Classrooms struggle with attention. Abstract ideas stay abstract. Some students move fast while others fall behind. Skills practice often stops at theory because time and tools run out. You see this every day, and it creates friction for both teachers and learners. Where do students get stuck when lessons shift from simple facts to complex ideas?
Augmented reality in education overlays digital objects, labels, and media on the physical classroom environment so students can see and explore what they are learning. It does not replace lessons. It adds clarity to them. This matters because most schools already rely on digital tools. An OECD 2024 report shows that more than nine in ten 15-year-olds have access to a computer for schoolwork at home, and over 80% use a digital device at school at least once a week.
Devices alone do not fix learning gaps. How do you turn screen time into real understanding? This guide shows seven benefits, three examples, key risks, rollout steps, and a partner checklist for teams that need results.
What This Guide Gives You
- AR shows up as 3D objects for science, full scenes for history, guided stories for language, practice overlays for skills, and location based activities for field learning.
- Augmented reality in education leads to clearer understanding, longer focus, stronger recall, safer hands on practice, better group work, flexible pacing, and student built content.
- In science, students inspect cells and circuits, in math they rotate shapes to solve volume problems, and in language and history they analyze interactive scenes.
- Distraction, overload, device issues, content errors, and privacy risks stay in check when AR runs in short sessions on managed devices with approved material.
- Schools move from one unit pilots to wider use and then to student made AR lessons, with learning data and classroom flow guiding every step.
The 5 Main Ways AR For Education Shows Up In Classrooms
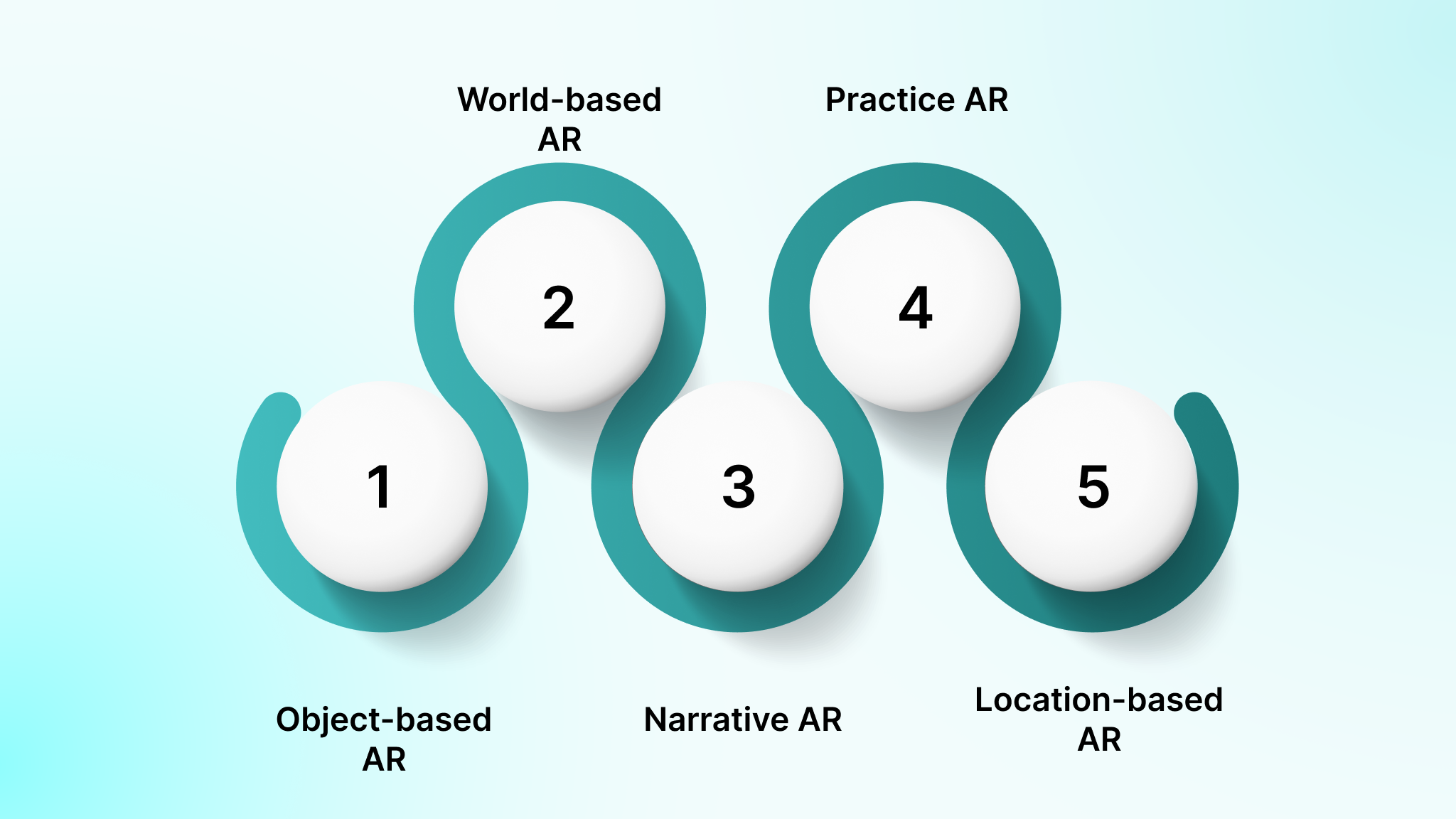
These are formats you can plan around, not app names. When you pick the right format, you decide what students see, touch, and produce. That choice shapes how well augmented reality in education supports science labs, math practice, or language work.
Below are the five classroom formats you will use most. Each one maps to a clear subject need and content source.
The five formats used in AR for education
1. Object-based AR: Used when students need to inspect and rotate 3D items such as molecules, organs, or geometric solids.
- Science and math benefit most.
- Content usually comes from libraries like Merge EDU or ClassVR, with some teacher-made models.
2. World-based AR: Used when students step into a scene such as a historical site or a simulated habitat.
- History and geography work well here.
- Content often comes from platforms like CoSpaces or Assemblr, plus student-built scenes.
3. Narrative AR: Used when lessons run as guided stories or missions.
- Language arts and social studies fit best.
- Content comes from curated story packs or teacher-authored scripts.
4. Practice AR: Used when skills need repetition and visual guidance.
- Science labs, handwriting, and vocational training rely on this.
- Content usually comes from structured libraries with feedback rules.
5. Location-based AR: Used when learning ties to physical space such as field studies or campus maps.
- Geography and environmental science rely on this.
- Content mixes platform data with teacher-made overlays.
Note: Tool examples are included to make planning concrete. You can apply the same formats with any AR platform that supports the workflow.
Quick Decision Guide For Picking The Right AR In Education Format
Pick the format after you pick the learning goal. Augmented reality in education only works when the task, not the app, leads the lesson. A 2025 quasi-experimental biology study showed that AR-based lessons produced an 81.0 percent post-test average compared to 76.1 percent for traditional classes, a clear 5 percent learning gain.
Use this simple mapping to guide your choice.
| Learning Goal | AR Task Type | Evidence Of Learning |
| Understand structure | Object AR | Labeled 3D model with explanation |
| Compare environments | World AR | Screenshot plus written analysis |
| Explain a process | Narrative AR | Audio or text walkthrough |
| Practice a skill | Practice AR | Accuracy and retry scores |
| Apply knowledge in place | Location AR | Observations tied to location |
Two failure modes show up often. Novelty overload happens when students spend more time exploring visuals than the concept. Weak assessment happens when AR use is not tied to a clear output.
Use this short checklist before every AR in education activity.
- Do you have at least one clear product to grade?
- Do you know how long the AR segment will run?
- Do you have enough devices for your group size?
- Can students move and talk without breaking class flow?
Also Read: 25+ Examples of AI in Education and Teaching
Once you know which AR format fits each learning goal, the next question is what it actually changes for students in class. That is where the real gains of augmented reality in education start to show.
7 Benefits Of Augmented Reality In Education
These benefits depend on lesson design, not the app alone. You get results when augmented reality in education is tied to clear goals, short activities, and measurable outputs. Each benefit below includes a classroom example and a way to check if it worked.
Use this section as a planning tool. You will see what students do, what they produce, and what you can measure.
What every benefit below will include
- A concrete classroom use case
- One or more signals you can track
- A way to connect AR work to grading or feedback
Benefit 1: Better Concept Clarity For Abstract Topics In Augmented Reality In Education
Molecules, geometry, and anatomy confuse students because they exist in three dimensions while books flatten them. When you rely on static diagrams, students build mental models that are often wrong. Augmented reality in education lets you put those models in front of them.
Use an object based AR tool such as Merge EDU or ClassVR to place a rotating 3D model of a cell or a molecule on each desk. Students see the structure, then move it, zoom it, and isolate parts.
What students do in class
- View the 3D object on a tablet
- Rotate and zoom to inspect layers
- Tap labels to reveal names and functions
- Compare two versions such as healthy vs damaged cells
What students explain after
- A short written or spoken description of how parts connect
- One cause and effect link between two parts
- One error they corrected after seeing the model
What you measure
- Concept check with 5 to 8 items
- Explanation rubric with clarity and accuracy
- Error patterns such as wrong part labels or reversed structures
Benefit 2: Higher Attention And Time On Task With Augmented Reality In Education
The first three minutes of a lesson decide if students stay with you. Passive slides and long talks lose them. AR adds interaction that keeps them focused on a single task.
Use a 5 to 7 minute AR segment where students explore a single object or scene. Follow it with a short reflection prompt in your LMS or on paper.
A simple routine you can run
- Minute 1 to 2, students open the AR view
- Minute 3 to 5, they explore one target item
- Minute 6 to 7, they answer one focused prompt
What you track
- Time on task during the AR window
- Number of students who submit the reflection
- One exit ticket with a single concept question
What to avoid
- Long open ended AR sessions
- Switching between many scenes in one block
Benefit 3: Stronger Memory And Recall Through Augmented Reality Learning
Memory matters when students need to retrieve knowledge later, not when they feel excited in the moment. AR helps because spatial placement and movement anchor ideas in the brain. You still need to control how much information appears.
Run an activity where students label and rotate a 3D model, then close it and explain from memory.
A recall focused activity
- Show a 3D heart or geometric solid
- Students label five parts
- They rotate and compare two views
- You hide the model
- Students draw or describe it from memory
What to assess
- A delayed quiz later that week
- One transfer task that uses the same concept in a new problem
- Common gaps such as missing parts or reversed order
What to limit
- Too many labels on screen
- Unrelated animations
Benefit 4: Safer Skills Practice And Fewer Errors Using Augmented Reality In Education
Lab work, equipment use, and clinical steps leave little room for mistakes. AR gives students visual guidance before they touch anything. That reduces risk and builds confidence.
Use a practice AR system that overlays steps on a real setup. Platforms used in vocational and health training show where to place tools and what to check next.
A basic practice loop
- Student follows on screen steps
- System flags missed actions
- Student retries the step
- You review the result
What to measure
- Accuracy score per attempt
- Time per step
- Self reported confidence after practice
Where this fits best
- Science labs
- Technical workshops
- Health and safety drills
Benefit 5: Better Participation And Collaboration In AR In Education Activities
Some students dominate. Others stay silent. Roles give everyone a reason to act. AR works best when you plan for shared control.
Use a three role structure in small groups.
Group roles
- Operator runs the AR view
- Recorder notes observations
- Explainer reports findings
A group inquiry example
- Students explore a virtual habitat
- Recorder lists three species
- Explainer connects them in a food chain
What to watch for
- One student controlling the device
- Groups without clear turn taking
- Access needs such as larger text or audio cues
Benefit 6: More Ways To Differentiate Instruction With Augmented Reality Education
Students come in with different skills and learning styles. AR lets you offer several entry points in the same lesson.
Set up a task with four paths.
Entry points
- Observe a model
- Label key parts
- Explain a process
- Create a new example
Scaffolds you can add
- Hints on screen
- Guided questions
- Extension tasks for fast finishers
What to measure
- Progress checks per tier
- Quality of explanations
- Completion rates by path
Benefit 7: Higher Student Ownership When Learners Create Augmented Reality Examples In Education
Viewing AR is one step. Authoring AR changes how students think. When they build something, they must understand it.
Use a simple creation pipeline.
Creation flow
- Storyboard the idea
- Build the AR scene
- Peer test it
- Present it
One deliverable
- An AR exhibit that teaches one concept
Rubric categories
- Accuracy
- Clarity
- Interaction design
- Reflection on what they learned
Also Read: Ultimate Guide to EdTech App Development in 2025
Now that you have seen what AR changes for learning, the next step is putting it into daily lessons. The examples below show how those benefits look when students actually use them.
3 Augmented Reality Examples In Education You Can Copy
These examples work as templates. Each one has a goal, setup, flow, and a way to judge success. You can run them with tablets or phones, and adjust time based on your schedule.
What each example shows
- Devices needed
- Time window
- What counts as success
Example 1: AR In Education Examples For Science, 3D Models And Inquiry Checks
Target one concept such as cell parts or circuits. Students use object based AR to explore and explain.
Setup
- Tablets or phones
- A 3D model from a library such as Merge EDU
Flow
- Prompt with one question
- Students explore the model
- They record three observations
- They explain one relationship
Quick assessment
- Name two parts
- Explain one function
- Predict one change if a part fails
Classroom rules
- Work in pairs
- One device per pair
- Screens down during discussion
Example 2: Augmented Reality In Education For Math And Geometry Visualization
Students struggle with nets, volume, and transformations. AR lets them see and move shapes.
Setup
- Tablets
- A shape library from tools like GeoGebra AR
Flow
- Place a 3D shape
- Resize and rotate it
- Calculate volume or surface area
- Justify the result
Checkpoint
- Students show their steps
Extension
- Students create one AR challenge for peers
Example 3: AR Education For Language And History Through Interactive Scenes
Context drives comprehension. AR scenes give students a place to analyze.
Setup
- Phones or tablets
- A scene built in CoSpaces or a similar tool
Flow
- Students explore the scene
- They describe what they see
- They compare two elements
- They reflect in writing or audio
Artifacts
- Short narration
- Evidence board
Guardrails
- Source checks
- Fact review by you
Also Read: How Machine Learning is Transforming Education
These examples show what works when everything is set up right. The next step is knowing what can go wrong and how to keep those lessons running smoothly.
What Can Go Wrong With Augmented Reality In Education & How To Fix It
Most failures with augmented reality in education come from weak planning and poor classroom flow. When AR feels chaotic, students lose focus and teachers lose control. You avoid that by knowing the risks before you start.
Below are the five problems you will face most often and one fix for each.
The five risks and school ready fixes
- Distraction: Fix it with short AR windows of five to seven minutes and one clear task on screen.
- Cognitive overload: Fix it by limiting labels, animations, and on screen prompts to only what supports the lesson goal.
- Device friction: Fix it by using managed tablets or phones with preloaded apps and locked home screens.
- Content accuracy: Fix it with teacher approved libraries and a review step for any student made AR.
- Privacy: Fix it by choosing apps that collect minimal data and work on school managed accounts.
Accessibility and comfort also matter. You should allow seated use, limit camera motion, and offer non AR alternatives for students who need them.
Privacy, Safety, And Device Controls For AR In Education
Administrators worry about data, camera access, and student accounts. Those concerns are valid because AR apps use cameras and cloud services. In the US, student data handling falls under FERPA and COPPA. In the UK and EU, it falls under GDPR and UK GDPR. These frameworks require that schools limit data collection, control access, and keep clear records of how student data is used.
Use managed devices and restrict what can run.
Practical controls you should apply
- Mobile device management such as Google Admin or Apple School Manager.
- App allow lists so only approved AR tools run.
- Camera and microphone permissions set by policy.
Follow the minimal data principle. Collect less. Store less. Retain less. Student names, faces, and locations should not be kept unless the lesson requires it.
School approval checklist
- Does the app work with school logins?
- Can you turn off data sharing?
- Is camera use limited to the lesson?
- Can you delete student data on request?
Also Read: Learning Management Systems: Benefits, Types & Trends
Once you have the risks under control, the focus shifts to putting AR into everyday teaching. That is where a clear rollout plan keeps everything working as it should.
How To Roll Out Augmented Reality In Education Without Chaos
A rollout works when you treat it as a program, not a one week purchase. You move from small tests to full use with clear checks along the way. This keeps teachers and IT in sync.
Use a four phase plan.
Four phase rollout
| Phase | What You Do | What You Measure |
| Pilot | One unit in one subject | Engagement and short quizzes |
| Integrate | Add to more lessons | Usage and learning checks |
| Scale | Expand to grades or schools | Support tickets and uptime |
| Student Made | Students build AR | Quality of projects |
Teacher enablement keeps this running. Give teachers time to try the tools, templates for lessons, and simple routines for setup and cleanup.
Planning a pilot or school wide rollout? Contact DEVtrust to connect your AR platform with LMS systems, user management, and reporting so programs run smoothly from the first class to full deployment.
Lesson Design For Augmented Reality Learning, A Simple Planning Chain
Every AR lesson should follow the same chain. Objective to AR task to evidence to assessment. When you skip a link, the activity becomes noise.
Use these five reusable task types.
AR task types
- Explore
- Investigate
- Create
- Practice
- Explain
Pair them with short reflection and exit tickets.
Reflection and exit pattern
- One question about what they saw
- One question about what it means
- One short concept check
Keep AR segments short so students stay focused and you keep time for discussion.
Also Read: Top 10 Best School Management Software for 2025
Once your rollout and lesson flow are clear, the last piece is choosing who will help you build and run it. That decision shapes how reliable your AR program stays over time.
How To Choose The Right AR In Education Partner
You avoid vendor lock in and proofless demos by asking for evidence. A partner should show you how AR fits your curriculum and your tech stack. Demos without data are not enough.
Use a checklist.
What to require
- Curriculum fit
- Privacy posture
- Content quality
- Support model
You also need a pilot plan with success metrics and a classroom workflow.
Ask for proof.
Evidence to request
- Example lesson plans
- Deployment plan
- Usage and learning reports
Comparing vendors or planning a custom AR learning platform? Contact DEVtrust to get engineering support, integrations, and data controls that keep AR programs reliable at scale.
AR In Education Vendor Checklist For Schools And Product Teams
These are questions you can use on a call. They keep the discussion focused on learning, technology, and operations.
Learning
- How do lessons map to standards?
- What student work gets graded?
- How do you show learning gains?
Technology
- How do you handle student data?
- Can you limit camera access?
- Does it work with school logins?
- How do updates roll out?
Operations
- What reports do you provide?
- How do teachers get support?
- What does a pilot look like?
Now that you know what to demand from a partner, it helps to see how those requirements look in a real delivery team. That is where DEVtrust fits into the picture.
How DEVtrust Helps You Implement Augmented Reality In Education
Integrations, scale, reliability, privacy, and analytics decide whether augmented reality in education works beyond a single classroom. Small pilots are easy, but problems start when you connect AR to your LMS, manage devices, protect student data, and track learning across grades.
DEVtrust builds AR ready EdTech platforms that fit into your school or district systems. Its software links content, users, and classroom data through secure APIs and cloud infrastructure so AR runs inside real teaching workflows.
What DEVtrust delivers for AR in education
- LMS and roster integration so teachers do not manage accounts manually, using Google Classroom API, SSO patterns, and class sync
- Role based access and device policy support to control camera permissions, app access, and student logins across tablets and phones
- Secure authentication with Firebase Auth and school friendly SSO so only approved users access AR activities
- Cloud based delivery on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to keep AR content, logins, and reporting stable as usage grows
- Learning and usage analytics that track engagement, task completion, and outcomes without over collecting student data
- CI/CD pipelines so lesson updates, content fixes, and new features reach classrooms without downtime
- AI driven tutoring and feedback workflows using OpenAI and Azure OpenAI to support explanations, practice, and reflection
DEVtrust combines application engineering, cloud systems, and education focused AI so your AR programs remain compliant, reliable, and measurable at scale.
Conclusion
Good augmented reality in education starts with aligned goals, short classroom segments, clear evidence of learning, and a safe rollout plan. When you connect AR tasks to what you want students to know and do, the technology stays in service of teaching. When you track results and control access, it stays reliable at scale.
When AR is planned and executed well, students gain clearer understanding of abstract topics, spend more time focused on tasks, and retain what they learn. Skills practice becomes safer and more consistent, group work becomes more balanced, and teachers can support different learning paths in the same lesson. Students also take ownership by creating their own AR work, while science, math, and language lessons run on reusable, structured AR templates instead of one-off activities.
If you add AR without structure, you risk distraction, wasted licenses, and learning data you cannot trust. DEVtrust helps you build AR ready EdTech platforms that connect content, users, and analytics into one system you can run and measure with confidence.