Companies deploying AI chatbots often struggle to balance automation with reliability. Poorly planned implementations can result in inconsistent responses, high inference costs, and systems that fail under real-world workloads, limiting customer satisfaction and internal efficiency.
The challenge is real, and thus organizations are increasingly relying on chatbots for both customer support and operational tasks. The global chatbot market was valued at USD 7.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 27.29 billionby 2030, highlighting rapid adoption and rising expectations for intelligent, production-ready solutions.
In this article, you will discover practical steps to build AI chatbots that actually perform in production. From deciding the business objective to integrating APIs and establishing monitoring workflows, each step focuses on measurable impact and real-world reliability.
Key Takeaways
- AI chatbots use NLP to enable dynamic, human-like conversations and automate tasks across customer and internal workflows.
- Clear business objectives, target users, and constraints guide architecture, integrations, and model choices.
- Following structured steps, from objectives to production monitoring, ensures reliable, scalable chatbots.
- Using the right tools, clear intents, secure APIs, and well-designed conversation flows improves usability and efficiency.
- Challenges like unpredictable inputs, integration issues, and scalability are managed through testing, monitoring, and iterative updates.
What Is an AI Chatbot?
An AI chatbot is a software tool that uses artificial intelligence, particularly natural language processing (NLP), to interact with users through text or voice. Unlike traditional software, it understands and responds to human language, enabling dynamic conversations.
AI chatbots differ from rule-based bots, which follow predefined scripts by learning from data to handle varied inputs. Examples like ChatGPT (for general conversation), Alexa (for voice assistance), and Facebook Messenger bots (for customer support) show their versatility.
The purpose of an AI chatbot is to automate tasks, answer queries, or guide users, saving time and resources. Whether you are helping customers or scheduling meetings, these tools enhance efficiency and engagement.
Now that you understand AI chatbots, let us explore their practical applications across industries.
Also Read: Ecommerce Mobile App Development Guide and Steps
Use Cases for AI Chatbots
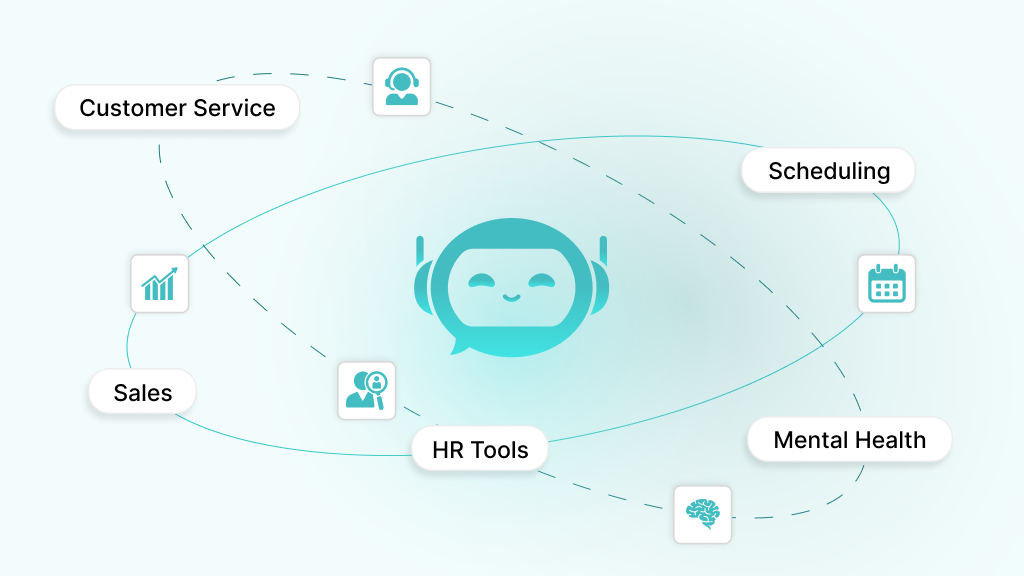
AI chatbots are changing how businesses and organizations operate by automating repetitive tasks and improving user interactions. Their versatility makes them valuable in diverse sectors, from customer service to healthcare. Understanding these use cases helps you identify how a chatbot can address your specific needs:
- Customer Service and Support: Handle FAQs, resolve issues, or guide users through troubleshooting, available 24/7 to improve satisfaction.
- Lead Generation and Sales: Qualify leads, recommend products, or process orders, boosting conversions in e-commerce or B2B settings.
- HR and Internal Tools: Simplify employee onboarding, answer HR queries, or manage leave requests, enhancing workplace efficiency.
- Personal Productivity and Scheduling: Book meetings, send reminders, or organize tasks, helping users stay productive.
- Healthcare Triage or Mental Health: Assess symptoms, provide self-care tips, or offer mental health support, improving access to care.
These use cases highlight the broad potential of chatbots, guiding your project’s focus. Up next, let us cover the factors you must be aware of to get started.
Key Factors to Consider to Develop AI Chatbots
Building an AI chatbot requires preparation to ensure success. You need to clarify your goals, gain foundational knowledge, and gather the right tools. This approach helps you avoid common pitfalls and build a chatbot that aligns with your objectives.
- Define Your Purpose and Users: Decide what your chatbot will do (e.g., answer customer queries) and who it serves (e.g., shoppers or employees).
- Understand NLP Basics: Learn core NLP concepts like intents (user goals) and entities (specific details) to enable natural conversations.
- Required Tools and Skills: Familiarize yourself with programming (Python or JavaScript), APIs, and platforms like Dialogflow or Rasa. Basic coding knowledge is also essential for custom builds.
With these prerequisites in place, you are ready to begin the AI based chatbot development process. Up next, we will see how to build your upcoming AI chatbot.
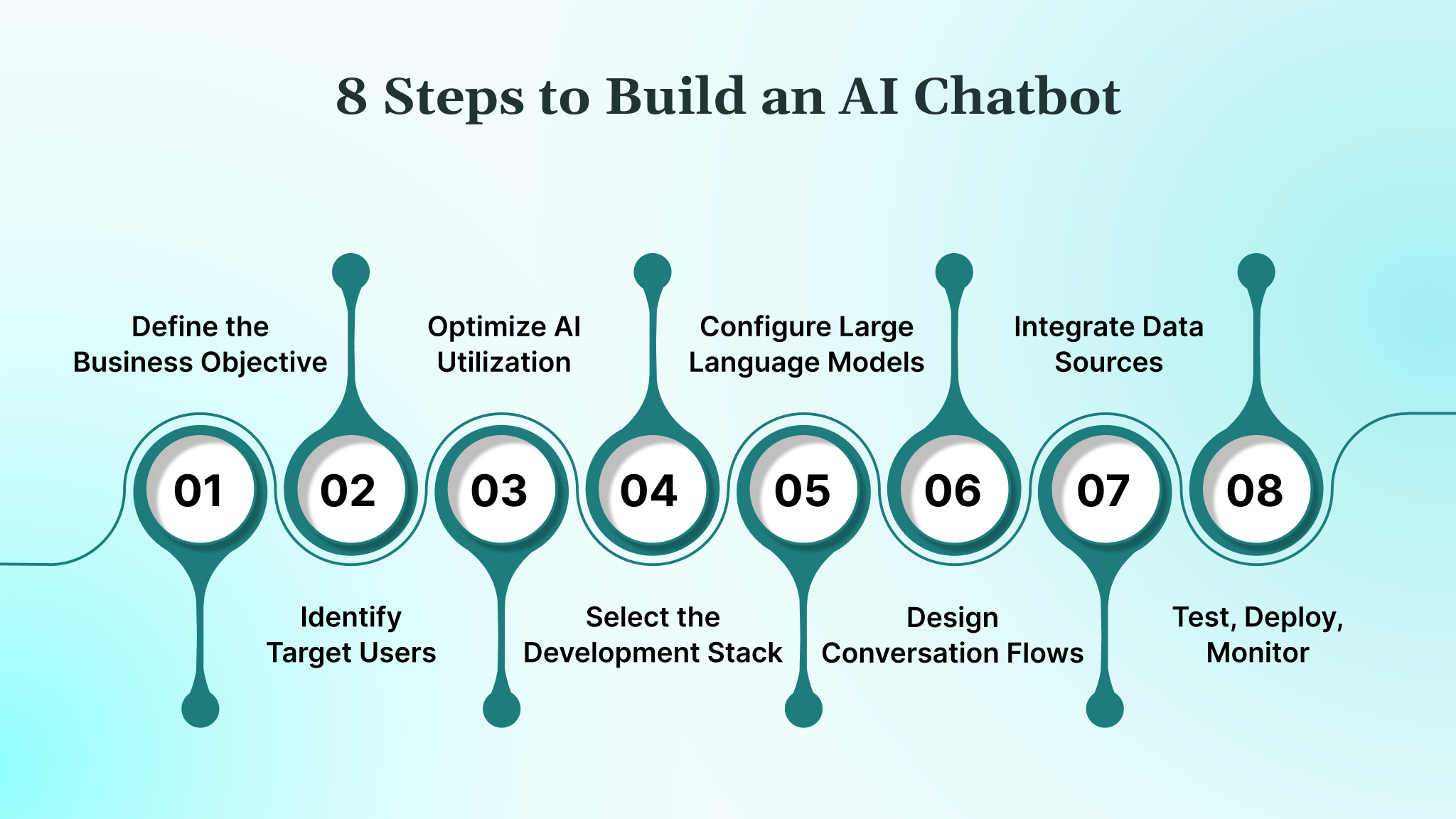
8 Steps to Build an AI Chatbot
Building an AI chatbot does not only mean adding conversational UI. It is about designing a system that integrates with your workflows, respects constraints, and delivers measurable business outcomes at scale. Let’s understand this through the steps outlined below:
1. Define the Business Objective and Success Metrics
When creating an AI chatbot, the first decision is not the model or tool, but the problem it solves. A chatbot can reduce support load, qualify leads, automate internal queries, or guide users through transactions. This objective determines how smart the chatbot needs to be, which systems it connects to, and how success is measured once it goes live.
What to do in this step:
- Define one clear outcome, for example, “Deflect 30–40% of L1 support tickets.”
- Choose 2–3 chatbot KPIs such as intent resolution rate, fallback rate, or CSAT.
- Capture current workflow metrics to compare pre- and post-chatbot performance.
2. Identify Target Users, Use Cases, and Constraints
An AI chatbot behaves very differently depending on who it serves. A customer-facing chatbot must optimize for speed and clarity, while an internal chatbot can handle system-level queries. Constraints such as compliance, data access, response time, and supported channels must be locked early because they directly affect chatbot architecture and model choice.
What to do in this step:
- Define user groups clearly, for example, customers, support agents, or internal teams.
- List the top chatbot use cases with expected inputs and outputs.
- Document constraints like PII handling, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or response-time SLAs.
3. Optimize AI Utilization for Efficiency
Even AI chatbots shouldn’t use full AI processing for every interaction. Identify which queries genuinely need AI understanding and which can be handled with lightweight logic. This reduces latency, cuts costs, and keeps responses fast.
What to do in this step:
- Map interactions that require AI comprehension versus simple scripted responses.
- Use AI for complex, open-ended user intents.
- Use predefined logic for predictable flows like FAQs, order tracking, or authentication.
4. Select the Development Stack and Deployment Architecture
Building an AI chatbot requires more than a frontend widget. You need a backend that manages sessions, orchestrates APIs, logs conversations, and scales reliably. A weak architecture results in slow responses, broken integrations, and poor observability once usage grows.
What to do in this step:
- Choose a backend stack such as Node.js or Python for chatbot services.
- Decide how the conversation state will be stored, for example, Redis or a database.
- Define cloud infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines, and environment isolation.
5. Choose and Configure Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs power the chatbot’s intelligence, but raw capability alone is not enough. Latency, cost per token, data residency, and model control matter more in production. Proper configuration ensures consistent responses and prevents unpredictable behavior.
What to do in this step:
- Select hosted or self-hosted LLMs based on compliance and cost needs.
- Create task-specific prompt templates for each chatbot use case.
- Set temperature, max tokens, and fallback rules to control responses.
6. Design Conversation Flows, Context, and Guardrails
AI chatbots need structure to remain reliable. Context handling defines what the chatbot remembers, while guardrails control how it responds when unsure. This is essential to prevent hallucinations, incorrect answers, or unsafe outputs.
What to do in this step:
- Design conversation flows for success and failure scenarios.
- Define how long the chatbot context is retained and when it resets.
- Add escalation paths to route complex queries to human agents.
7. Integrate Data Sources, APIs, and Communication Channels
A chatbot becomes valuable only when it connects to real systems. These integrations must be secure, resilient, and optimized for each channel. The same chatbot behaves differently on web, mobile, or messaging platforms.
What to do in this step:
- Build an integration layer to manage API calls and retries.
- Secure data access using tokens, role-based permissions, and audit logs.
- Adapt chatbot responses for web chat, Slack, WhatsApp, or in-app use.
8. Test, Deploy, Monitor, and Iterate in Production
Launching an AI chatbot is not the end of the process. Continuous testing and monitoring are required to manage cost, accuracy, and user experience as usage grows. Production feedback is also essential for long-term improvement.
What to do in this step:
- Run load and edge-case tests before deployment.
- Track latency, cost per conversation, and fallback frequency.
- Review chatbot logs regularly and refine prompts and flows.
When these steps are executed correctly, an AI chatbot becomes a reliable production system, not an experiment. However, you still need to consider following some of the best practices for building these bots.
Best Practices for Building AI Chatbots
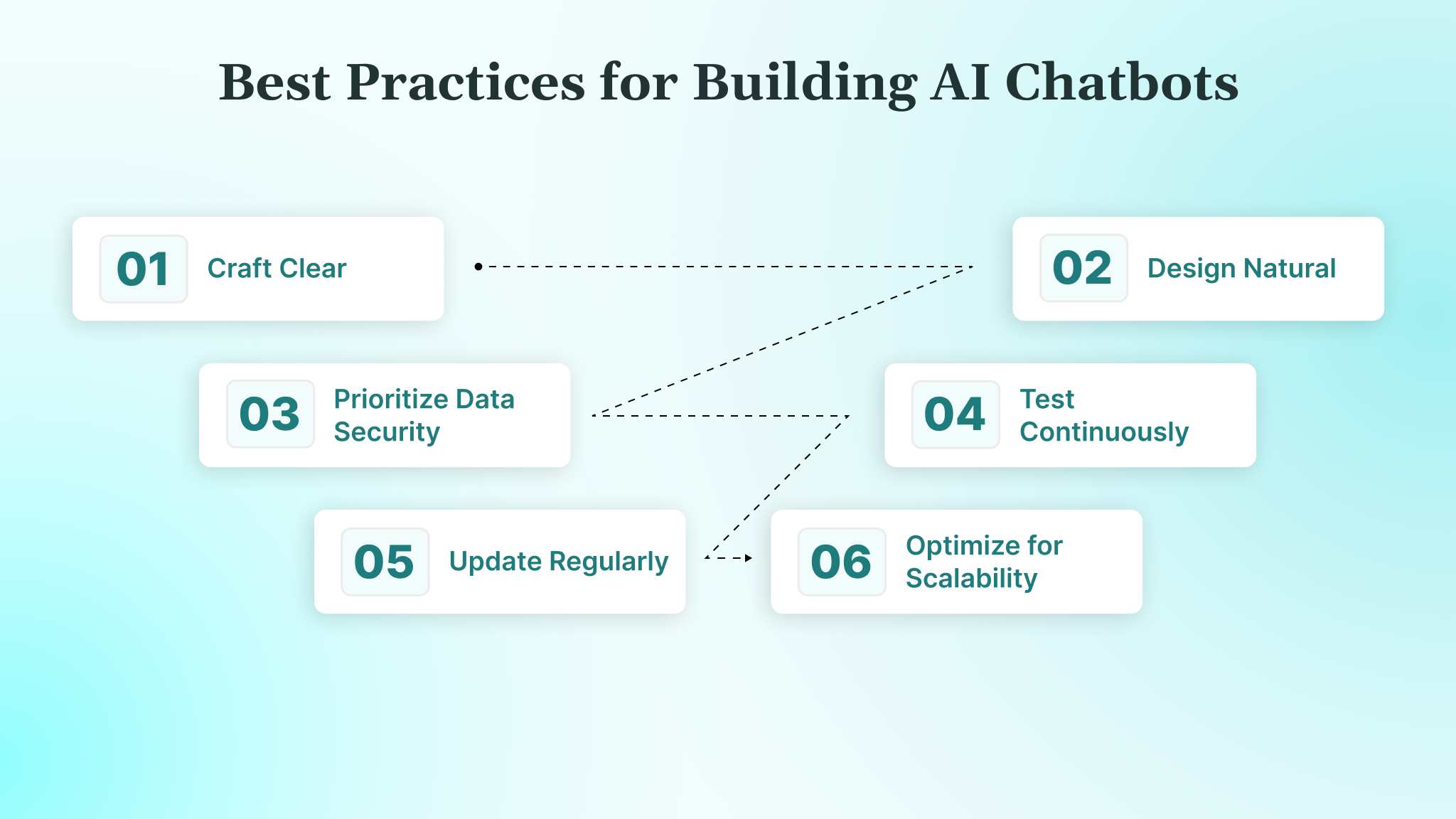
Following best practices ensures your chatbot is effective, user-friendly, and secure. Below, we outline key practices to guide your development process, helping you create a chatbot that stands out for its quality and functionality.
- Craft Clear and Specific Intents: Define precise user intents, such as “book_appointment” or “check_status,” to ensure your chatbot understands user goals accurately. Use tools like Dialogflow or Rasa to categorize intents clearly, reducing misinterpretations. For example, separate “cancel order” from “modify order” to avoid confusion and regularly review intent performance to refine accuracy.
- Design Natural, Conversational Responses: Write responses in a friendly, concise tone that feels human, avoiding overly technical or robotic language. For instance, instead of “Query processed successfully,” say, “Got it! Your request is complete.” Include prompts or buttons to guide users and test responses with real users to ensure they feel engaging and natural.
- Prioritize Data Security and Privacy: Protect user data with HTTPS encryption and secure API authentication, such as OAuth or API keys. Comply with regulations like HIPAA by anonymizing sensitive data and obtaining user consent for data collection.
- Test Continuously Across Scenarios: Test your chatbot regularly, covering all conversation paths, edge cases, and unexpected inputs. Use tools like Botium or manual testing to verify responses.
- Maintain and Update Regularly: Keep your chatbot’s training data fresh by adding new user phrases and refining intents based on analytics. Schedule monthly reviews to incorporate feedback and update responses, ensuring your bot stays relevant as user needs or business goals evolve.
- Optimize for Scalability: Design your chatbot to handle increasing user volumes by using scalable hosting like AWS or Azure. Implement caching for frequently accessed data, like FAQs, to reduce server load, and plan for modular updates so you can add features without overhauling the entire system.
These practices set a strong foundation for a successful chatbot. Up next, let us explore the tools and technologies that support chatbot development.
Popular Tools and Technologies for Custom AI Chatbot Development

Choosing the right tools and technologies simplifies chatbot development and enhances functionality. From platforms to programming languages, these options cater to different skill levels and project needs. Here are some of the most popular tools you should consider:
1. Chatbot Platforms
Dialogflow (Google) offers a user-friendly interface for NLP-powered chatbots, integrating easily with WhatsApp or websites, ideal for quick setups. Rasa, an open-source Python platform, provides customization for advanced users, perfect for tailored NLP models. Microsoft Bot Framework suits enterprise-grade bots with Azure integrations, while OpenAI’s API delivers powerful conversational AI for natural responses.
2. Programming Languages
Python is beginner-friendly, with libraries like Rasa for NLP tasks. JavaScript (Node.js) excels for web-based chatbots, supporting real-time integrations. C# works well with the Microsoft Bot Framework for enterprise applications, offering robust development support.
3. NLP APIs
OpenAI GPT provides advanced language understanding for conversational bots, though it requires API cost management. Google Cloud NLP simplifies intent detection, whileWit.ai offers free, flexible NLP for multilingual chatbots. Amazon Lex supports voice and text for versatile applications.
4. Hosting Solutions
Heroku is great for quick deployments with free tiers, ideal for small projects. AWS provides scalable options like Lambda for serverless bots. Azure offers secure, enterprise-ready hosting, and Netlify supports JAMstack bots with static front-ends and serverless functions.
5, Additional Tools
Postman tests API integrations, ensuring reliable data flow. Git and GitHub manage code versioning. Chatbase tracks performance metrics, helping you refine user interactions, while VS Code simplifies coding with useful extensions.
These tools help you build robust chatbots efficiently. Finally, let us address common challenges and how to overcome them.
Also Read: 8 Best AI Productivity Tools in 2025 to Streamline Your Workflow
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Building an AI chatbot can be complex, especially for beginners. Anticipating challenges helps you stay prepared and maintain progress. Here are some common hurdles and practical solutions:
1. Grasping NLP Complexity
Natural language processing concepts like intents, entities, and context can feel overwhelming. Start with beginner-friendly platforms like Dialogflow, which simplify NLP setup with visual interfaces. Follow online tutorials, such as those on YouTube or freeCodeCamp, to learn incrementally and practice with small, focused intents to build confidence.
2. Managing Unpredictable User Inputs
Users may ask vague or off-topic questions, like “What is up?” or misspellings, which can confuse your bot. Design robust fallback responses, such as “I am not sure what you mean. Try asking about orders.” Test with diverse inputs and use tools like Rasa’s interactive learning to refine how your bot handles ambiguity.
3. Resolving Integration Issues
Connecting your chatbot to APIs, like a CRM or payment system, can lead to errors, like incorrect data or timeouts. Use Postman to test API endpoints before integration, ensuring they return expected data. Document API credentials securely and check rate limits to avoid disruptions, especially for high-traffic bots.
4. Keeping Users Engaged
Long or repetitive conversations can bore users, leading to drop-offs. Keep responses short, ideally under 20 words, and use interactive elements like buttons or quick replies to simplify navigation. Analyze user sessions with tools like Chatbase to identify where users lose interest and adjust flows accordingly.
5. Overcoming Resource Constraints
Building a custom AI chatbot requires time, skills, or budget, which may be limited. Start with no-code platforms like Tidio for quick prototypes, then transition to custom tools like Rasa as your skills grow. Allocate time for learning by setting weekly goals, like understanding one NLP concept at a time.
6. Ensuring Scalability and Performance
A chatbot that works for 10 users may struggle with 1,000. Choose scalable hosting like AWS Lambda or Heroku, and optimize your code with caching for common queries. Monitor performance metrics like response time and plan for load balancing to handle traffic spikes without downtime.
By addressing these challenges, you can keep your project on track. Now, let’s see how DEVtrust can help you in building an AI Chatbot effectively.
How DEVtrust Builds Production-Ready AI Chatbots?
Many AI chatbot initiatives fail after the PoC stage. Teams select LLMs too early, underestimate integration complexity, or deploy chatbots without proper guardrails, monitoring, or compliance controls. The result is unreliable responses, rising inference costs, and systems that cannot scale beyond limited use cases.
At DEVtrust, we design AI chatbots as production systems from day one. Our approach aligns business objectives with architecture, model selection, and deployment workflows, ensuring chatbots are secure, observable, and built to integrate cleanly with existing platforms.
We offer:
- LLM-backed chatbots using OpenAI or Azure OpenAI with structured prompting and fallback logic
- RAG-based architectures with secure data access and audit logging
- API orchestration via Node.js or Python, with Redis-backed session management
- Cloud-native deployment with CI/CD, monitoring, and cost controls
These capabilities enable us to translate complex technical design into tangible business results, as demonstrated in our work with one of the leading FinTech clients.
DEVtrust partnered with Financial Chatbot to create an AI-powered platform that delivers real-time insights to investors. The solution integrated OpenAI with TradingView, Yahoo Finance, FinnHub, TradingEconomics, and CryptoCompare APIs, enabling users to check stock prices, compare assets, and predict trends efficiently.
Here’s how the platform improved performance:
- Improved decision-making by 50%
- Enhanced interactive user experience by 40%
- Boosted investment insights by 30%
- Ensured up-to-date crypto data 99% of the time
This case demonstrates how DEVtrust combines LLM integration, real-time data aggregation, and intuitive UI design to deliver actionable, reliable financial insights to investors.
Also Read: How to Develop AI Software: A Complete Guide
Conclusion
Building an AI chatbot requires aligning business goals with architecture, integrations, and user experience. With a clear strategy, you can deploy chatbots that reduce operational load, improve response quality, and scale reliably.
At DEVtrust, we craft AI chatbots that are secure, scalable, and production-ready. Using platforms like Rasa, Dialogflow, and OpenAI, we integrate chatbots with your systems to optimize customer support, sales, and internal workflows, ensuring measurable business outcomes.
Ready to optimize your operations with an intelligent chatbot? Contact DEVtrust today to develop a solution that boosts efficiency, enhances user experiences, and drives tangible results.