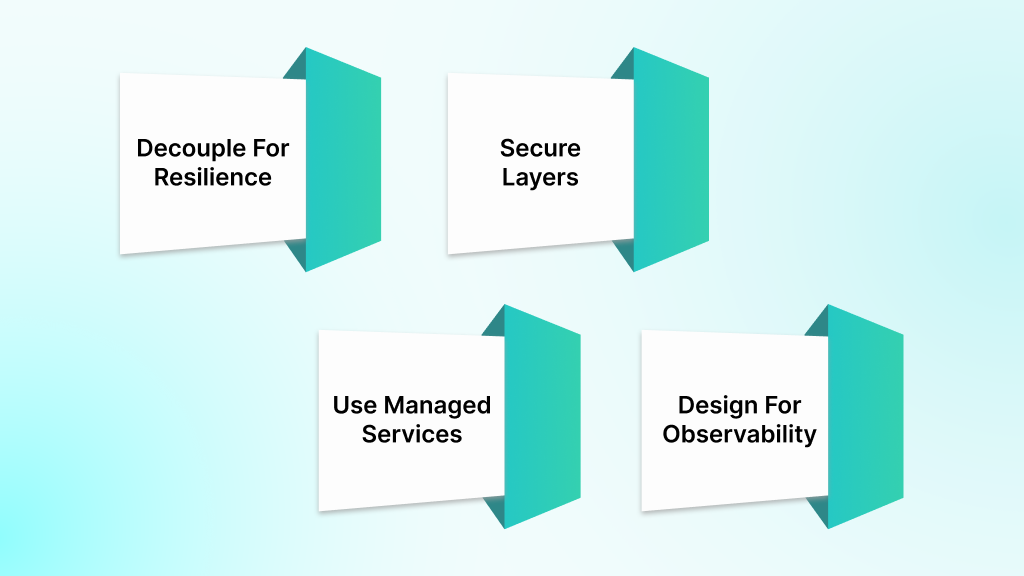
Building reliable and secure systems on AWS starts with strong practices. These ensure your integrations remain scalable, safe, and maintainable. The following expert guidelines draw from AWS’s best-in-class recommendations and real-world architecture experience.
Decouple For Resilience
Decoupling services helps isolate faults and reduce dependencies. AWS’s Well‑Architected Framework specifically advises implementing loosely coupled components, like using queues, event streams, and workflows to shield one component from failures in another.
As experts, we design systems so that each part functions independently. That way, one failure does not bring everything down. Loose coupling also simplifies updates, scaling, and monitoring over time.
Secure Your Integration Layers
Security must be central to any integration design. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) best practices include using short-lived credentials and regional endpoints.
This reduces risk and limits the exposure window. As integration layers connect services, applying least-privilege access, encryption in transit, and strict authentication ensures that only intended communications occur. That builds trust and shields your system from unauthorized access or data leaks.
Use Managed Services To Reduce Overhead
Favoring AWS-managed integration tools shifts the heavy lifting to AWS. Managed services reduce your operational responsibilities, letting AWS handle scaling, patching, and availability.
This means fewer maintenance tasks and a lower risk of configuration errors. Using services like SNS, EventBridge, and Step Functions frees your team to focus on business logic, not infrastructure upkeep.
Design For Observability And Monitoring
Effective observability ensures you can understand and act on system behavior. AWS’s Monitoring & Observability guide recommends capturing metrics, tracing, and logs across workload events to detect and respond to issues quickly.
In practice, that means enabling CloudWatch, X-Ray, and structured logging from day one. This level of visibility supports performance tuning, debugging, and compliance, especially in distributed environments.
By integrating these expert practices, you elevate the quality and durability of AWS-backed systems. This foundation supports growth, resilience, and efficient operation over time. AWS integration holds some interesting use cases in the real world.
Real‑world AWS Integration Use Cases
Seeing theory in action helps solidify strategy. Below are three expert-level AWS integration use cases. Each showcases how specific patterns and services solve real business problems.
Serverless Workflows
In high-scale environments, serverless workflows empower teams to build reliable systems with minimal infrastructure overhead. AWS’s documentation highlights applications from mobile back-ends to IoT pipelines that scale automatically when demand spikes, yet cost near zero during idle periods.
In practice, this architecture suits scenarios like image processing or batch jobs, where components trigger via API Gateway, flow through Step Functions, and run with Lambda. The result: systems that adapt to demand while minimizing cost and administrative burden.
SaaS Ingestion With EventBridge
Modern apps often need to integrate data from external SaaS providers. EventBridge provides a serverless event bus that seamlessly ingests and routes SaaS events, such as ticket updates or CRM changes, into AWS services or Lambda functions.
This approach eliminates custom polling or middleware. Teams benefit from built-in routing rules, transformation, and security. It is ideal for use cases like syncing Zendesk tickets or handling payment notifications from Stripe, without managing code or infrastructure. Know how DEVtrust helped Inflated achieve data accuracy using seamless CRM‑to‑ERP sync.
Legacy App Modernization
Updating monolithic or batch-based systems to modern architectures is a challenge for many enterprises. AWS Step Functions and Lambda together enable gradual refactoring of legacy workflows, without requiring a full rewrite.
For example, moving scheduled data jobs into Step Functions can automate retries, parallelization, and observability. Businesses can see a reduction in operational costs and great performance gains using event-driven serverless workflows. This pattern allows modernization with minimal risk and incremental value delivery.
These integration patterns demonstrate real AWS-driven transformation. Each uses managed services to reduce complexity, improve resilience, and accelerate delivery. When combined with expert architectural guidance from DEVtrust, these patterns translate into a tangible business impact.
How DEVtrust Adds Value to Your AWS Integration Journey
AWS integration is about designing systems that scale, adapt, and stay secure over time. Organizations often struggle to choose the right tools, align architecture with business needs, and maintain those connections effectively.
That is where DEVtrust makes a real difference. With a deep understanding of AWS’s native services, DEVtrust helps teams move from architectural ambiguity to stable, maintainable integrations.
You may be modernizing a legacy system, building event-driven apps, or streamlining SaaS communication; whichever it is, DEVtrust delivers with precision.
Our approach focuses on upfront clarity, secure automation, and continuous optimization. We do not just deploy infrastructure; we ensure the integration layer supports long-term performance and operational simplicity.
What DEVtrust brings to the table:
- Architecture planning based on AWS’s decision frameworks
- Implementation using native tools like API Gateway, EventBridge, and Step Functions
- Secure access control, IAM policy configuration, and encryption best practices
- CI/CD setup for integration deployments and automated updates
- Monitoring, alerting, and lifecycle optimization through CloudWatch and X-Ray
With DEVtrust, AWS integration becomes a clear, guided process, not guesswork. Talk with DEVtrust to move faster, stay compliant, and build the kind of backend architecture that supports your digital ecosystems.
AWS Integration Services: Choosing The Right Strategy For Seamless App Connectivity
Explore AWS integration services along with strategies, tools, best practices, and how you can build scalable connectivity on AWS for modern applications.
Contact Us