Global fintech adoption surpassed three billion users in 2024, as digital banking, real-time payments, blockchain platforms, insurtech, wealthtech, and AI-led automation moved into the financial mainstream. What began as consumer convenience has evolved into core financial infrastructure supporting everyday payments, lending, investing, and risk management at a massive scale.
Behind this growth sits a tightly coupled technology stack. Fraud detection, credit scoring, personalized investing, and open finance depend on machine learning models, API-first architectures, real-time data pipelines, and secure interoperability standards. These systems must operate continuously, accurately, and under strict regulatory oversight.
Building fintech software, therefore, requires precise architecture, resilient integrations, strict security controls, and technologies such as double-entry ledgers, event-driven systems, encryption, and scalable cloud infrastructure. Whether you’re designing a digital bank, lending engine, or payment workflow, the fundamentals stay the same: precision, reliability, and compliance must guide every decision.
This guide explores the complete fintech development ecosystem, from core technologies to the engineering practices needed to build secure, scalable financial products.
Key Takeaways
- Fintech now functions as a global financial infrastructure, serving billions of users and requiring systems that handle money, identity, and sensitive data with absolute precision.
- Compliance requirements such as KYC/AML, PCI-DSS, and GDPR shape every layer of fintech software, influencing architecture, data models, and transaction logic.
- Different fintech categories like payments, lending, trading, and digital banking demand different engineering patterns, each with its own constraints around consistency, throughput, integrations, and risk.
- Modern fintech relies on advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, biometrics, cloud-native infrastructure, and open banking APIs to deliver secure, scalable, and automated financial services.
- Building a production-ready fintech platform requires a structured engineering approach: feasibility analysis, compliance mapping, strong architecture, resilient integrations, hardened security, extensive testing, and careful deployment.
What Is Fintech Software Development?
Fintech software development is the creation of digital platforms that manage financial operations such as payments, lending, identity verification, wealth management, and regulatory reporting. It focuses on building systems that manage financial transactions and sensitive data with strict accuracy, security, and compliance requirements.
Because these platforms must comply with standards such as KYC, AML, PCI DSS, GDPR, and emerging RegTech regulations, fintech engineers design products with robust transaction logic, audit-ready data models, and secure integrations.
Modern development also leverages technologies such as AI, blockchain, and open banking APIs to automate decision-making, enhance transparency, and deliver safer, faster financial services.
Types of Fintech Software and What They Mean for Engineering
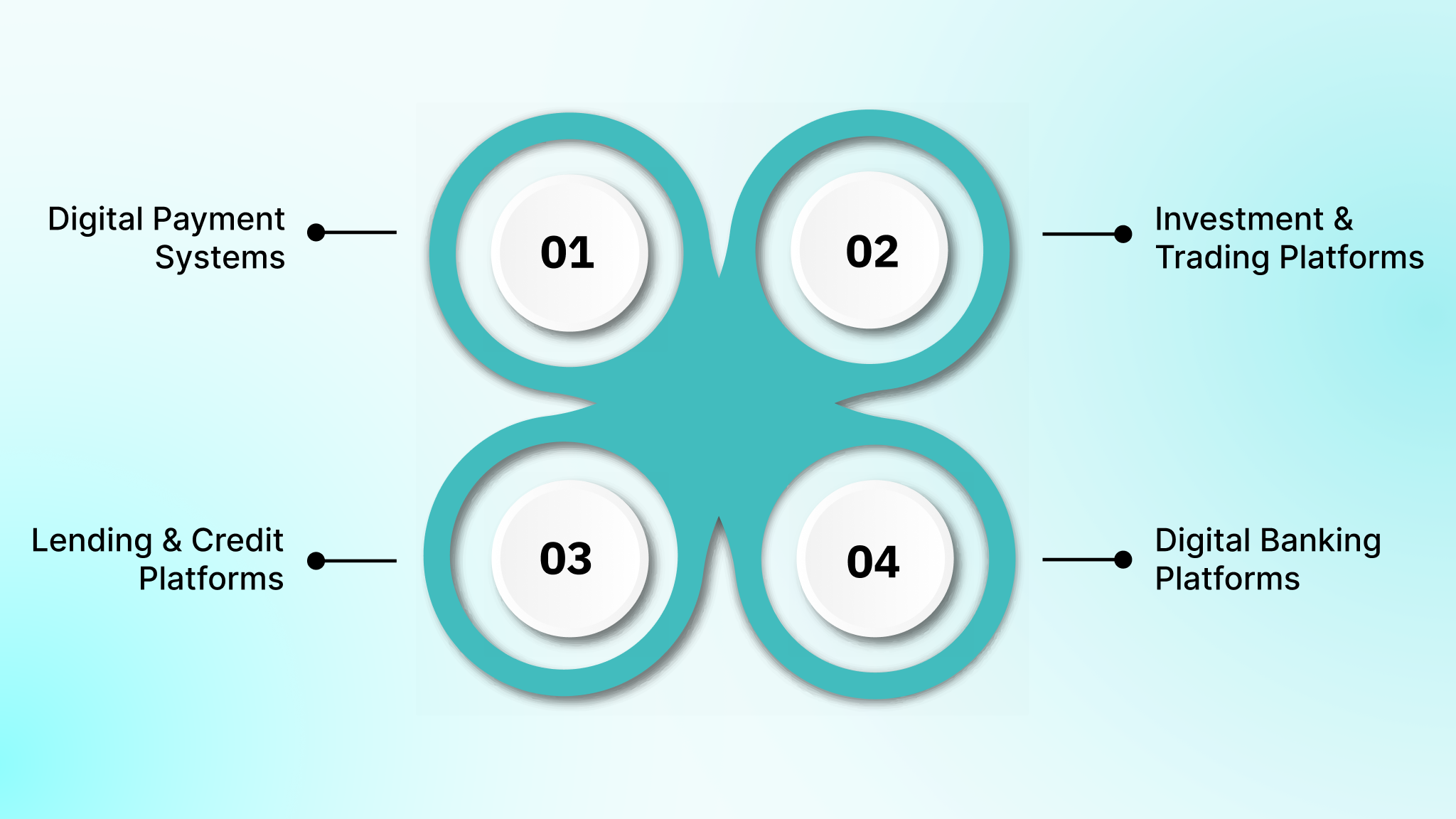
Fintech applications differ significantly in how they handle transactions, data models, integrations, and compliance requirements. Each category introduces its own architectural constraints and technical considerations, which shape how the system is built and how it behaves under real financial workloads.
Digital Payment Systems (High-Throughput, High-Integrity Systems)
Payment platforms are engineered to move money with accuracy and low latency. The core challenge is idempotent transaction processing, ensuring a payment is never double-charged even under retries, network failures, or webhook delays.
Key engineering requirements:
- Transaction engine with idempotency keys to guarantee exactly-once payment execution.
- Double-entry ledger as a source of truth for balance changes.
- Provider integrations (Stripe, Dwolla, PayPal, card processors) using webhook reconciliation.
- PCI-DSS scope reduction via tokenization or hosted fields.
- Risk scoring + rule engine for real-time fraud detection.
- Multi-currency handling through FX APIs and rate-locked transactions.
Payments are ultimately state machines, and engineering teams must account for failures at every transition: authorize, capture, refund, settle, dispute.
Investment & Trading Platforms (Data-Intensive, Low-Latency Systems)
Investment apps demand complex data processing pipelines and strict synchronization between market data, orders, positions, and risk models. Performance and consistency matter more here than UI polish.
Key engineering requirements:
- Market data ingestion via WebSockets, FIX APIs, or real-time streams.
- Order management system (OMS) with microsecond-level timestamp accuracy.
- Portfolio calculators using event sourcing to recompute positions and P&L.
- Backtesting engine for strategy simulation.
- Latency-optimized architecture (in-memory caching, message queues, co-located servers).
- Risk + compliance modules for trade restrictions, KYC flags, and AML checks.
- Integration with clearing/brokerage APIs (Alpaca, Interactive Brokers, Finnhub, etc.)
Investment platforms are essentially data pipelines coupled with deterministic state machines, where even small performance issues can cascade into major financial errors.
Lending & Credit Platforms (AI-Driven Decision Engines)
Lending systems revolve around identity verification, risk modeling, and loan lifecycle management. These workflows involve sensitive data, regulatory oversight, and heavy automation.
Key engineering requirements:
- KYC/AML identity verification using document OCR, biometrics, and database checks.
- AI/ML credit scoring models trained on alternative data.
- Document processing pipeline (OCR + validation + storage).
- Loan management system (LMS) for disbursement, repayment schedules, and interest accrual.
- Integration with credit bureaus like TransUnion, Experian, and Equifax via secure APIs.
- Automated compliance for disclosures, audit logs, and adverse action reasons.
Lending apps are highly regulated, so explainability of ML decisions and full auditability of loan changes are mandatory engineering requirements.
Digital Banking Platforms (Core-System Integrations + High Security)
Digital banking apps extend or replace traditional core banking systems. The engineering complexity comes from balancing customer experience with regulatory-grade reliability and security.
Key engineering requirements:
- Core banking integration layer with message queues, adapters, or ISO 20022 APIs.
- Account + balance engine backed by an immutable ledger.
- Real-time notifications (transactions, limits, fraud alerts) using event streaming.
- Secure authentication (OAuth2, MFA, biometric, device fingerprinting).
- Check deposit flows using image analysis + fraud screening.
- Bill pay & ACH rails with NACHA compliance.
- Open Banking / PSD2-ready APIs with consent management.
Digital banking is essentially a secure orchestration layer on top of legacy systems, with added UX, analytics, and API-driven functionality.
Also read: Top Fintech Startup Ideas to Consider in 2025
Fintech Product Development Blueprint for Engineering Teams
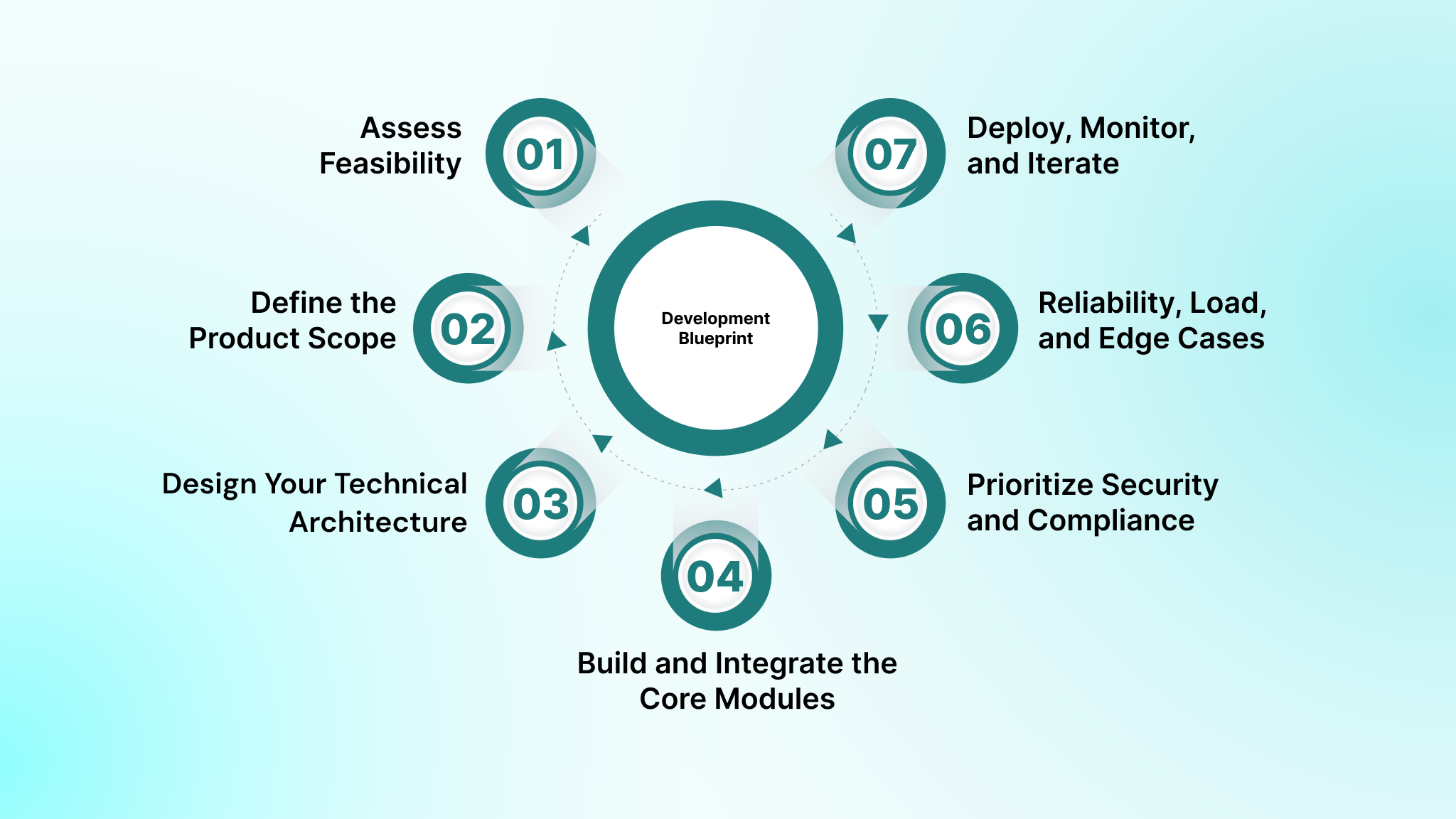
Fintech software is closer to building a regulated financial system than a typical application. Each phase introduces constraints on compliance, data handling, financial flows, and operational reliability.
The seven steps below outline how a fintech platform is engineered from the ground up. Each step focuses on the technical decisions, system behaviors, and controls required to build a platform that securely handles identity, transactions, and financial data at scale.
1. Assess Feasibility and Regulatory Boundaries
This phase determines the legal, operational, and architectural limits of your fintech product. Each product category, such as payments, lending, banking, and trading, comes with specific regulatory obligations and integration constraints. You must establish what is permissible, what requires a sponsor bank, and what technical resources the system depends on before design begins.
Key Determinations in This Phase:
- Product classification (payments, lending, trading, digital banking, wallets, etc.).
- Licensing model: direct regulatory approval vs. BaaS sponsorship.
- Applicable compliance frameworks (KYC, AML, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, GDPR, PSD2).
- Required third-party integrations (Plaid, Stripe, Dwolla, TransUnion, Experian, etc.).
- Data classification and sensitivity mapping.
- Target transaction volume, concurrency, and stress conditions.
- Compliance-driven constraints on data storage and event logging.
2. Define the Product Scope and Success Metrics
This phase converts the product concept into functional and technical requirements. You should document every user flow, define the system behaviors supporting them, and establish measurable performance and reliability targets.
These metrics guide engineering trade-offs and ensure the platform is optimized for financial accuracy and operational integrity.
Technical Scope & KPIs Defined Here:
- Full mapping of user flows (onboarding → verification → funding → transactions → support).
- Inputs, outputs, and validation requirements for each workflow.
- Operational KPIs influencing architecture:
- Transaction success rate.
- API latency thresholds.
- Fraud false-positive tolerance.
- KYC verification completion rate.
- Reconciliation lag windows.
- System failure definitions and SLA/SLO expectations.
- Priority sequencing based on compliance and risk exposure.
3. Design Your Technical Architecture
Architectural design defines how financial logic, identity verification, ledgering, and integrations interact under load. Fintech systems demand data integrity, auditability, and consistency above everything else. This step ensures the platform can handle real money movements while maintaining deterministic and fault-tolerant behavior.
Core Architectural Decisions:
- Authentication and identity model (OAuth2, MFA, device fingerprinting, biometrics).
- KYC/AML orchestration pipelines (document checks, liveness, sanctions screening).
- Transaction engine design (idempotency, retry handling, ordering guarantees).
- Ledger architecture (double-entry, append-only journal, event sourcing).
- Event-driven patterns for real-time updates and notifications.
- Integration layer structure: adapters, gateways, and retry queues.
- Observability architecture (structured logs, metrics, traces, audit events).
- Deployment approach: modular monolith vs. microservices.
- Data modeling for immutability, traceability, and regulatory retention.
4. Build and Integrate the Core Modules
This is where the core financial workflows are engineered. Each module, including identity, payments, lending, trading, and ledgering, must be robust against asynchronous failures, duplicate events, partial updates, and inconsistent third-party responses. This is the most engineering-heavy phase of any fintech project.
Core System Modules Implemented:
- Identity verification logic (OCR, biometrics, sanctions lists, liveness).
- Payment workflows: tokenization → authorization → capture/settlement → refund/reversal.
- Dispute and chargeback management flows.
- Lending engines (risk scoring, pricing logic, underwriting models, loan lifecycle).
- Trading engines (order routing, execution, positions, P&L computation).
- Ledger system (balance updates, journal entries, immutable audit trail).
- Event streaming + webhook processors.
- Reconciliation processes to sync with banks, processors, and bureaus.
5. Prioritize Security and Compliance
This step ensures your platform enforces strict access control, encrypts sensitive operations, logs financial events immutably, and implements fraud detection mechanisms. These controls must integrate directly into workflows that affect money and identity.
Security & Compliance Controls Implemented:
- Encryption for data in transit and at rest (KMS, envelope encryption).
- Hardened API authentication (short-lived tokens, rotation, IP restrictions).
- Role-based access control for admin and support systems.
- Immutable audit and event logs meet regulatory standards.
- Fraud detection rules, anomaly scoring, and velocity checks.
- Threat modeling across all financial workflows.
- Compliance-aligned logging and retention policies.
- Monitoring for abnormal access, device anomalies, or transaction spikes.
6. Test for Reliability, Load, and Edge Cases
Fintech systems must behave correctly under high traffic, delayed or duplicated provider responses, edge-case identity failures, and complex transaction states. This stage validates system behavior in real-world conditions, so your platform remains accurate, stable, and compliant, even when external services fail.
Critical Test Scenarios:
- External provider outages (Plaid, Stripe, Dwolla, bureaus).
- Delayed, duplicated, or missing webhooks.
- High-load and stress conditions on transaction and ledger services.
- KYC and identity verification failure paths.
- Fraud detection edge cases and bypass attempts.
- Ledger reconciliation accuracy across all external systems.
- Contract tests for every third-party API.
- Sandbox testing across all financial integrations.
7. Deploy, Monitor, and Iterate
Deployment in fintech requires careful rollout strategies and continuous monitoring of financial health metrics. Your team must track transaction failures, fraud anomalies, provider outages, and reconciliation gaps in real time. This ensures the platform stays stable, compliant, and operational as it scales.
Deployment & Monitoring Requirements:
- Blue/green or canary deployments for safer releases
- Automated rollback triggers for financial anomalies
- Full observability stack (metrics, logs, traces, structured financial logs)
- Alerts for:
- Failed or stuck transactions
- Settlement or withdrawal delays
- Fraud signal spikes
- Third-party API degradation
- Runbooks for payment incidents and ledger inconsistencies
- Post-deployment verification of financial correctness
Related: Banking Software Development: Comprehensive Solutions and Insights
Key Technologies Powering Fintech Software Development
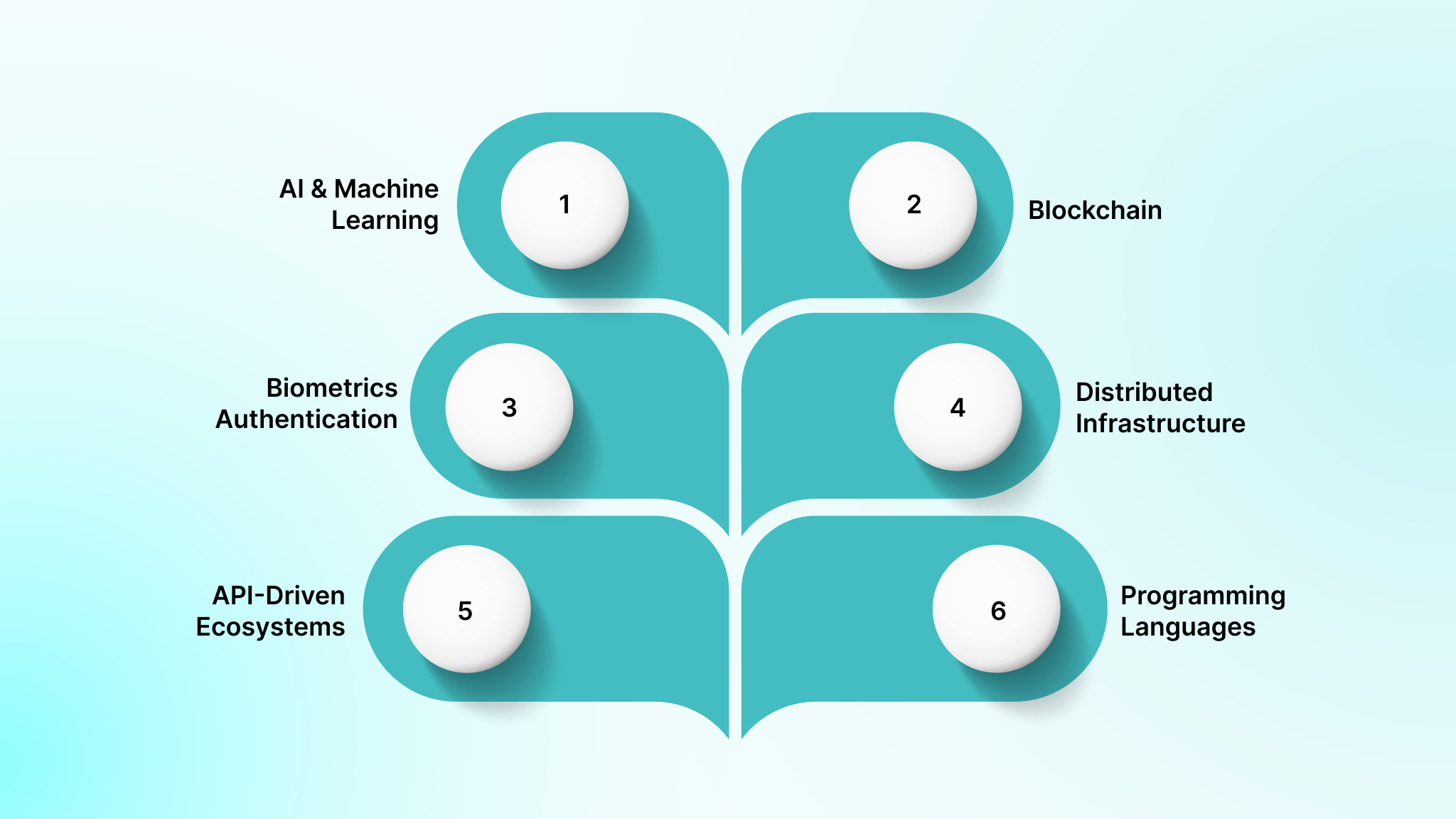
Fintech’s technical stack has evolved from basic server applications to modern, API-centric, and cloud-native architectures. The tools below represent the technologies most commonly used to build current fintech systems.
AI & Machine Learning
Used for fraud detection, credit scoring, underwriting models, anomaly detection in transactions, and automated financial insights. ML pipelines typically include real-time feature engineering, model scoring inside the decision path, and explainability layers required for regulatory audits.
Blockchain
Applied in settlement, asset tokenization, auditability, and transparent recordkeeping. Blockchain introduces verifiable event logs, smart contract automation, and reduced dependency on intermediaries, useful for cross-border payments and compliance-led processes.
Biometrics Authentication
Used to secure identity flows (KYC), account access, and transaction approval. Techniques include biometric checks, liveness detection, behavioral analytics, and device fingerprinting to reduce account takeovers and meet PSD2/SCA requirements.
Cloud & Distributed Infrastructure
Modern fintech systems rely on cloud-native architectures such as serverless functions, microservices, event streaming, and multi-region deployments. These provide auto-scaling, resilience, and isolation for critical components such as ledger services, payment engines, and KYC pipelines.
Open Banking & API-Driven Ecosystems
Fintech software integrates with banks, credit bureaus, payment processors, and data providers through standardized APIs. This includes account information APIs, payment initiation APIs, identity services, transaction categorization engines, and financial data aggregators.
Programming Languages & Databases
Common stacks include Python, Node.js, Java, and Go for backend logic; React or Next.js for frontends; PostgreSQL for ledgers and transactional integrity; and NoSQL or time-series databases for analytics and event logs.
Key Challenges in Fintech Software Development (and How to Solve Them)

Fintech products operate in a tightly regulated environment where money, identity, and sensitive data must be handled with absolute accuracy. The challenges below reflect the real constraints engineering teams face when building financial systems.
1. Complex and Evolving Compliance Ecosystem
Fintech teams must comply with overlapping rules (KYC, AML, PCI-DSS, PSD2, GDPR) that differ across countries and product types. Missing one requirement can block launch or trigger penalties.
Solution: Create a compliance matrix early and separate region-specific logic into modular components. Use tokenization and hosted fields to reduce PCI scope and maintain audit-ready logging for all financial events.
2. Fraud and Risk Management
Fraud in fintech evolves constantly: synthetic identities, account takeovers, chargeback abuse, and transaction laundering. Static rules fail quickly.
Solution: Combine rules with behavioral checks, velocity limits, and identity risk scoring. Log every decision, add real-time anomaly alerts, and adjust rules continuously based on fraud patterns.
3. Integration Dependence on Banks and Payment Networks
Fintech products rely on third-party systems (banks, processors, bureaus), each with different API behaviors, latency, failure modes, and webhook reliability.
Solution: Use retry queues, idempotency keys, and reconciliation jobs to ensure the internal ledger always remains the source of truth, even when external providers misfire.
4. Legacy Systems and Banking Infrastructure Constraints
Banks often expose outdated or inconsistent protocols. Data may arrive late, in batches, or with missing details. Legacy rails limit real-time features.
Solution: Build adapter layers around each provider and normalize all incoming data. Use staged processing to convert bank responses into your platform’s consistent internal format.
5. Financial Data Accuracy and Ledger Integrity
Money must never be duplicated, disappear, or be posted incorrectly. Race conditions, partial failures, or webhook delays can corrupt balances.
Solution: Use a double-entry ledger with append-only records. Enforce strict idempotency on all financial actions and reconcile frequently with processors and banks.
6. User Identity and Verification Challenges
Fintech onboarding depends on accurate identity verification. Document quality issues, liveness-detection failures, and mismatched records cause drop-offs or risk exposure.
Solution: Use multi-step verification (document analysis, liveness, sanctions screening) and apply different verification paths based on risk level or transaction limits.
Development Models for Fintech Software: Key Tradeoffs to Evaluate
Every fintech team eventually faces the same decision: build the product internally, outsource it, or combine both approaches. There isn’t a universal answer. The right choice depends on your compliance requirements, the complexity of your integrations, the strength of your existing engineering team, and the budget you can allocate. Below are the development models most fintech companies rely on, along with the limits and advantages that come with each approach.
In-house Development
- Pros: Direct control over architecture, security, code quality, and institutional knowledge.
- Challenges: Hard to hire engineers who understand KYC/AML flows, ledgering, payment rails, and compliance requirements. Team growth is slow and expensive, and ongoing payroll makes long-term maintenance costly.
- Best for: Companies building a regulated core product (banking, payments, lending) that must remain proprietary.
Outsourced Development
- Pros: Immediate access to fintech-specific engineering skills, faster delivery, and lower long-term cost. Ideal when you need integrations with banking APIs, payment processors, credit bureaus, or compliance frameworks.
- Challenges: Requires proper partner vetting to ensure experience with financial data, audit requirements, and money-movement accuracy.
- Best for: Companies needing rapid execution, specialized fintech expertise, or support scaling beyond internal capacity.
Hybrid Model
- Pros: Keeps strategic decision-making internal while leveraging external specialists for complex areas like core banking integrations, ledger systems, fraud logic, or regulatory workflows. Highly flexible and cost-efficient.
- Challenges: Requires clear ownership boundaries and stable communication between teams.
- Best for: Companies with a small internal team that wants control but lacks bandwidth or deep financial engineering experience.
When choosing the right approach, consider your compliance obligations, the complexity of your integrations, your timeline, and the level of technical oversight you want to maintain.
For many fintech products, a hybrid approach offers the best balance: internal ownership of the product vision supported by external engineers who already understand the financial ecosystem.
Why DEVtrust Is the Right Partner for Fintech Software Development
Outsourcing fintech software development comes with its own challenges. Many teams lack real experience with compliance, payments, KYC/AML, or ledger design, and they often aren’t equipped with the right technical stack or financial engineering background to build reliable, audit-ready systems. This leads to broken verification flows, unstable payment integrations, missing audit trails, and products that cannot pass regulatory scrutiny.
DEVtrust solves this by bringing a team that builds financial-grade systems every day. We design secure, compliant, and scalable fintech platforms that handle identity verification, money movement, reconciliation, and risk scoring with the precision these workflows require.
Our engineers work directly with the financial ecosystem, including Plaid, Stripe, Dwolla, TransUnion, Yodlee, trading APIs, and banking partners, so integrations behave consistently under real-world load.
What DEVtrust brings to your fintech product:
- Full-stack fintech development: We build end-to-end systems, from onboarding and KYC flows to payment processing, ledger logic, wallets, lending engines, and reporting dashboards.
- Deep experience with financial integrations: We integrate with banking APIs, processors, bureaus, accounting tools, and payment gateways, reducing the risk of failed connections or inconsistent data.
- Compliance-aligned architecture: Double-entry ledger models, audit trails, PCI-aligned payment flows, secure data storage, and structured logging built for regulatory reviews.
- Scalable, cloud-ready infrastructure: AWS, Azure, and GCP architectures designed for reliability, failover, and predictable performance during peak financial activity.
- AI and automation where it matters: Fraud detection, risk scoring, document analysis, reconciliation automation, and intelligent support systems.
When reliability, compliance, and financial accuracy matter, you need a team that understands the rules, the risks, and the infrastructure behind modern financial products. DEVtrust gives you that foundation so your product can scale confidently.
Conclusion
Fintech software development represents unprecedented opportunities for organizations ready to capitalize on digital financial transformation. The market’s explosive growth rewards companies that can deliver secure, compliant, and user-centric financial solutions.
Your fintech vision deserves expert implementation that addresses regulatory requirements, security challenges, and user experience expectations. The window for market entry continues narrowing as competition intensifies and regulatory requirements become more stringent.
DEVtrust’s proven expertise in fintech software development and regulatory compliance can help bring your vision to life as market-leading solutions. Our team’s experience with comprehensive fintech platforms ensures your project meets industry standards while delivering exceptional user experiences.