When it comes to choosing a programming language, developers often face a critical decision: Python or Java? Both have their strengths, but choosing the right one can shape your project. We understand how overwhelming this can be. There are many factors to consider, such as speed, readability, learning curve, and project type, which can make it difficult to decide where to start.
Python has been dominating the programming world in 2025, holding a 25.87% share in the TIOBE Index. Java, with 8.84%, remains the fourth most popular language. However, this shift in popularity does not necessarily mean Python is the right fit for your specific project or development needs. The decision should be based on what works best for your goals, whether it is ease of use, performance, or scalability.
This blog will help you make a strategic choice by exploring key differences between Python and Java. We will cover their features, use cases, syntax, performance, and more. You will get a clear understanding of which language fits your development goals.
Key Takeaways
- Python thrives in rapid development, particularly in AI (Artificial Intelligence), Machine Learning (ML), and data science, due to its flexibility and simplicity.
- Java excels in large-scale, performance-critical applications, making it the go-to for enterprise systems and mobile app development.
- Python’s rich ecosystem for scientific and data-focused tasks contrasts with Java’s dominance in backend and enterprise-level frameworks.
- Python’s flexibility makes it suitable for both beginners and experts, while Java’s strict structure provides a strong foundation for mastering complex programming concepts.
What is Java?
Java is an advanced, object-oriented programming language used for building a wide range of applications. It was developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995. Over the years, Java has emerged as one of the most popular languages used in software development.
Core Features and Characteristics of Java
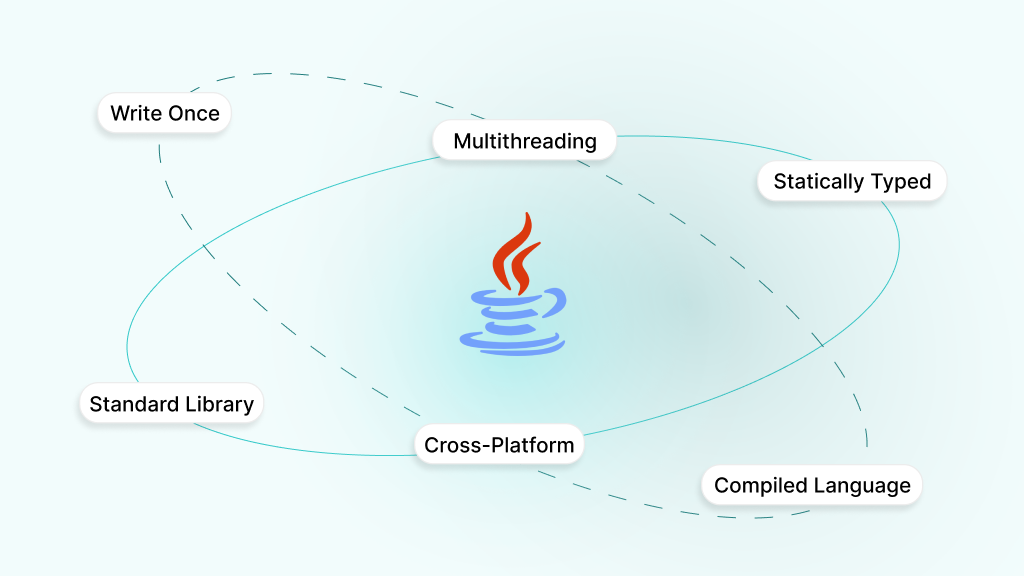
- Write Once, Run Anywhere: Java was built with the concept of “write once, run anywhere,” which means that the compiled Java code can be run and executed on any platform with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This portability is one of Java’s standout features.
- Statically Typed: Java is also known for its statically typed nature. This means that variables and method signatures must be explicitly declared. Static typing enables thorough error checking during compile-time, enhancing code quality and minimizing runtime errors.
- Compiled Language: Unlike interpreted languages, Java is a compiled language. Java code is first compiled into bytecode, which is then interpreted by the JVM. This process results in faster execution speeds compared to interpreted languages like Python.
- Cross-Platform: Thanks to the JVM, Java applications can run on various operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. This makes Java a go-to language for enterprise-level applications that require deployment across multiple systems.
- Robust Standard Library: Java provides an extensive standard library that covers a broad spectrum of functionalities. This includes tools for networking, file handling, data manipulation, and concurrency.
- Multithreading & High Performance: Java is designed with multithreading capabilities, allowing multiple threads of execution to run simultaneously. This enables developers to build highly responsive, parallel processing applications that perform efficiently even under heavy loads.
Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing the Confusion
Despite the similar names, JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted scripting language majorly used for client-side web development. In contrast, Java is a compiled, object-oriented language used for general-purpose programming.
JavaScript is primarily used to add interactive elements to websites, including features like animations and form validation, and runs directly within the web browser. It is different from Java, which is used for building full applications. JavaScript is essential for front-end development and is supported by all modern web browsers.
Pros and Cons of Java
Java comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Developers often opt for Java due to its reliability and performance, but there are also certain trade-offs to consider.
Pros of Java:
- Simplicity: The syntax in Java is clear and consistent, which makes it easier for beginners to learn and use the language effectively.
- Security: Java provides robust security features, such as memory management and access control, that help protect against vulnerabilities like unauthorized pointer access.
- Widespread Use and Community Support: The massive community of Java offers rich resources, tutorials, and a wealth of support for developers at all levels.
- Backwards Compatibility: Java’s commitment to backwards compatibility ensures that older code continues to run on newer versions, simplifying long-term maintenance.
- Automates Memory Process: The automatic memory management of Java through garbage collection helps prevent memory leaks and optimizes resource use without manual intervention.
- Supports Functional Programming: Java integrates functional programming paradigms, which provide a more expressive and declarative approach to writing code.
Cons of Java:
- Memory Consumption: Java’s memory footprint can be higher due to the JVM overhead and object management. This may impact applications running on devices with limited resources.
- Verbose Syntax: The syntax of Java can be lengthy, making it harder to write and maintain code, especially for smaller tasks.
- Slower Than Native Code: While Java is fast, it is not as quick as languages like C or C++ that compile directly to machine code.
- Garbage Collection Delays: The garbage collection mechanism of Java can slow down application performance, especially during cleanup processes.
- Complexity for Small Projects: Java may be overkill for small applications due to its complex setup and verbose nature.
- Less Flexibility in Scientific Computing: Java is not as widely used for tasks like data analysis and machine learning, where languages like Python excel.
- Limited Desktop GUI Support: While Java provides graphical user interface (GUI) tools, they are not as polished or user-friendly as those of other frameworks, especially for complex desktop applications.
Now that we have an understanding of Java, next, we will explore its diverse applications and real-world use cases.
Application and Use Cases of Java
Java is a widely used programming language for various applications across multiple industries. Let us explore how Java is leveraged in real-world scenarios, showcasing its flexibility, scalability, and versatility.
1. Web Development
Java is a powerful tool for building dynamic web applications, especially with frameworks like Spring. Due to its scalability and robust security features, it is an excellent choice for web solutions.
Example: Java is often used in the development of online banking systems, where high security and reliable performance are crucial.
2. Enterprise Software and Microservices
Java is a go-to choice for large-scale enterprise software. It enables the development of microservices architectures, allowing businesses to create modular, independent services that are easy to maintain and update.
Example: An e-commerce platform can utilize Java to develop microservices that manage various functions, such as order processing, inventory management, and customer data handling.
3. Mobile Application Development
Java serves as the main language used for developing Android applications. Its rich ecosystem, including powerful libraries and frameworks, makes it the best choice for creating mobile apps that are both efficient and secure.
Example: Many popular mobile apps, like Instagram and Spotify, are built using Java, ensuring a seamless and secure experience for millions of users. If you are looking to develop a mobile app with the same level of performance and security, partner with DEVtrust. We provide end-to-end custom development, from concept to deployment, ensuring your app scales and performs seamlessly across all devices.
4. Cloud Computing
Java is widely used in cloud development due to its scalability and strong performance. Cloud platforms leverage Java for building applications that can easily scale with user demand.
Example: Top companies like Netflix use Java for cloud-based services, ensuring that their platforms can handle millions of concurrent users without compromising performance.
5. Big Data Technologies
The speed and performance of Java make it a favorite for big data technologies. Frameworks like Hadoop and Apache Spark are written in Java, providing powerful tools for processing large volumes of data.
Example: Financial institutions use Java for processing real-time market data and performing high-frequency trading. This is due to its ability to efficiently manage large datasets.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Java has also gained traction in the AI field, particularly in developing intelligent applications and systems. With libraries like Deeplearning4j, Java is capable of building machine learning models and neural networks.
Example: Big Companies use Java to develop AI-driven applications, such as chatbots for customer service and recommendation systems for e-commerce platforms.
7. Internet of Things (IoT)
Due to its portability and capacity to manage complex, interconnected systems, Java is a great option for IoT applications.
Example: Java is commonly used in smart home devices, like thermostats and security cameras, allowing them to communicate efficiently and securely within an IoT ecosystem.
8. Game Development
Java is also widely used in game development, particularly for creating large-scale games and backend systems. Its portability ensures that games run on various platforms without modification.
Example: Games like Minecraft were originally developed using Java, enabling cross-platform play and easy updates for a global player base.
9. Desktop GUI Applications
Java is widely used for building graphical user interface (GUI) applications. With libraries like JavaFX and Swing, developers can create rich desktop applications with smooth user experiences.
Example: Java is used to create enterprise applications, such as inventory management or employee scheduling software, with robust GUI elements for easy interaction.
10. Embedded Systems
The efficiency and portability of Java make it a solid choice for embedded systems, which require fast execution and minimal resource consumption.
Example: Java is often found in smart devices, such as point-of-sale (POS) systems, where secure, real-time data processing is essential for smooth operation.
Just like Java powers the world’s most reliable systems, DEVtrust powers the future of your business with scalable, secure, and custom-built digital solutions. Let us bring your ideas to life. Get in touch with us today to start building the next big thing.
With these use cases in mind, now, we will shift our focus to another popular programming language: Python.
Also read:Top 15 Software Outsourcing Companies in 2025
What is Python?
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language recognized for its simplicity and ease of readability. Developed in the early 1991 by Guido van Rossum, Python was created to make programming easier and more intuitive. Its design philosophy prioritizes code readability, enabling developers to convey ideas in fewer lines of code than languages such as Java or C++.
Key Characteristics and Features of Python

- Dynamically Typed: Python is dynamically typed, which means you do not have to explicitly declare the types of variables. This reduces the complexity of the code and speeds up development.
- Interpreted Language: As an interpreted language, Python executes code one line at a time, making debugging simpler and allowing for faster testing and iteration. But it also results in slower execution compared to compiled languages.
- Minimalist Syntax: Python is designed to be clean and readable. Its minimalist syntax reduces clutter and makes it easier to understand, improving overall developer productivity.
- Extensive Standard Library: Python includes a vast library of modules and packages for tasks such as file handling, networking, and math operations. This allows developers to quickly integrate functionality into their applications without needing to write everything from scratch.
- Object-Oriented Programming Support: Python supports object-oriented programming (OOP). This means developers can create reusable, modular code using classes and objects, allowing for greater flexibility and maintainability. It helps in organizing and structuring large applications efficiently.
- Automatic Memory Management: Python handles memory allocation and garbage collection automatically, freeing developers from having to manage memory manually. This helps minimize the risk of memory leaks and enhances the stability of the program.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python can run on various platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, without requiring any modifications. This makes it a versatile option for developers seeking to create cross-platform applications.
- Large Ecosystem and Community Support: Python boasts a thriving ecosystem, featuring libraries and frameworks for a wide range of applications. Libraries like NumPy, TensorFlow, and Django make Python a go-to language for fields like data science, web development, and machine learning.
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: In Python, dynamic memory allocation means that memory is allocated as needed during runtime. This enables the flexible handling of data structures without requiring manual memory management.
Pros and Cons of Python
As the world’s most popular programming language, Python offers several advantages, but like any technology, it also has its drawbacks. Let us discuss the pros and cons of Python to help you understand when it is the best fit for your project.
Pros of Python:
- Versatility: Python’s ability to handle a wide range of applications, from web development to data science, makes it an incredibly versatile language.
- Fast Development: The dynamic typing and asynchronous code of Python allow for rapid development, making it ideal for quick prototyping and testing. Asynchronous programming in Python will enable tasks to run concurrently, improving efficiency for real-time applications.
- Flexible Programming Styles: Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including functional programming, which allows developers to write cleaner and more maintainable code by emphasizing functions as first-class objects. This versatility allows developers to select the most suitable approach, be it procedural, object-oriented, or functional, depending on the requirements of the project.
- Free and Open-Source: Python is freely available and open-source, with an active global community contributing to its ongoing development.
- Perfect for Data Science and Automation: With libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and TensorFlow, Python is widely regarded as the go-to language for data science, machine learning, and automation.
Cons of Python:
- Slow Execution Speed: As an interpreted language, Python executes code line by line, making it slower compared to compiled languages like Java or C++.
- Global Interpreter Lock (GIL): Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) of Python restricts execution to one thread at a time in a process. This limits concurrency and reduces performance in CPU-bound multi-threaded applications.
- Memory Intensive: Python consumes more memory than other languages, which can be problematic for applications with many objects active in memory.
- Runtime Errors: The dynamic typing nature of Python can lead to runtime errors, particularly if the code is not thoroughly tested.
- Limited Performance for CPU-Intensive Tasks: For performance-critical applications that need heavy CPU usage, the execution time can be a disadvantage.
- Verbose for Small Scripts: While Python is known for its simplicity, it can be overly verbose for small, simple scripts compared to more concise languages.
By considering these pros and cons, developers can determine if Python is the right tool for their specific needs.
With a clear understanding of Python’s capabilities, let us examine how it is used in various industries and real-world applications.
Application and Use Cases of Python
For Python, the flexibility and ease of use make it a powerful tool for developers. It works wonders across various applications, from web development to machine learning and data science. Let us explore how Python is used in different domains.
1. Data Analysis and Machine Learning
Python shines in data science and machine learning. With libraries like Pandas, NumPy, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, it simplifies complex data analysis, model building, and training.
Example: Building predictive models for customer behavior analysis using machine learning algorithms in a retail business.
2. Web Development
Python is a strong contender in backend web development, thanks to frameworks like Django and Flask. These frameworks simplify rapid development, reduce code redundancy, and offer high scalability.
Example: Developing dynamic websites using Django for backend and server-side logic.
3. Automation and Scripting
Python is frequently used for task automation, including file management, data extraction, and automation of repetitive processes. Its clear syntax makes it an ideal choice for scripting tasks.
Example: Writing a Python script to automate the process of scraping data from websites like news portals or e-commerce platforms.
4. Software Testing and Prototyping
Python supports rapid prototyping and testing with tools like PyTest and UnitTest. It is often used for writing tests, running prototypes, and verifying software functionality.
Example: Automating unit tests for a web application using PyTest to ensure code reliability and maintainability. If you want to build scalable, reliable, and custom software solutions, choose DEVtrust today. Our expertise in cloud integration, API development, and full-stack product development ensures your applications are built for success.
5. Scientific Computing
Python is extensively used in scientific computing. Libraries like SciPy and SymPy are used for numerical computations, simulations, and solving mathematical problems.
Example: Using SciPy to solve differential equations for a climate change modeling project.
6. GUI Applications
Python can be used to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) with frameworks such as Tkinter, PyQt, and Kivy. It makes building desktop applications easy and efficient.
Example: Developing a simple inventory management system with a graphical interface for small businesses using PyQt.
7. Multimedia
Python is widely used for multimedia tasks, including image processing and video manipulation. Libraries like Pillow and OpenCV facilitate these tasks.
Example: Building an image recognition application for automatically tagging photos based on their content using OpenCV.
8. Text Processing
Python simplifies text processing tasks, such as natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, and text summarization, with libraries like NLTK and spaCy.
Example: Using NLTK to analyze customer feedback and classify sentiments (positive/negative) for product reviews.
9. IoT and Embedded Systems
Python is used in building IoT systems, allowing developers to create programs that interact with physical devices. Libraries like MicroPython are often used for embedded programming.
Example: Programming Raspberry Pi-based home automation systems for controlling lights, thermostats, and other devices through a Python app.
Just like Python powers many leading applications, DEVtrust can help you bring your ideas to life. Whether you are building a data analytics tool or a machine learning solution, our tailored software development services can provide the perfect fit for your project. Get in touch with us today to build secure, scalable, and efficient solutions that drive real results.
Now that we have explored the applications of Python, let us compare its features and performance against Java to highlight the key differences.
Python vs Java: The Key Differences
While Python and Java share similarities as high-level programming languages, they have significant differences in terms of syntax, execution speed, and use cases. Here we explore how these two languages differ and what that means for developers when choosing the best fit for their projects.
| Aspect | Python | Java |
| Type of Language | Interpreted | Compiled |
| Syntax | Simpler, dynamic typing | More complex, static typing |
| Execution Speed | Slower (due to being interpreted) | Faster (compiled and optimized with JVM) |
| Memory Management | Automatic garbage collection | Allows developers to monitor and optimize memory usage through profiling tools and explicit management options, which can improve performance |
| Concurrency | Async programming is limited by the GIL | Robust multithreading and parallelism |
| Development Speed | Faster, concise code | Slower due to verbose syntax |
| Platform Independence | Requires an interpreter for each platform | Write once, run anywhere with JVM |
| Learning Curve | Easy, beginner-friendly | Steeper, requires understanding of strict syntax |
| Popular Frameworks | Django, Flask, TensorFlow, Pandas | Spring, Hibernate, Java EE |
| Performance | Lower performance in CPU-intensive tasks | Superior performance in high-load systems |
| Community & Libraries | Rich in data science and AI libraries | Large, mature community with robust libraries for enterprise systems |
| Mobile Development | Limited, not native | Strong, especially for Android |
Let us dive deeper into the specific details of the type system, syntax, and readability of each language to understand how they function in practice.
Also read: Complete Guide to SaaS Development Process: From Concept to Launch
Python vs Java: Type System, Syntax, Readability, and Code Examples
Choosing between Python and Java is more than just a matter of preference. It is about understanding the differences that affect how developers write code and maintain applications. The type system, syntax, readability, and code examples offer key insights into how each language functions. Let us break down these aspects in detail.
1. Type System
The type system plays a significant role in how data is handled and how errors are managed during development. Now we will compare how Python and Java approach types.
Dynamic Typing of Python
Python is dynamically typed, meaning variables do not require an explicit declaration of their types. This flexibility allows for fast and easy coding, but can lead to runtime errors that are hard to debug.
Example (Python):

In this example, the variable changes from an integer to a string dynamically. This is convenient but can lead to issues at runtime if types are mismanaged.
Static Typing of Java
In contrast, Java uses static typing. Here, the type of each variable must be declared at compile time, which reduces runtime errors but makes the code more verbose.
Example (Java):

Here, Java requires the type to be explicitly declared. If a type mismatch occurs, the code will fail to compile, offering early error detection and fewer runtime issues.
2. Syntax
The syntax of a programming language dictates how we write code and how easily it can be understood. Python and Java have significant differences in their syntax that influence how we write and read code.
Minimalistic Syntax of Python
The syntax of Python is designed to be simple and readable. It uses indentation to define code blocks, removing the need for curly braces or semicolons, making the code visually clean.
Example (Python):

In Python, indentation defines the code block structure, and the code is concise. There is no need for semicolons or braces to delimit functions or loops.
Structured Syntax of Java
Java’s syntax, while powerful, is more verbose. It requires curly braces {} to define code blocks and semicolons to end statements. This provides more structure, but at the expense of brevity.
Example (Java):

Java requires more lines of code to achieve the same result. While it provides more structure and clear boundaries for code blocks, it also makes the code more verbose.
3. Readability
Readability refers to how easily developers can understand the code. Python and Java approach readability in different ways, with Python emphasizing simplicity and Java prioritizing explicitness.
Python’s Readability
The clean and minimalist syntax of Python promotes readability. The use of indentation and whitespace makes it easier to understand the flow of the code without the distractions of unnecessary symbols.
Example (Python):

In Python, the use of indentation rather than braces and its lack of semicolons make the code easier to read. Each block of code is clearly defined, and its structure is intuitive.
Java’s Readability
In contrast, Java’s syntax uses semicolons, parentheses, and braces. While this adds structure, it also makes the code longer and potentially harder to read, especially for beginners.
Example (Java):

Java uses more lines and requires explicit statements like BufferedReader and FileReader. It also requires manual resource management, which adds complexity.
4. Code Examples: Comparing Python vs Java
Let us take a closer look at real-world examples that highlight how Python and Java compare in actual code.
Example 1: Iterating Over Data
In this example, we will compare how Python and Java handle iterating over a list or array.
Python:
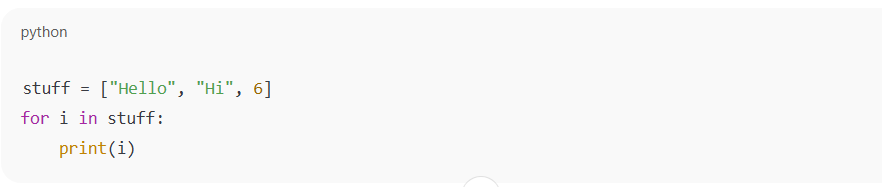
In Python, you do not have to declare the type of data in the list. This dynamic typing allows you to store mixed data types in one list.
Java:

In Java, you must declare the array type explicitly. The array can only hold data of the specified type (in this case, strings).
Example 2: Handling Files
Let us compare how Python and Java handle reading from a file.
Python:
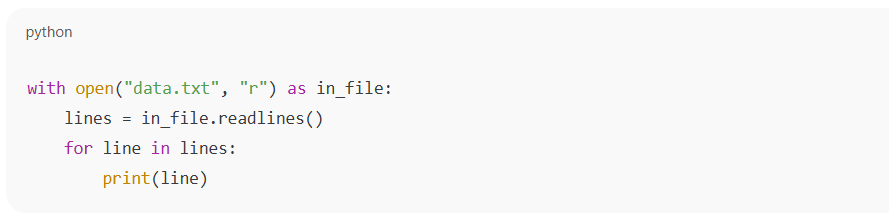
Python uses the with statement, ensuring that the file is automatically closed after reading. The code is simple and easy to read.
Java:

Java requires explicit code for file handling, using try blocks to manage resources and ensure proper closure. It increases code verbosity but enhances control over resource management.
When comparing Python and Java in terms of type systems, syntax, readability, and coding examples, it is clear that both languages offer distinct advantages. The decision between Python and Java often depends on the requirements of the projects, team expertise, and performance needs.
With these technical aspects in mind, let us now turn our attention to the popularity of Python and Java in the developer community.
Python vs Java: Which is More Popular?
Over the years, both Python and Java have had a significant impact, with each commanding a strong community of developers. However, recent data points reveal an exciting shift in their popularity rankings.
According to the latest report by GitHub, Python was ranked #1 last year, surpassing JavaScript as the most-used programming language on the platform. Java, on the other hand, ranked #4, showing a noticeable gap between these two languages. The rise of Python has been driven by its increasing use in fields such as data science, machine learning, and AI development, making it a preferred choice among developers worldwide.
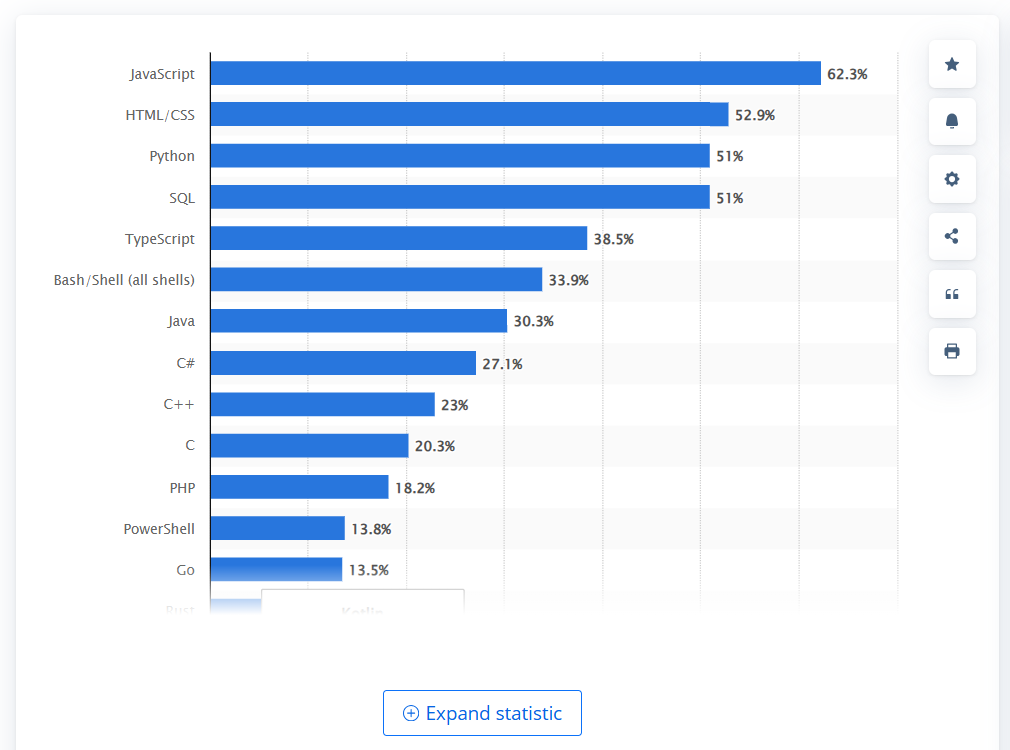
Adding to the trend, Statista reports that 51% of developers surveyed stated they used Python, while 30% used JavaScript, indicating the broad adoption of Python.
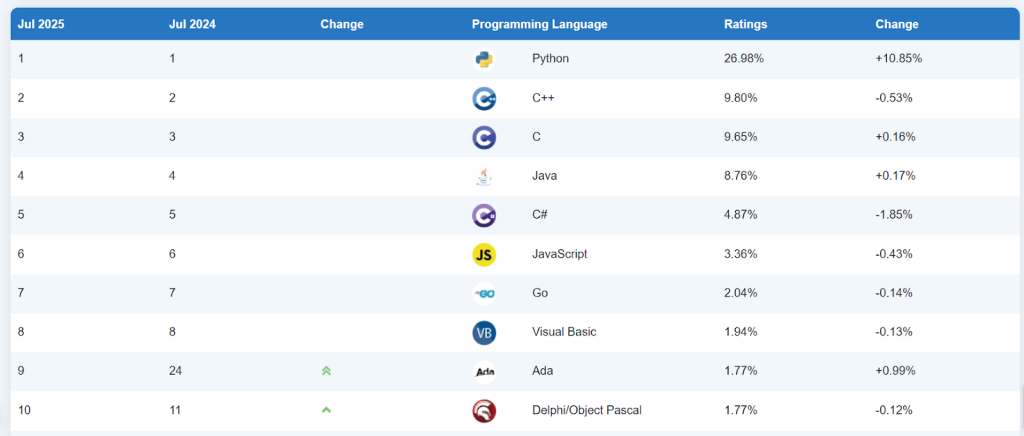
As of July 2025, the TIOBE Index also places Python firmly at #1, continuing its growth momentum. Meanwhile, Java remains at #4, showing its stable but slower progress in the race for dominance. This position highlights the increasing appeal of Python across various sectors, from web development to artificial intelligence, while Java maintains its stronghold in enterprise systems, Android development, and large-scale backend applications.
Both languages have their distinct advantages, but in terms of sheer popularity in 2025, Python continues to lead the charge, while Java remains a strong contender.
After reviewing their popularity, let us consider which language might be easier to learn, based on your experience and goals.
Python vs Java: Which One Should You Learn?
When choosing between Python and Java for learning, the decision often comes down to your personal goals and the field you want to enter. Both languages have their merits, but they appeal to different learners depending on the context of their projects.
Python is often considered the easiest language to start with due to its simple syntax and clear, readable structure. For those new to programming, Python offers a more accessible entry point, with its dynamic typing and fewer lines of code needed for tasks.
It is especially popular among beginners interested in data science, AI, and web development, as Python is known for its rich ecosystem of libraries like TensorFlow, Pandas, and Django. The language enables rapid prototyping and iterative testing, making it an ideal choice for rapid development cycles.
On the other hand, Java presents a steeper learning curve due to its more complex syntax and static typing. While its syntax is verbose compared to Python, this structure helps developers develop a solid understanding of programming fundamentals, especially for larger and more complex systems.
Java is ideal for those interested in enterprise software development, Android mobile development, and backend systems. While the learning curve might be more challenging, Java’s rigor often leads to better programming habits and a deeper understanding of computer science concepts.
Verdict: If you are a beginner with an interest in quick development and flexible applications, Python is the way to go. However, if you are looking for a language that will provide a deeper understanding of programming and work on large-scale systems, Java should be your choice.
Now that we have looked at which language is easier to learn, let us explore which one is a better fit for your projects and career.
Python vs Java: Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between Python and Java depends largely on your project requirements, career goals, and the kind of applications you want to build.
Python excels in versatility. It is favored in data science, machine learning, automation, and rapid prototyping. If your goal is to build and deploy small-to-medium applications quickly, or if you are diving into data analysis and AI, Python offers both ease of use and power.
Java, however, stands out in the enterprise software space. It is more commonly used in large-scale systems and backend development, especially where performance, security, and scalability are critical.
Verdict: Choose Python if your focus is on data-driven projects, AI, and quick development cycles. Choose Java if you are aiming for enterprise systems, Android development, or complex, high-performance applications.
Conclusion
Both Python and Java offer unique advantages and drawbacks, catering to different development needs. Python is ideal for quick prototyping, data science, and AI, while Java excels in large-scale applications and enterprise systems. Your choice depends on your project requirements and career goals.
If you are looking to bring your ideas to life with high-quality, scalable solutions, DEVtrust offers tailored software development services. From mobile apps to enterprise-grade systems, we ensure seamless integration and fast deployment.
Contact DEVtrust today and take your project to the next level with our expertise in full-stack development, cloud solutions, and API integrations.
Python vs Java: Key Features, Differences, and Use Cases
Compare Python vs Java in terms of features, performance, and best use cases. Discover which language is right for your next project or career path.
Contact Us